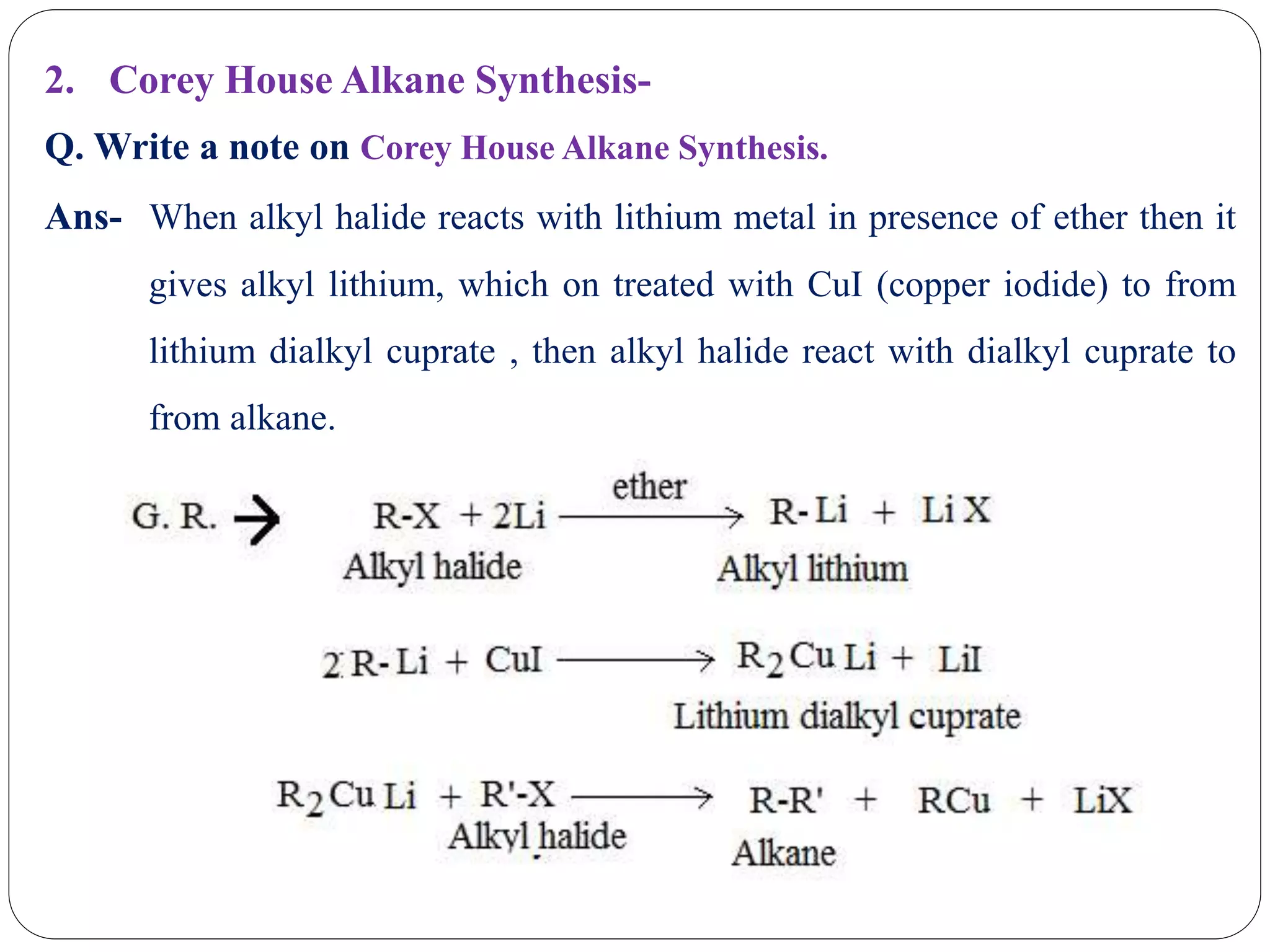
