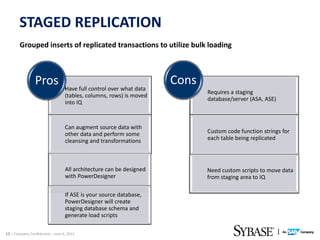
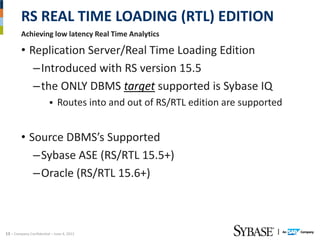
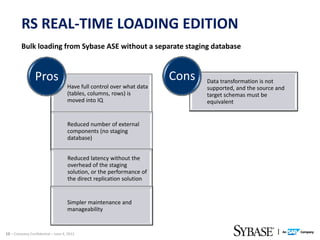
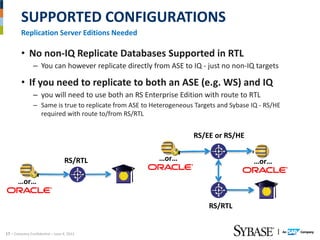
This document discusses Replication Server - Real Time Loading (RTL) for replicating data from a source database in real-time to Sybase IQ for analytics purposes. It provides dial-in numbers and passcode for a presentation on the topic. The presentation will cover limitations of pre-RS 15.5 replication solutions to IQ, an overview of RTL, and the new RTL update capabilities in RS.