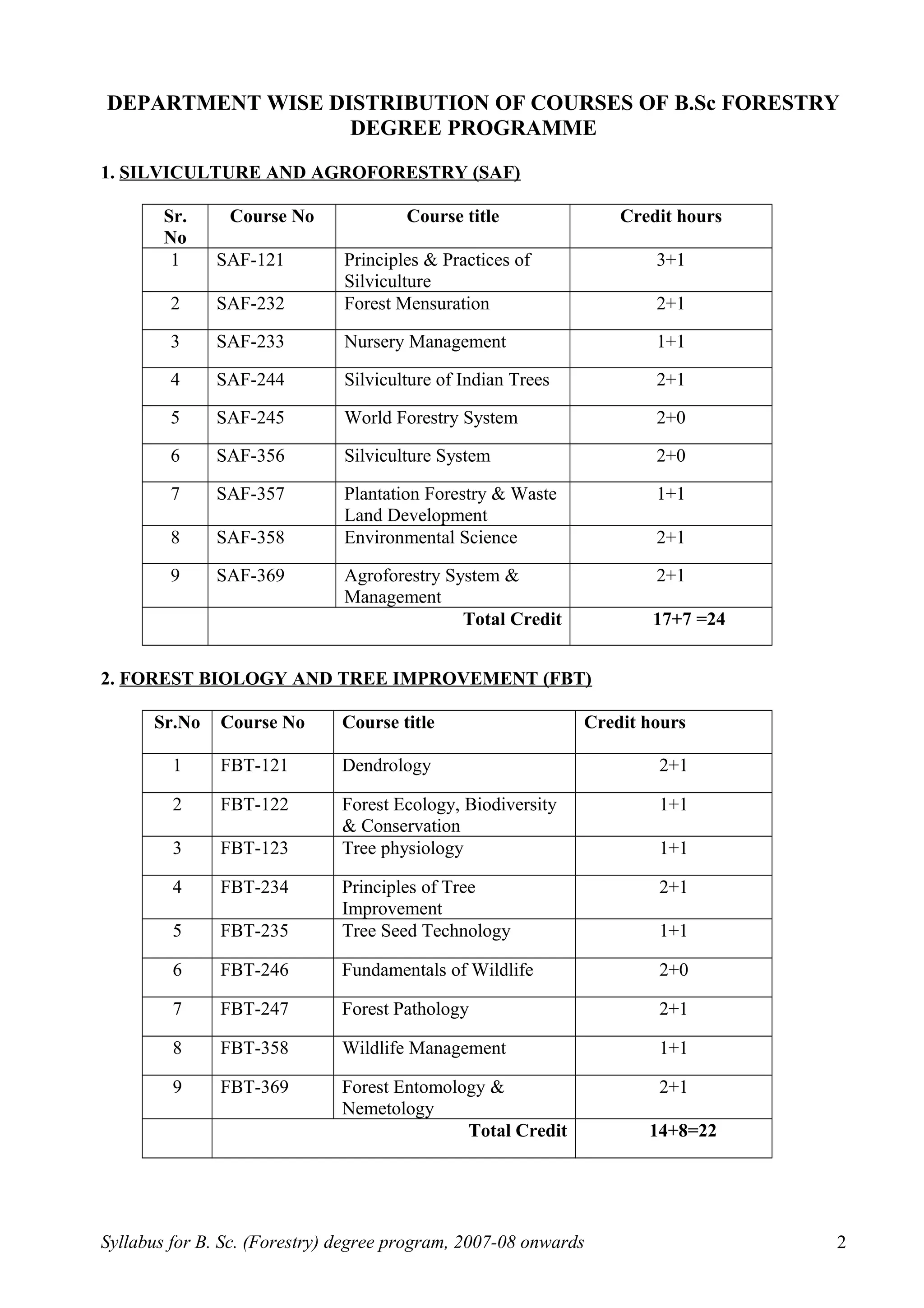
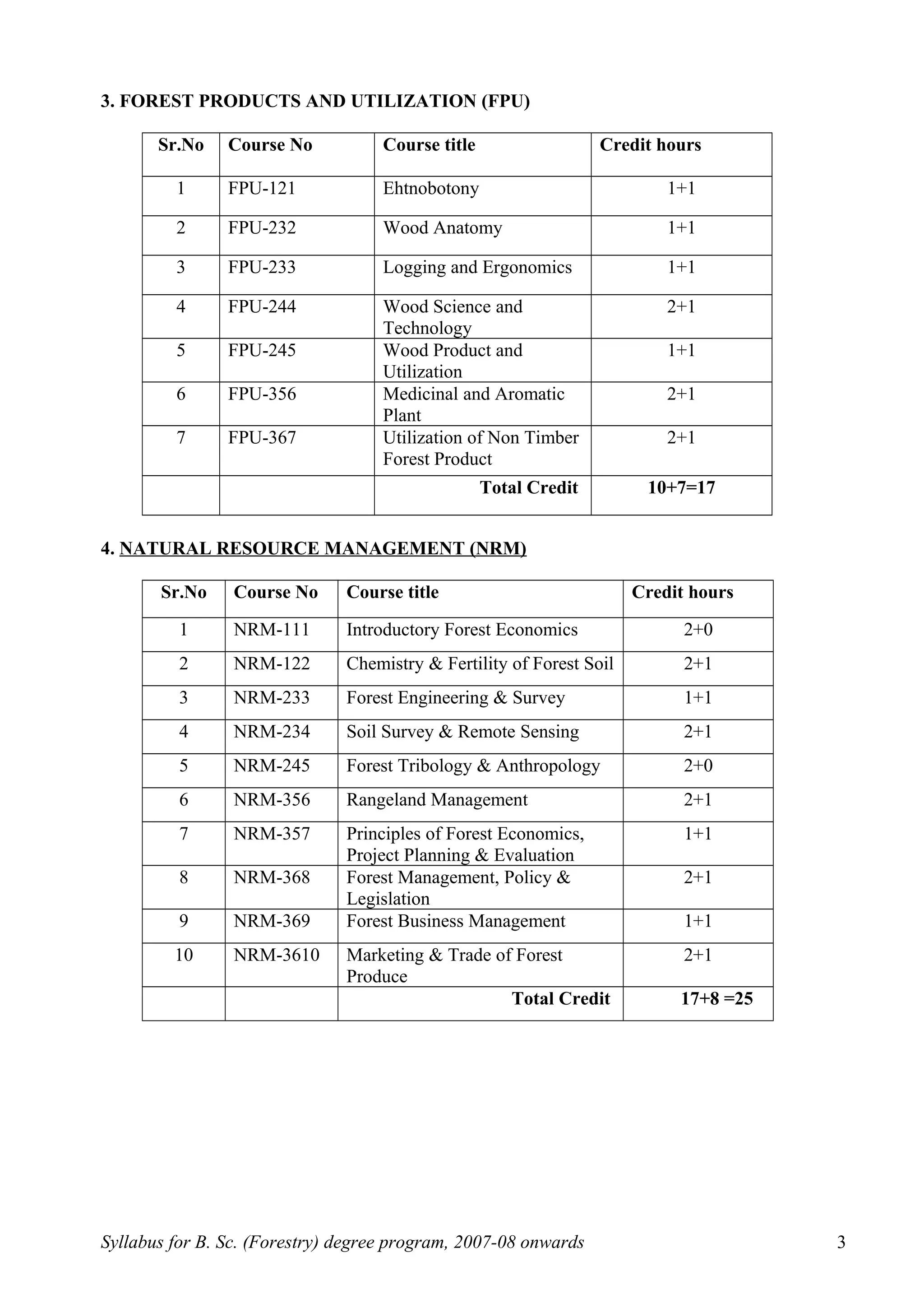
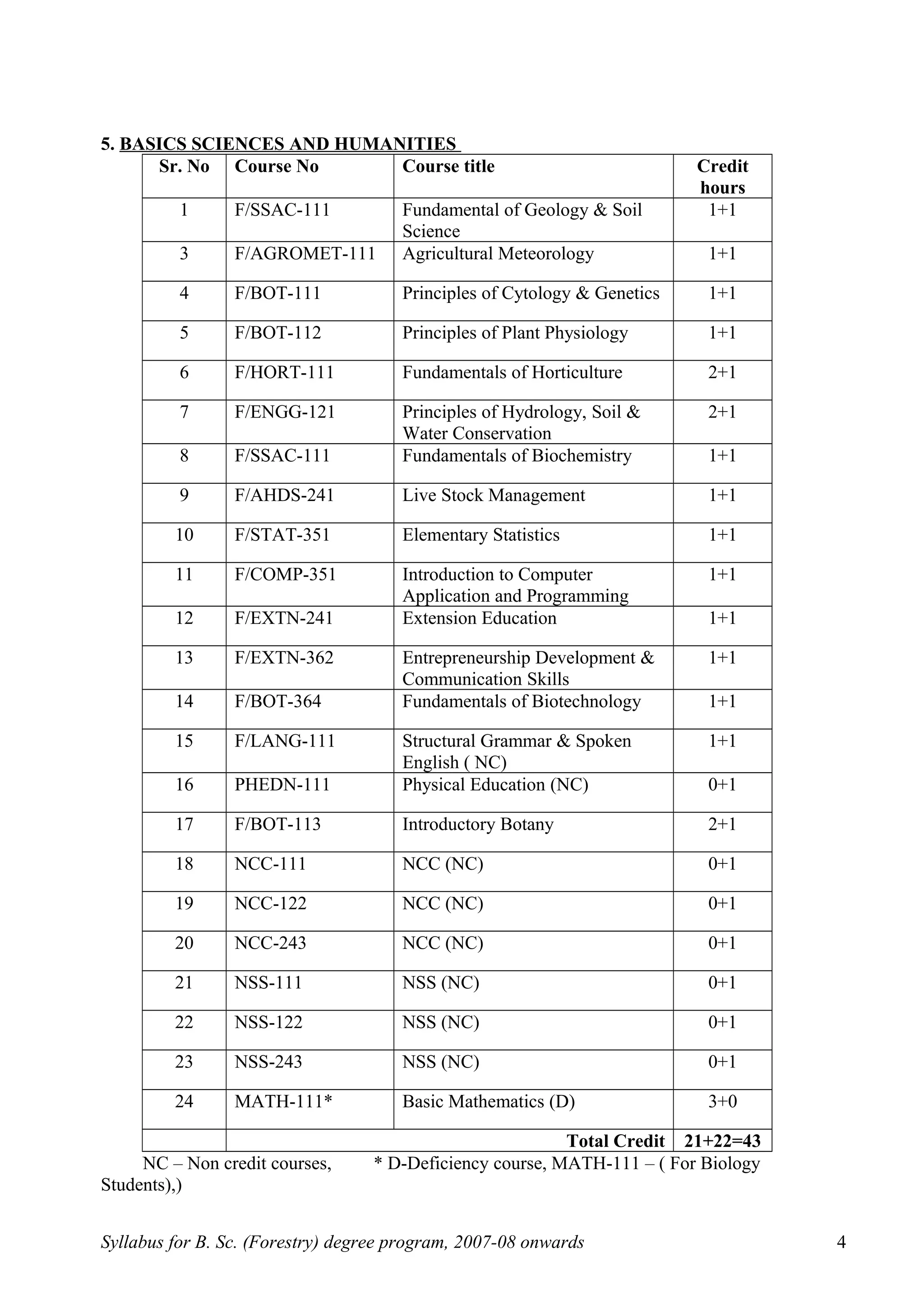
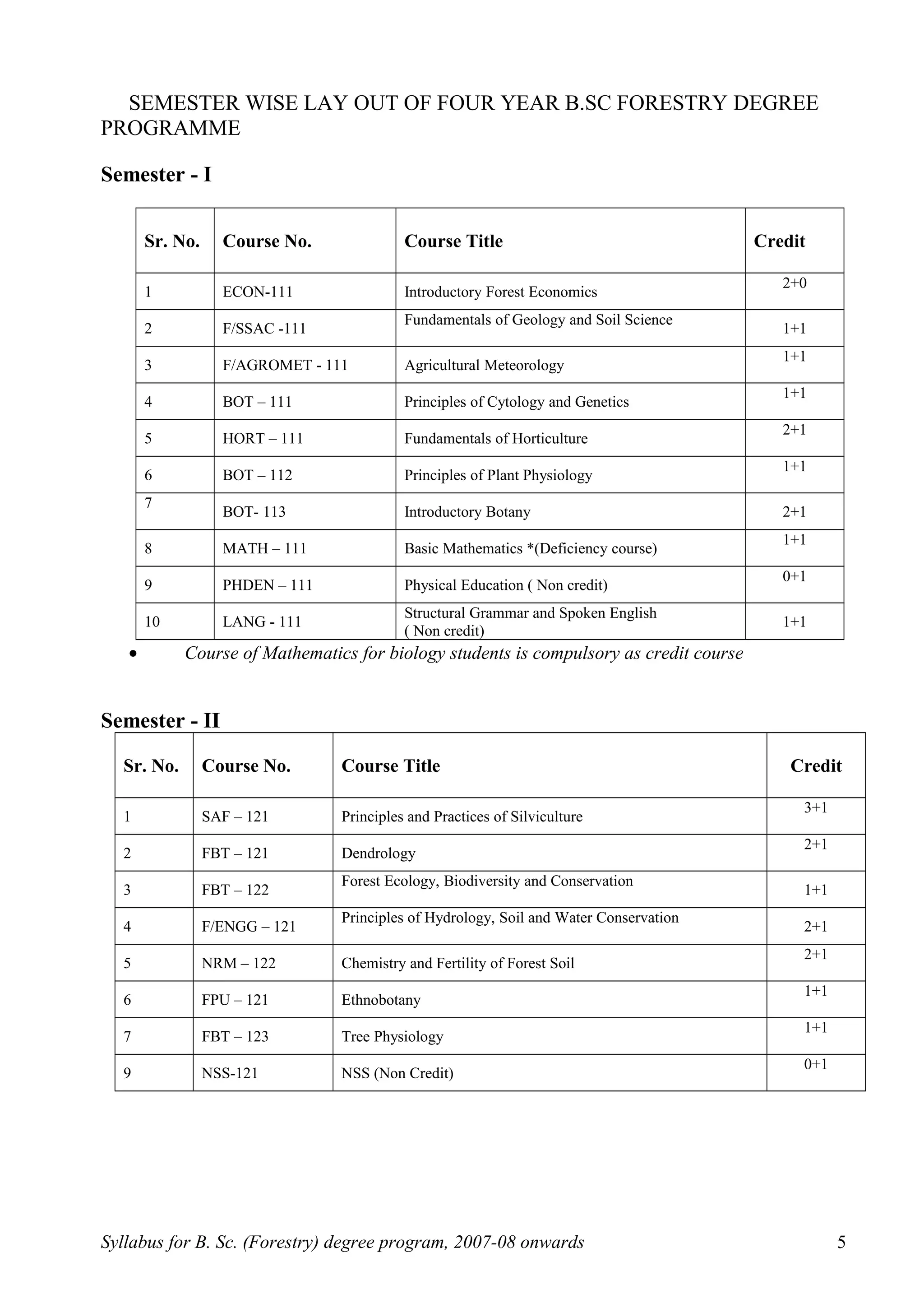
