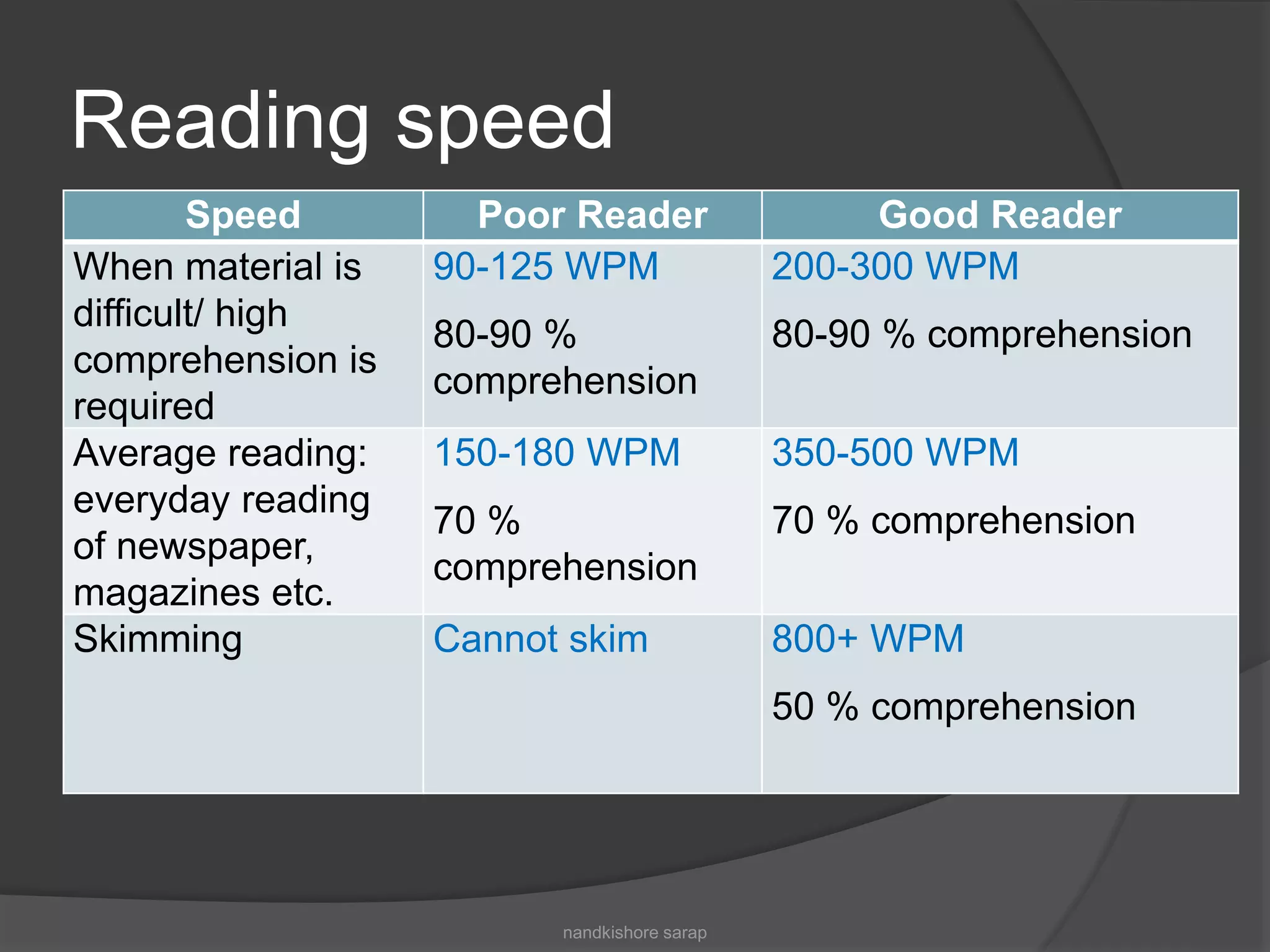
The document discusses reading skills and comprehension. It states that reading and listening are passive skills of comprehension, while speaking and writing are active skills of expression. It also discusses that reading comprehension requires understanding what is read as well as expressing it clearly. While reading is passive, good readers are active in comprehending, guessing, imagining, and reproducing what they read. The document provides tips for improving reading speed, comprehension, vocabulary, and pronunciation. It describes techniques for locating specific information and understanding word meanings, phrases, sentences and the logical relationship between sentences in a text.