The document discusses various reading strategies to help struggling students, including:
1) Learning walls which display essential words and concepts to reference while reading.
2) Word wall games like Wordo and Guess the Word to reinforce vocabulary.
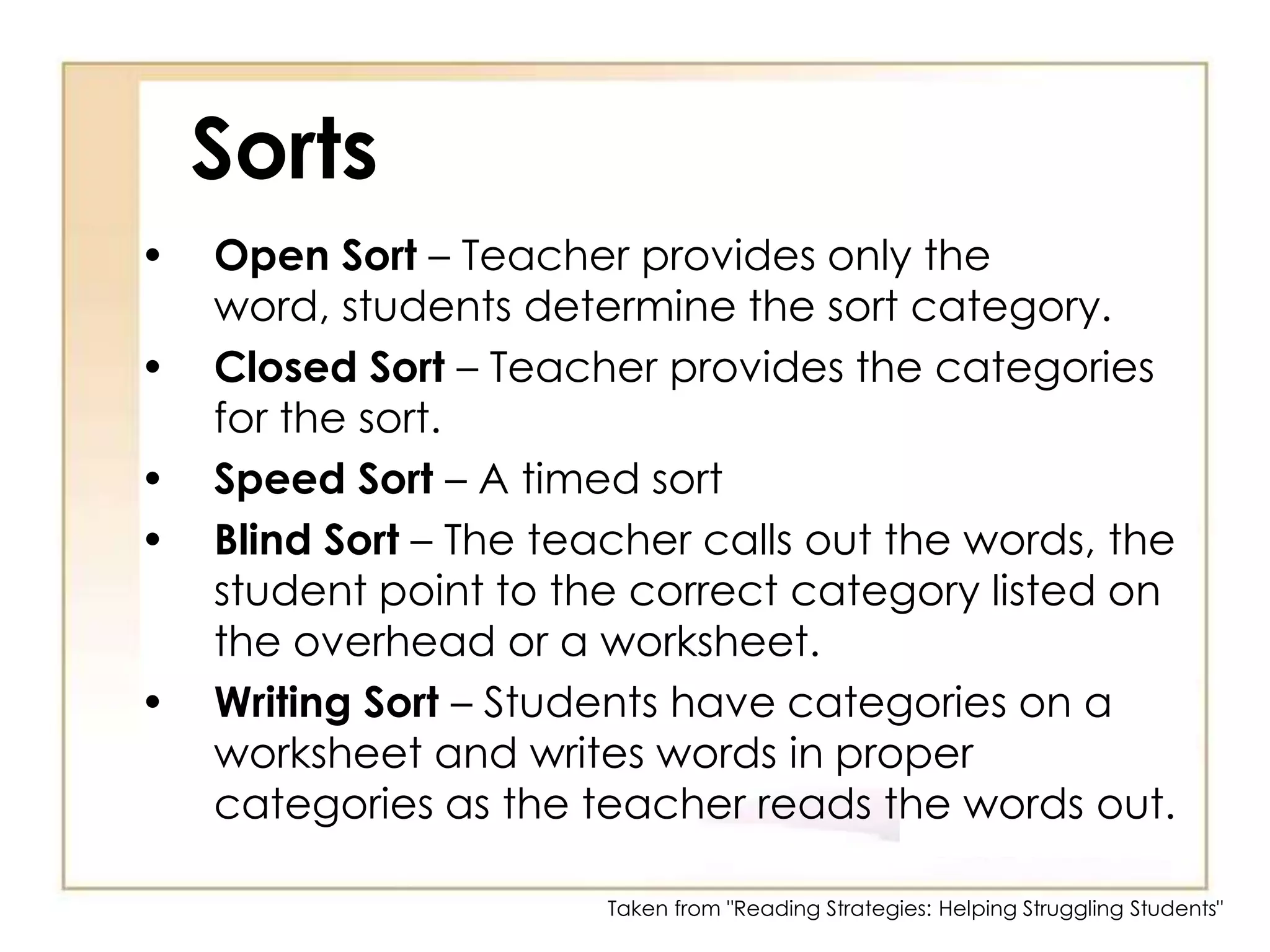
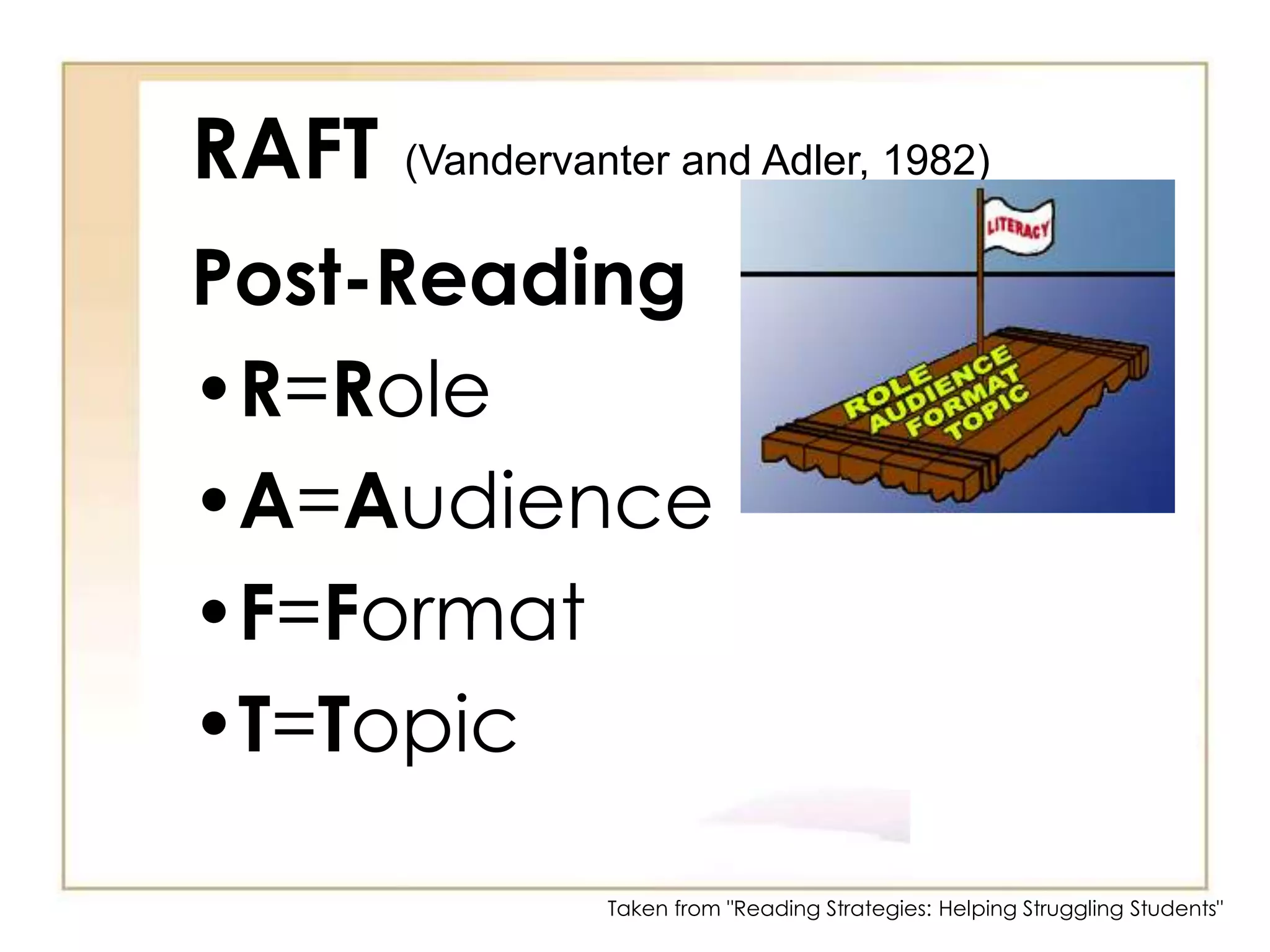
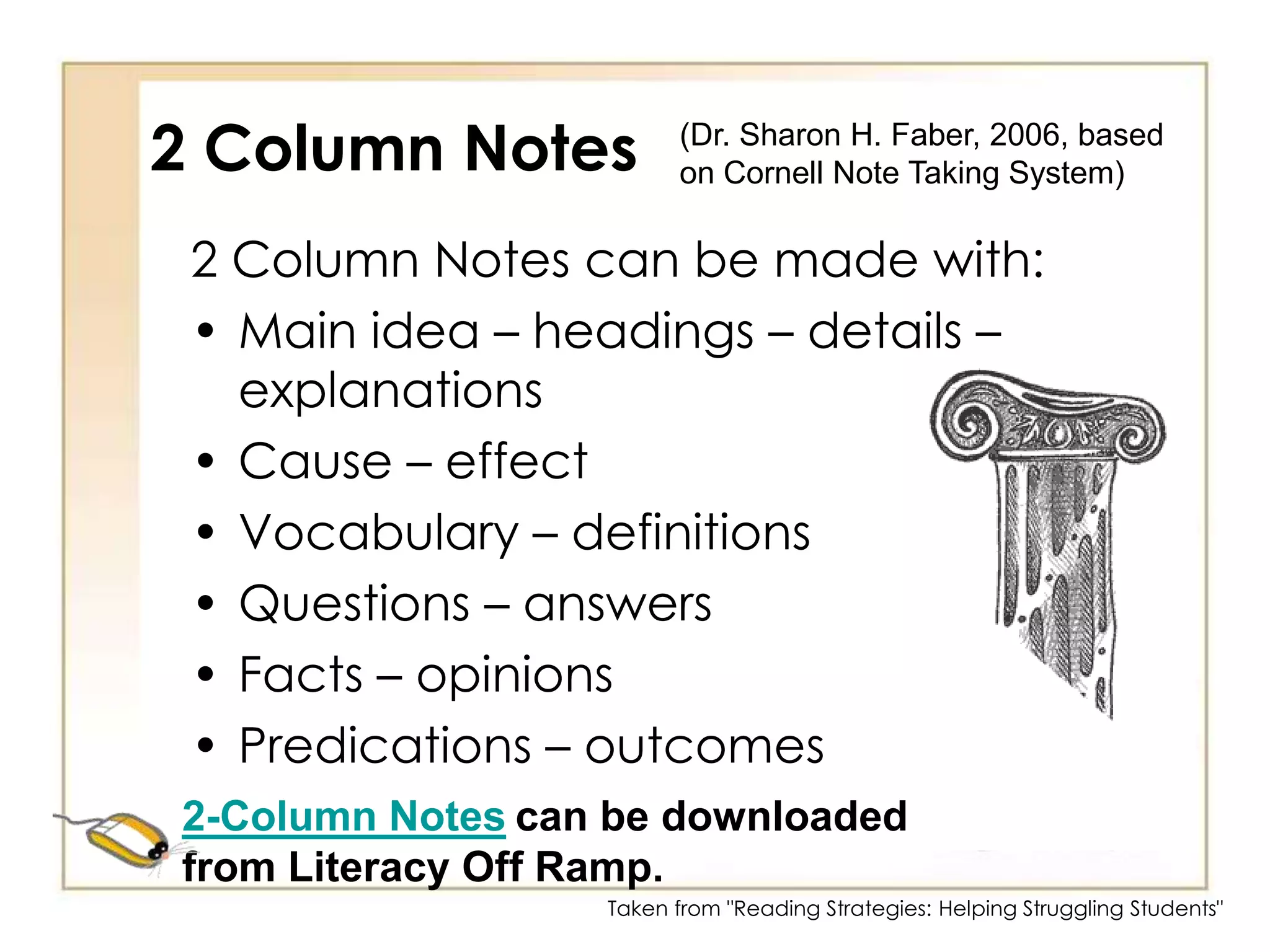