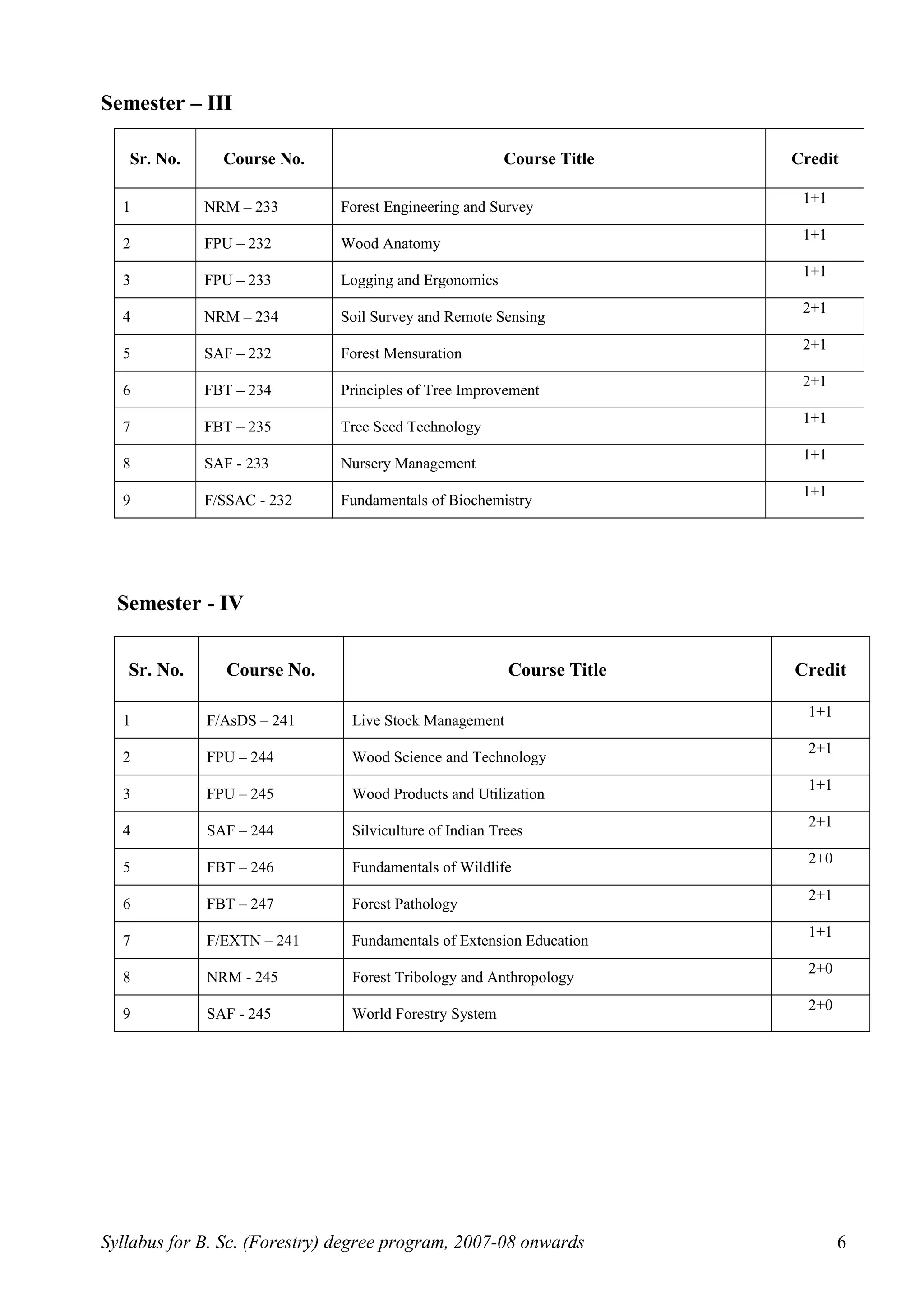
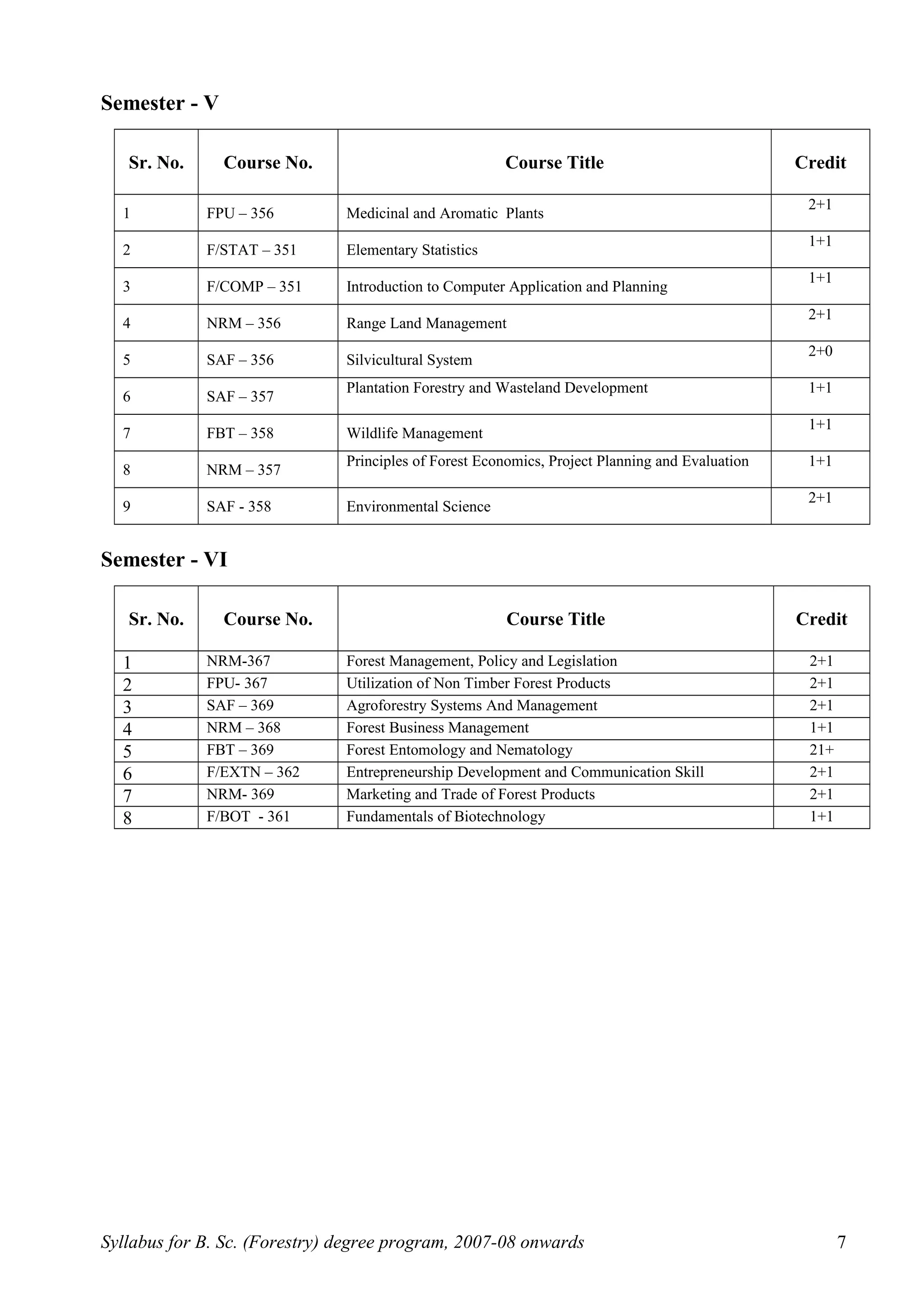
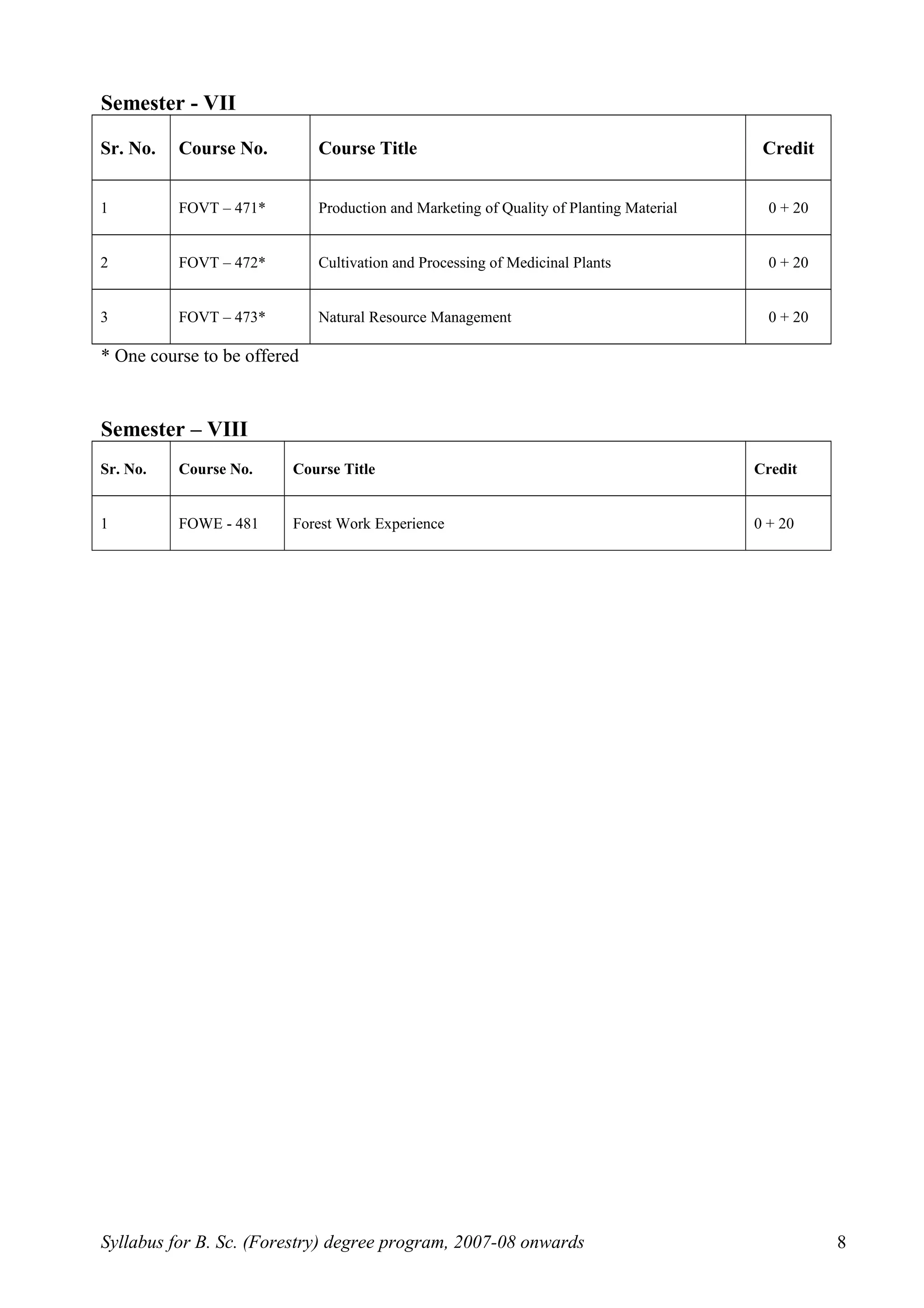
