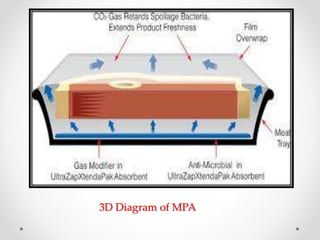
Vacuum packaging and modified atmosphere packaging are common fish packaging methods that help extend shelf life. Vacuum packaging removes oxygen which inhibits bacterial growth but risks anaerobic bacteria growth. Modified atmosphere packaging replaces air with gas mixtures like carbon dioxide to control microbes. Other packaging methods discussed include shrink packaging, aseptic packaging, and active and intelligent packaging technologies that absorb or release substances to further prolong shelf life and food quality. Active indicators can also provide information on food freshness and safety conditions.