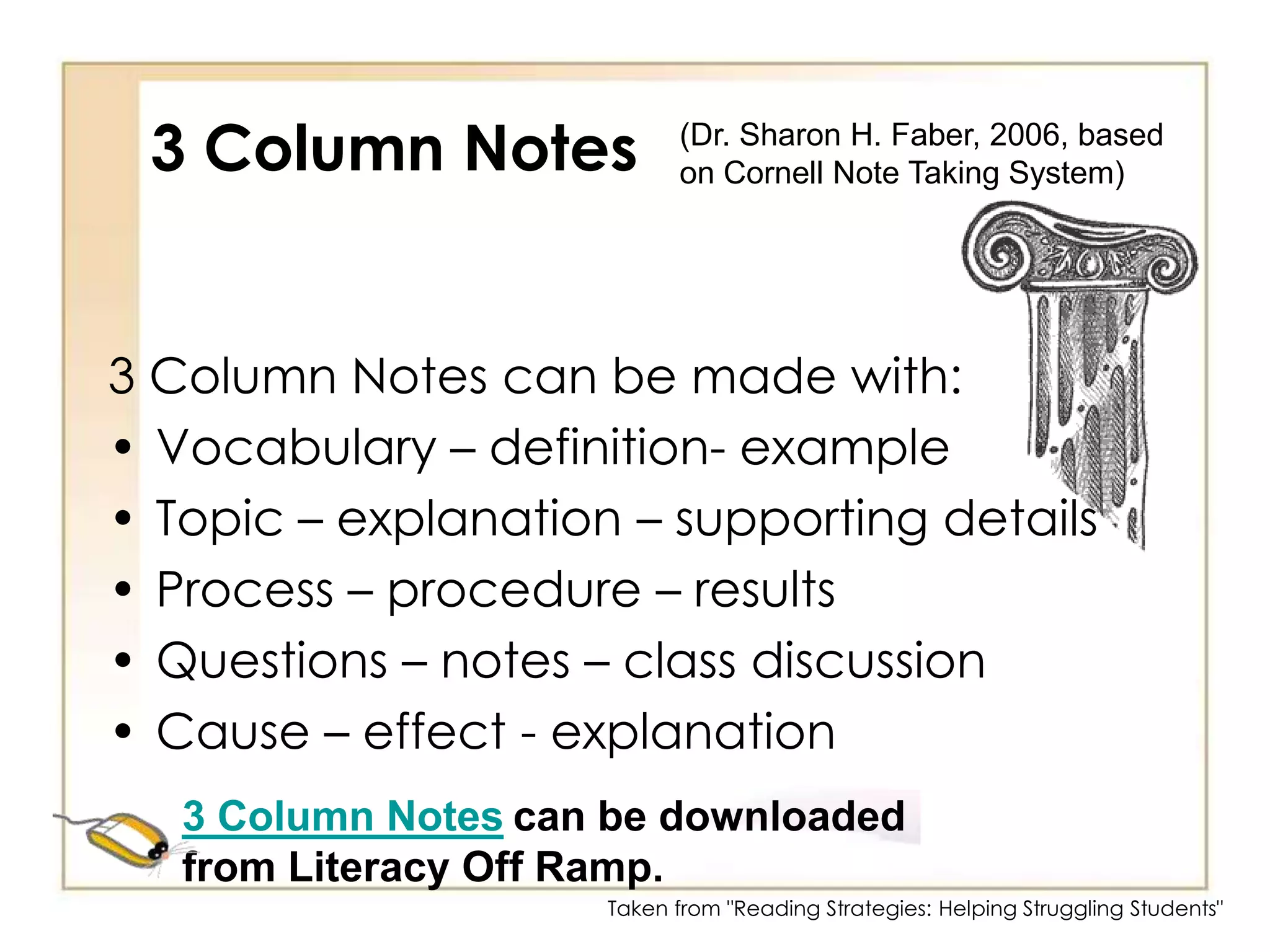
3) Note-taking strategies like 2-column notes, 3-column notes, and RAFT to organize information.