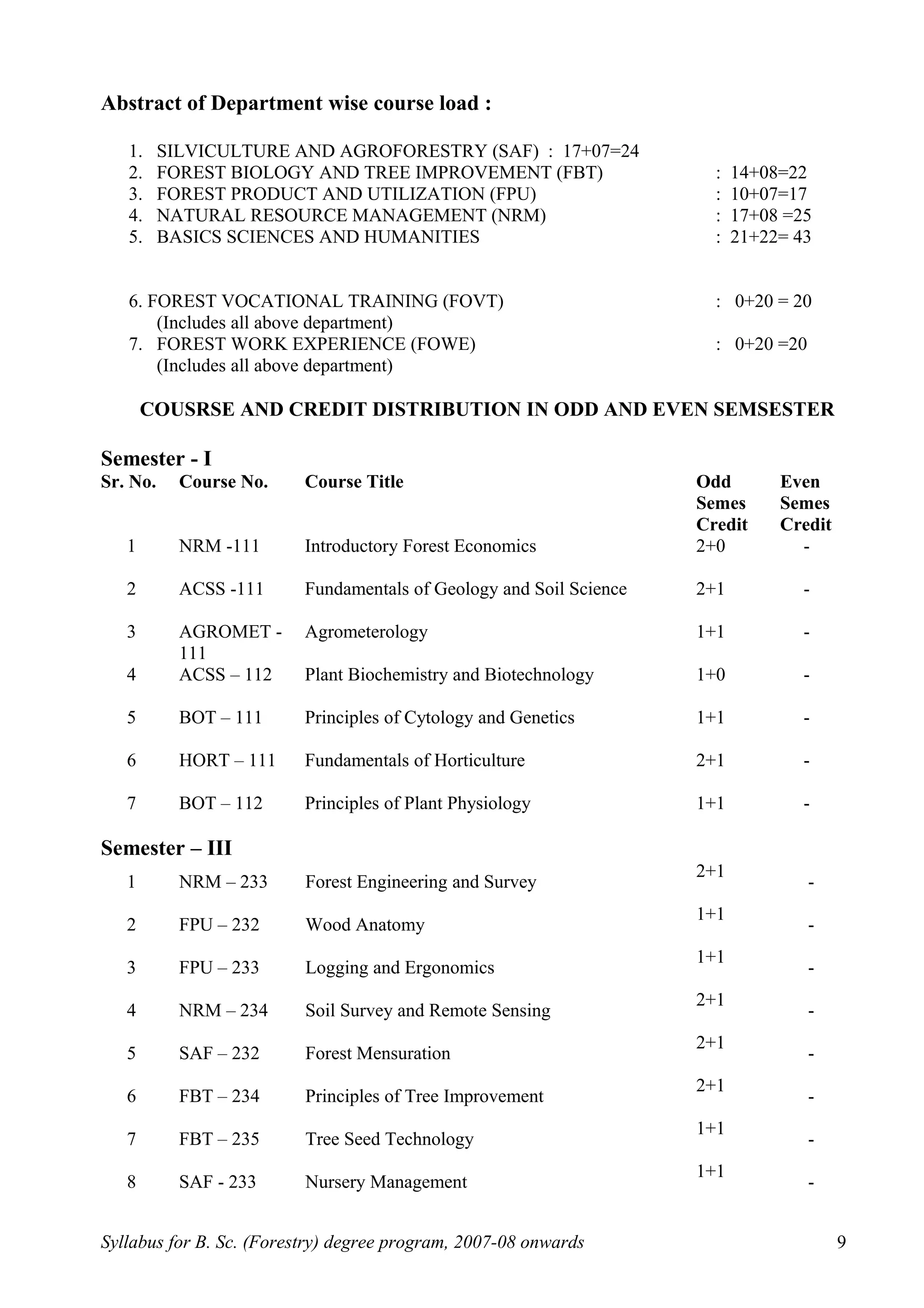
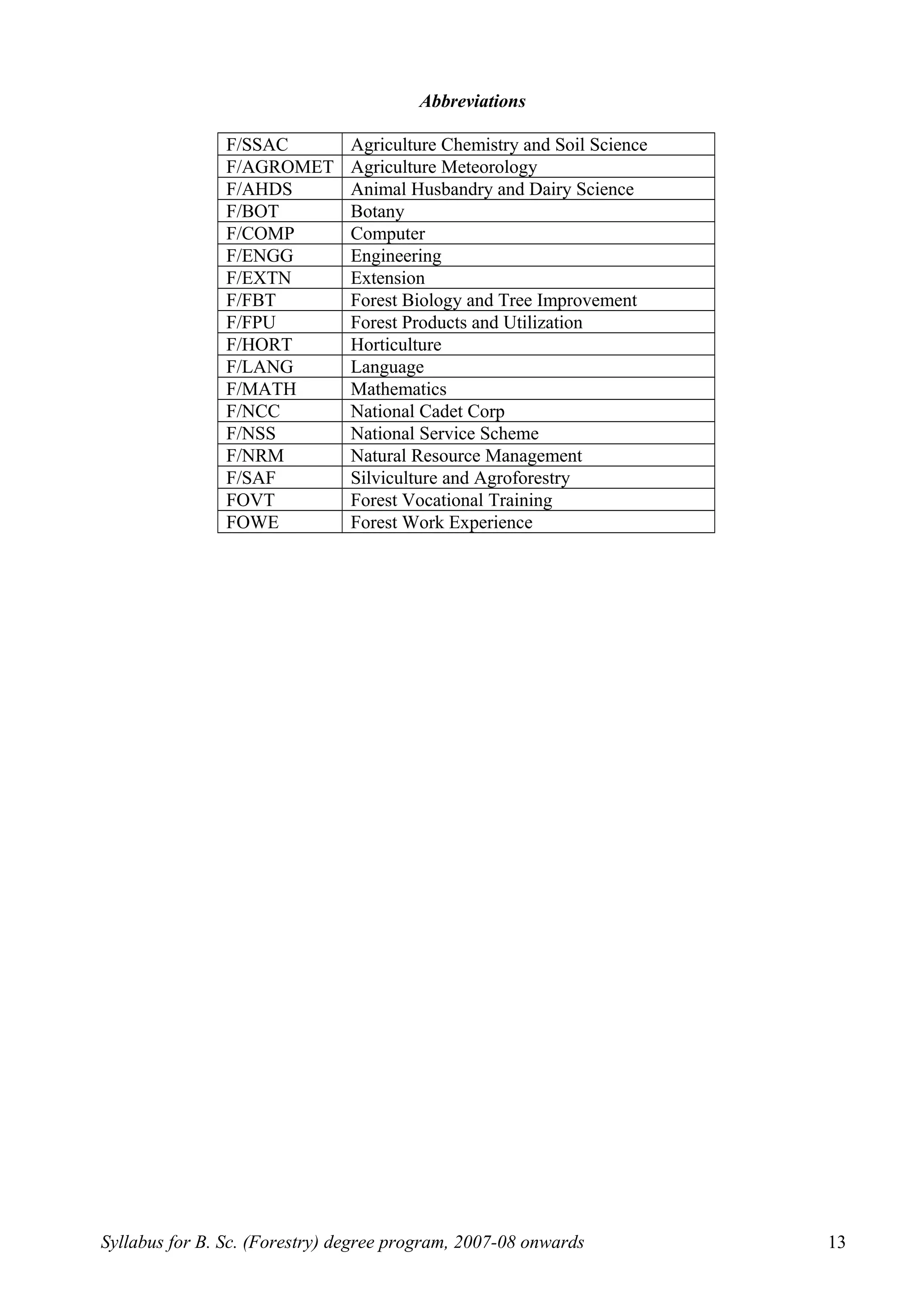
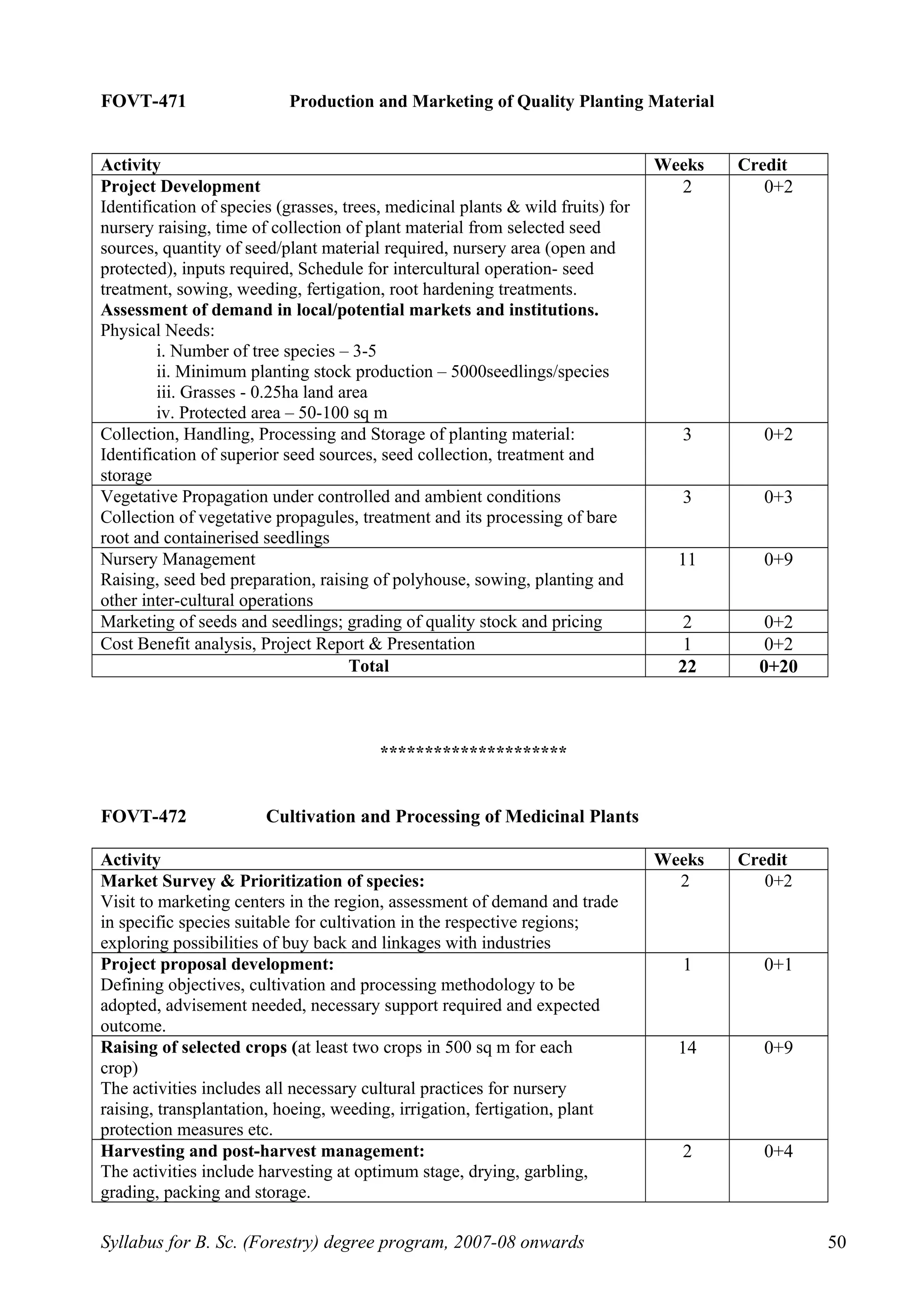
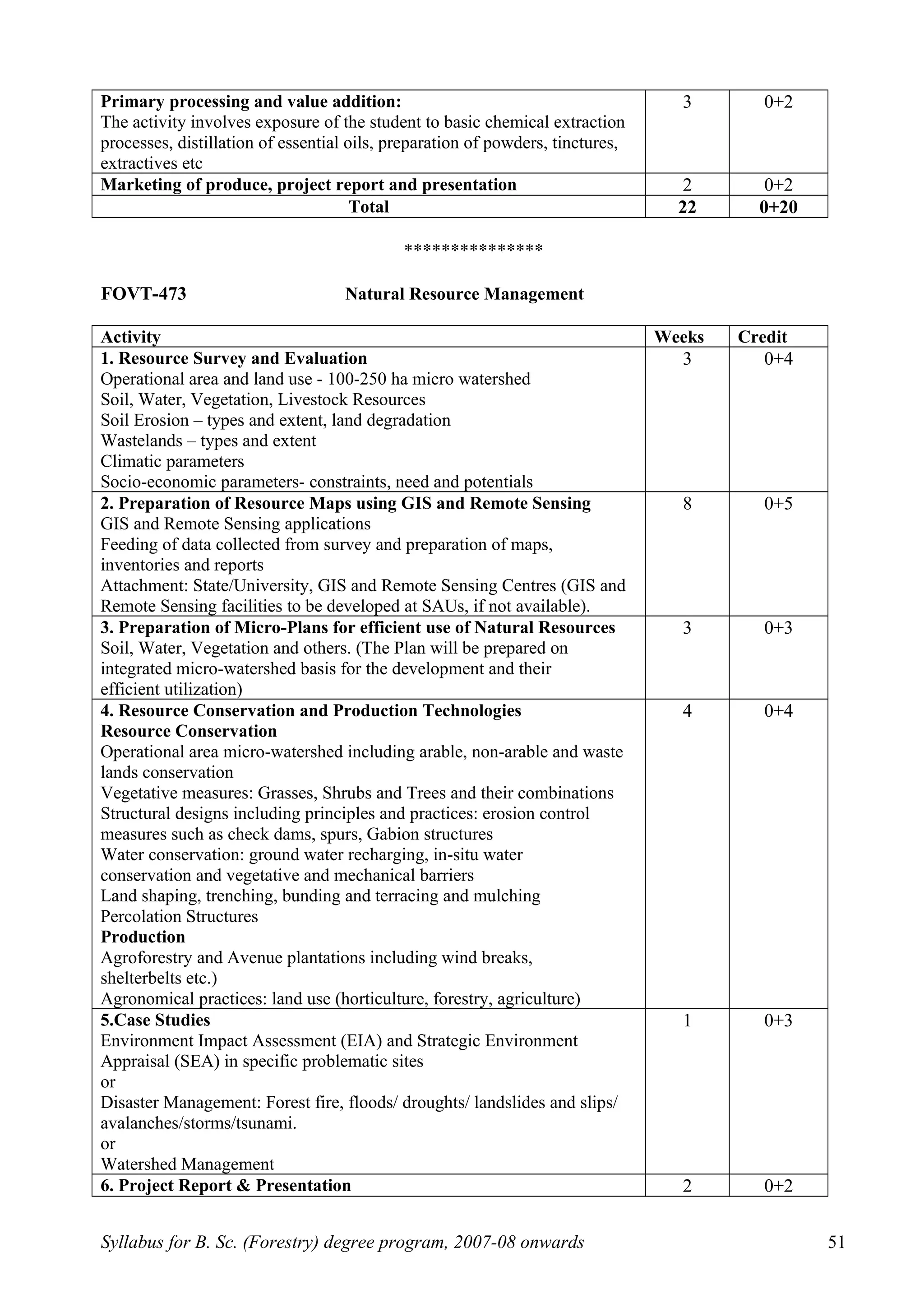
