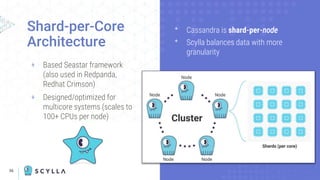
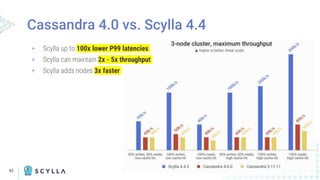
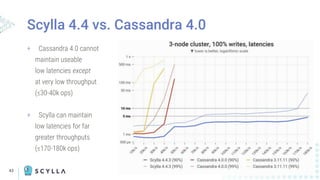
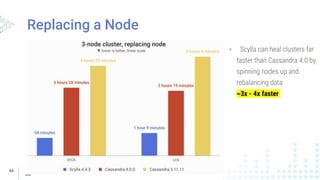
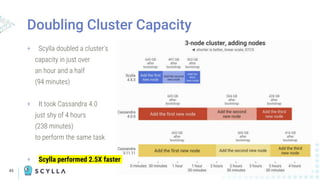
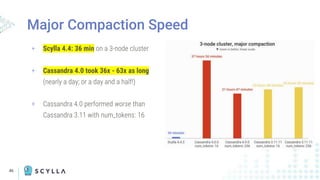
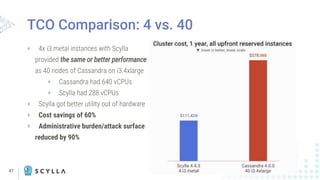
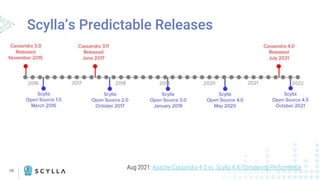
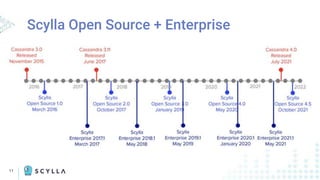
The document compares Apache Cassandra and ScyllaDB, highlighting that ScyllaDB is a high-performance, low-latency NoSQL database compatible with Cassandra and DynamoDB but designed for better efficiency through its shard-per-core architecture. It discusses evolutionary differences between the two, including software release cycles, performance benchmarks, and community perception, noting ScyllaDB's rapid development and enhancements. ScyllaDB offers features such as a dynamodb-compatible API and improved handling of lightweight transactions, making it a competitive choice for data-intensive applications.









![14
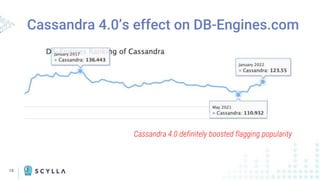
Scylla Moving Up in the [DB-Engines.com] Rankings
ScyllaDB was 4th fastest rising database in
the DB-Engines.com Top 100 from Jan
2021 to Jan 2022 [Rank #85, Score 3.91]
Source: https://db-engines.com/en/ranking
Cassandra remains #11 overall in the
DB-Engines.com ranks for Jan 2022
[Score 123.55]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandravs-220113200232/85/Cassandra-vs-ScyllaDB-Evolutionary-Differences-14-320.jpg)

![17
Common Ancestry
+ Cassandra and Scylla both
descend from the same historical
antecedents / whitepapers
+ Google’s Bigtable
+ Amazon’s Dynamo
+ Facebook’s Cassandra
+ [Not to be confused with
commercial offerings Google
Cloud Bigtable and Amazon
DynamoDB, or open source
Apache Cassandra]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandravs-220113200232/85/Cassandra-vs-ScyllaDB-Evolutionary-Differences-17-320.jpg)

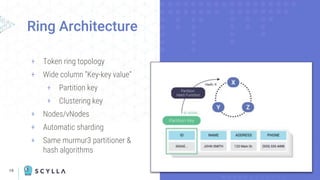

![21
Basic CQL CRUD
Operations
+ Create [INSERT]
+ Read [SELECT]
+ Update [UPDATE]
+ Delete [DELETE]
+ WHERE clause
+ ALLOW FILTERING
+ TTL functions
ᐩ Pretty much standard Cassandra
Query Language (CQL)
ᐩ Like SQL, at least at cursory
glance, but do not be lulled into a
false sense of familiarity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandravs-220113200232/85/Cassandra-vs-ScyllaDB-Evolutionary-Differences-21-320.jpg)






![28
Materialized Views
+ Cassandra: introduced in 3.0
[2017], but still experimental
+ Problems when base table gets
out of sync
+ To this day, major issues like
CASSANDRA-10346 are still open
ᐩ Scylla: production ready since 3.0 [Jan
2019]
ᐩ Serve as the infrastructural basis for
Secondary Indexes
ᐩ Can still get out of sync, but not easily
ᐩ Continually improving implementation
* Read more:
https://www.scylladb.com/2018/09/19/overheard-at-
distributed-data-summit/
“If you have them, take them out.”
— Nate McCall PMC Chair,
on Materialized Views in Cassandra [2018]*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandravs-220113200232/85/Cassandra-vs-ScyllaDB-Evolutionary-Differences-28-320.jpg)




![34
+ Plethora of K8s operators
+ DataStax K8ssandra 1.3+
+ Orange KassCop 2.0+
+ Bitnami Charts
+ [cass-operator deprecated]
+ Sidecars collocated/run on the same
instance as the DB server daemon
+ What Works and What Doesn’t:
https://k8ssandra.io/blog/articles/ku
bernetes-and-apache-cassandra-
what-works-and-what-doesnt/
Kubernetes Support
& Sidecars
ᐩ Scylla Operator offers great K8s
support — It just works
ᐩ Scylla Manager Agent is a sidecar
and already included by default with
Scylla Operator
ᐩ https://www.scylladb.com/product/
scylla-operator-kubernetes/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandravs-220113200232/85/Cassandra-vs-ScyllaDB-Evolutionary-Differences-34-320.jpg)