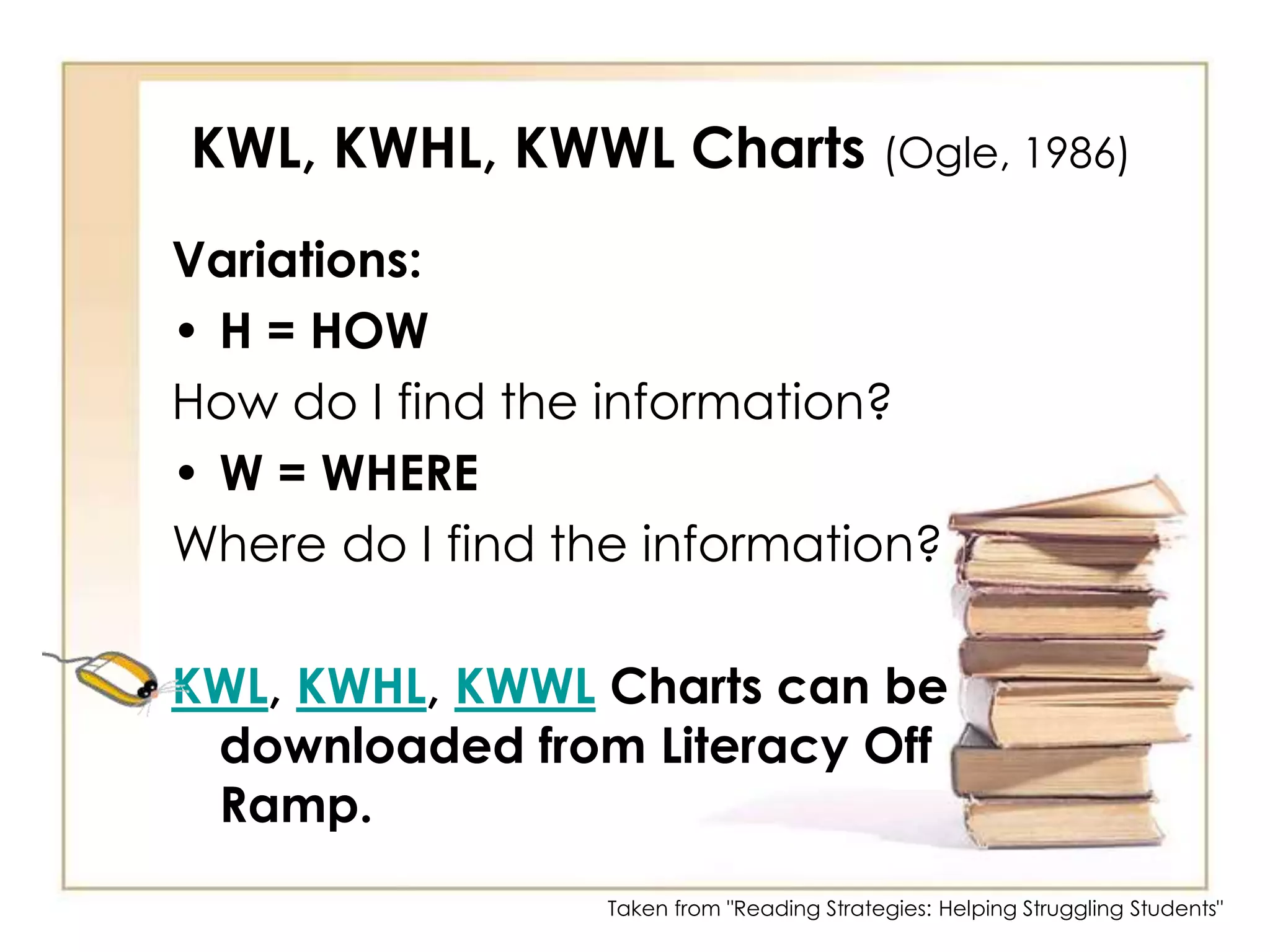
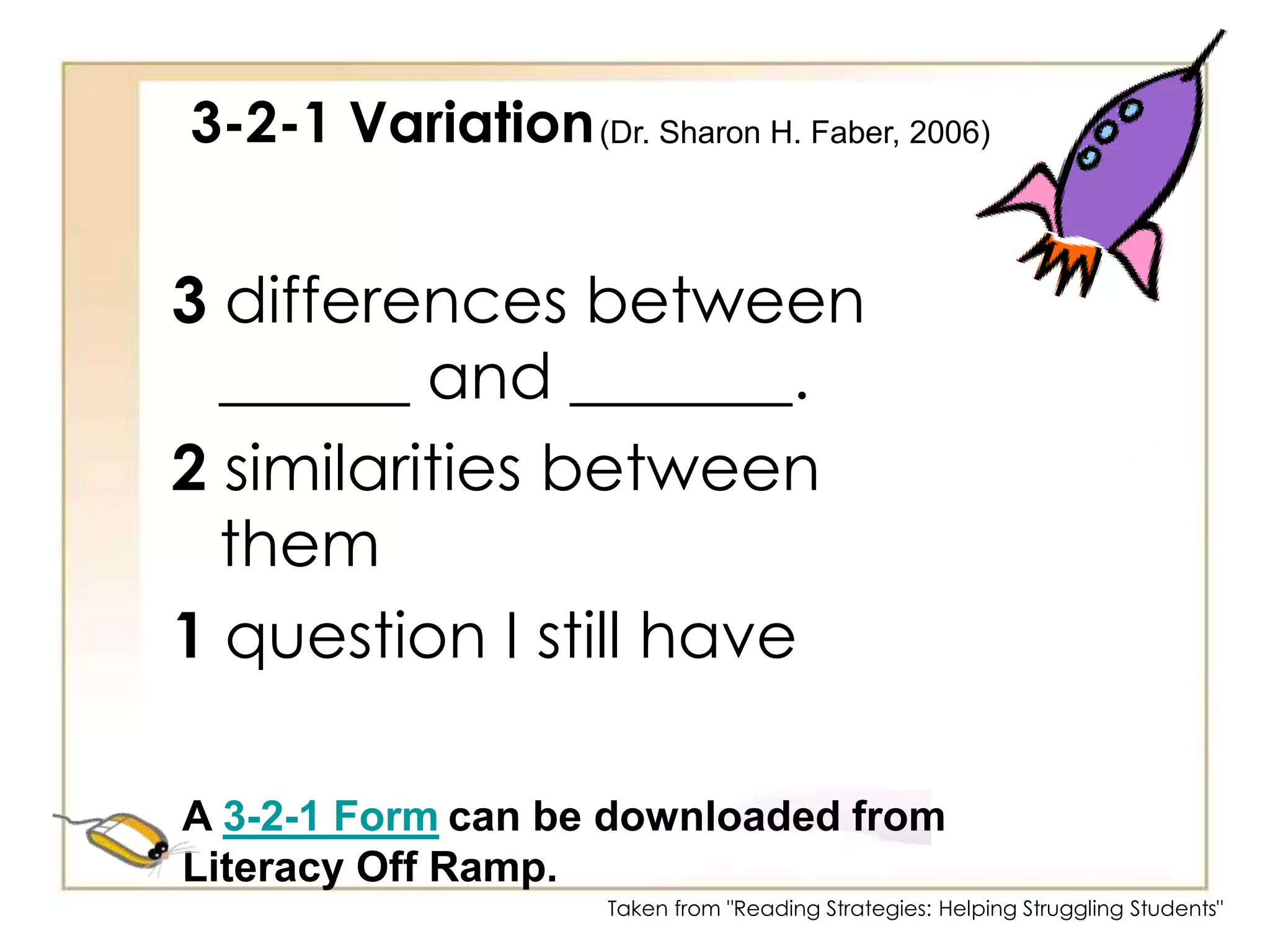
4) Comprehension strategies like QAR, anticipation guides, and reciprocal teaching to improve understanding.