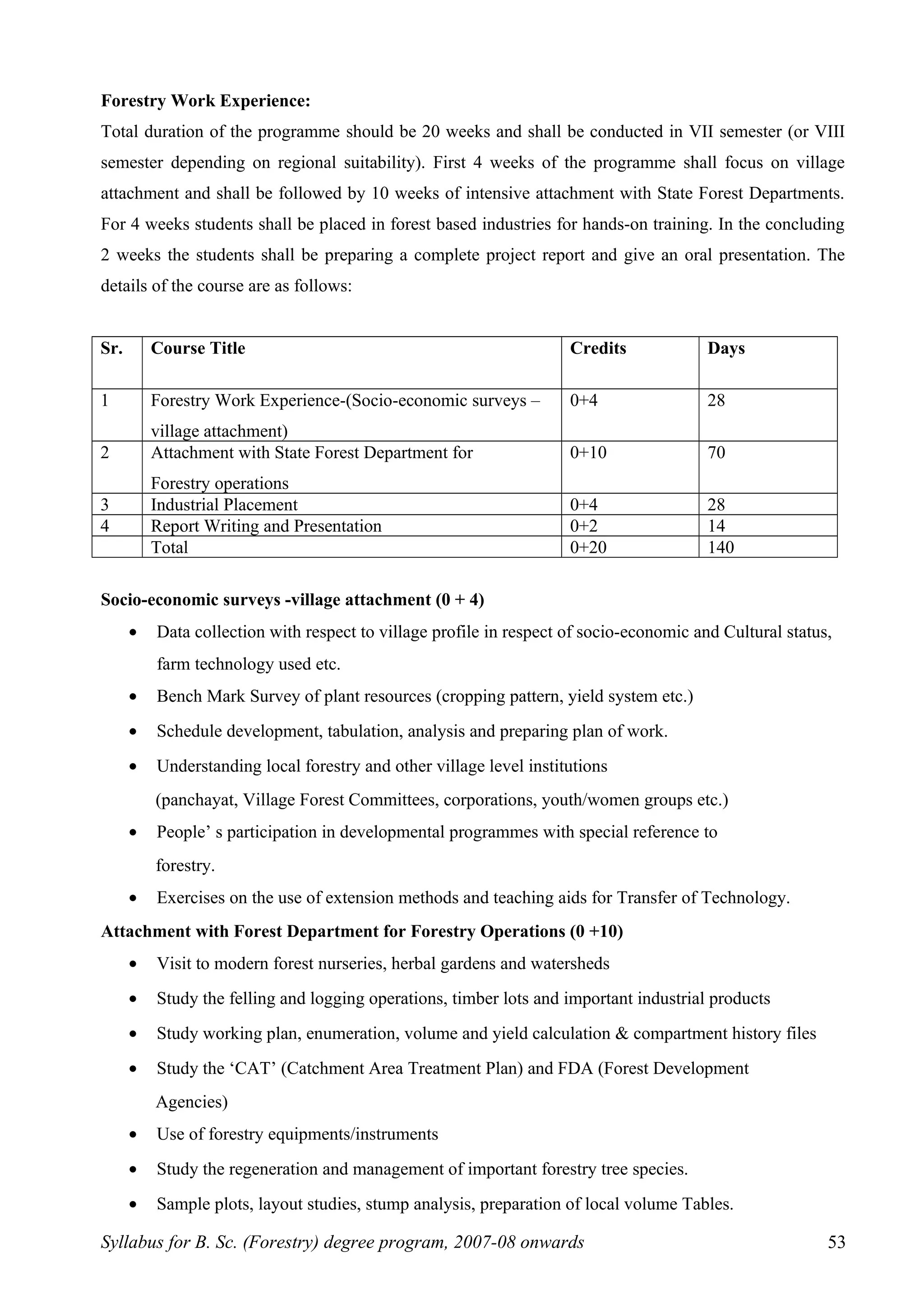
This document outlines the syllabus for a B.Sc. in Forestry degree program from 2007-2008 onwards. It details the course distribution across 5 departments: Silviculture and Agroforestry, Forest Biology and Tree Improvement, Forest Products and Utilization, Natural Resource Management, and Basic Sciences and Humanities.
Over the 4-year program, students will complete 160 credits including courses in areas like silviculture, forest mensuration, tree physiology, forest ecology, wood science, soil science, forest economics, and more. The syllabus also schedules the courses across 8 semesters, providing the semester-wise course breakdown and credit allocation. Non-credit compulsory courses like NCC, NSS