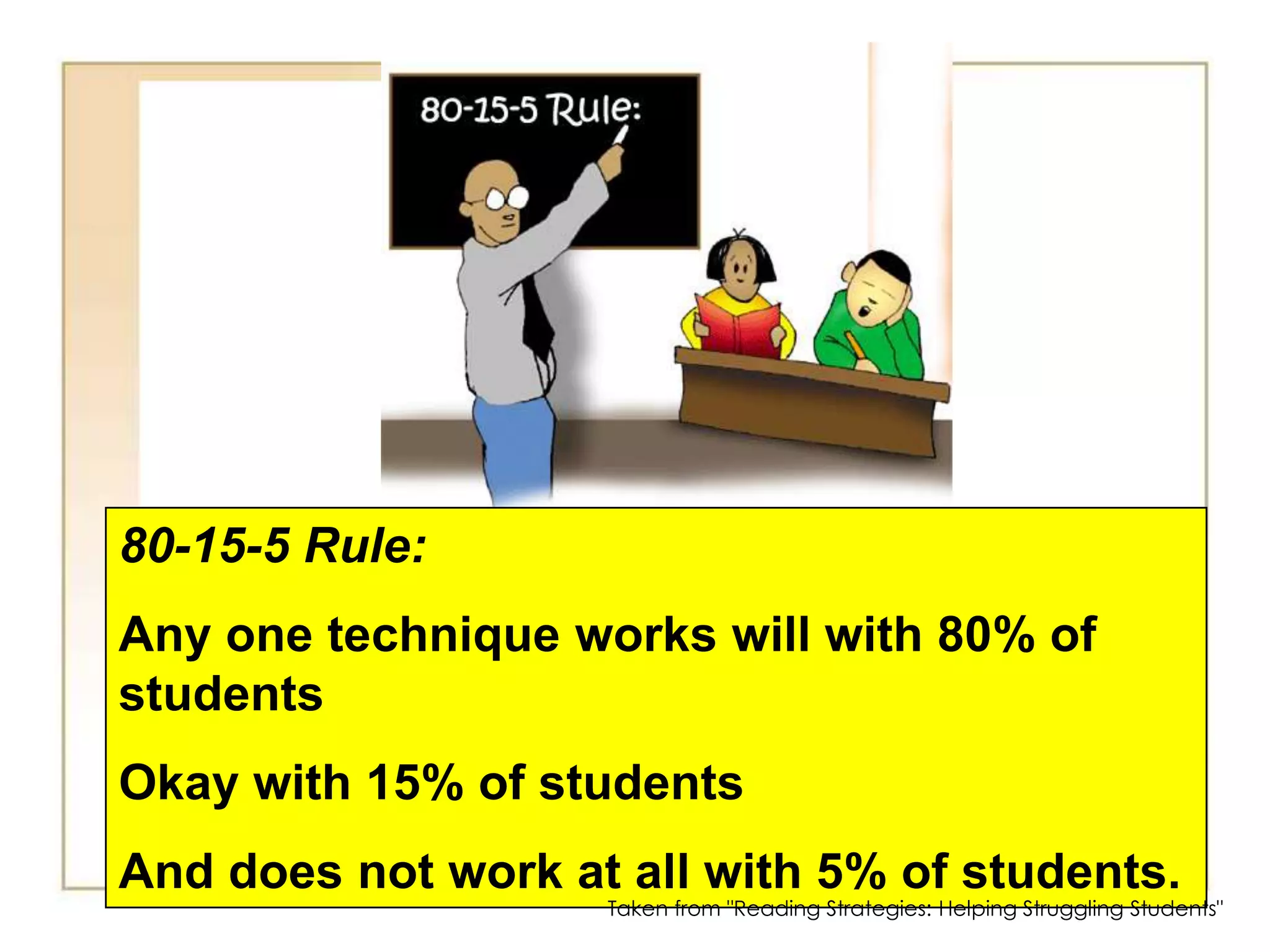
5) The 80-15-5 rule emphasizes that new strategies must be thoroughly taught and practiced to benefit students.