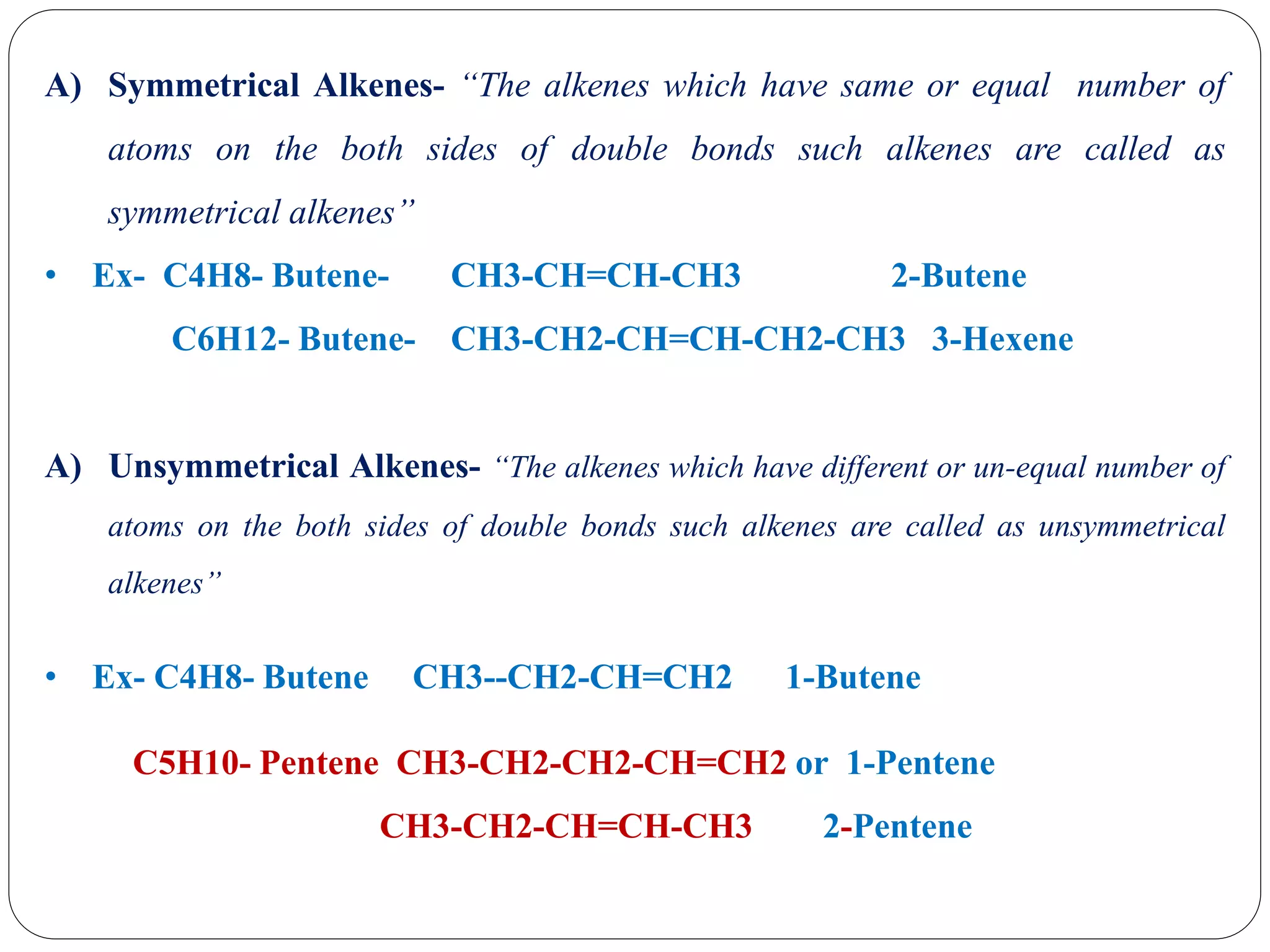
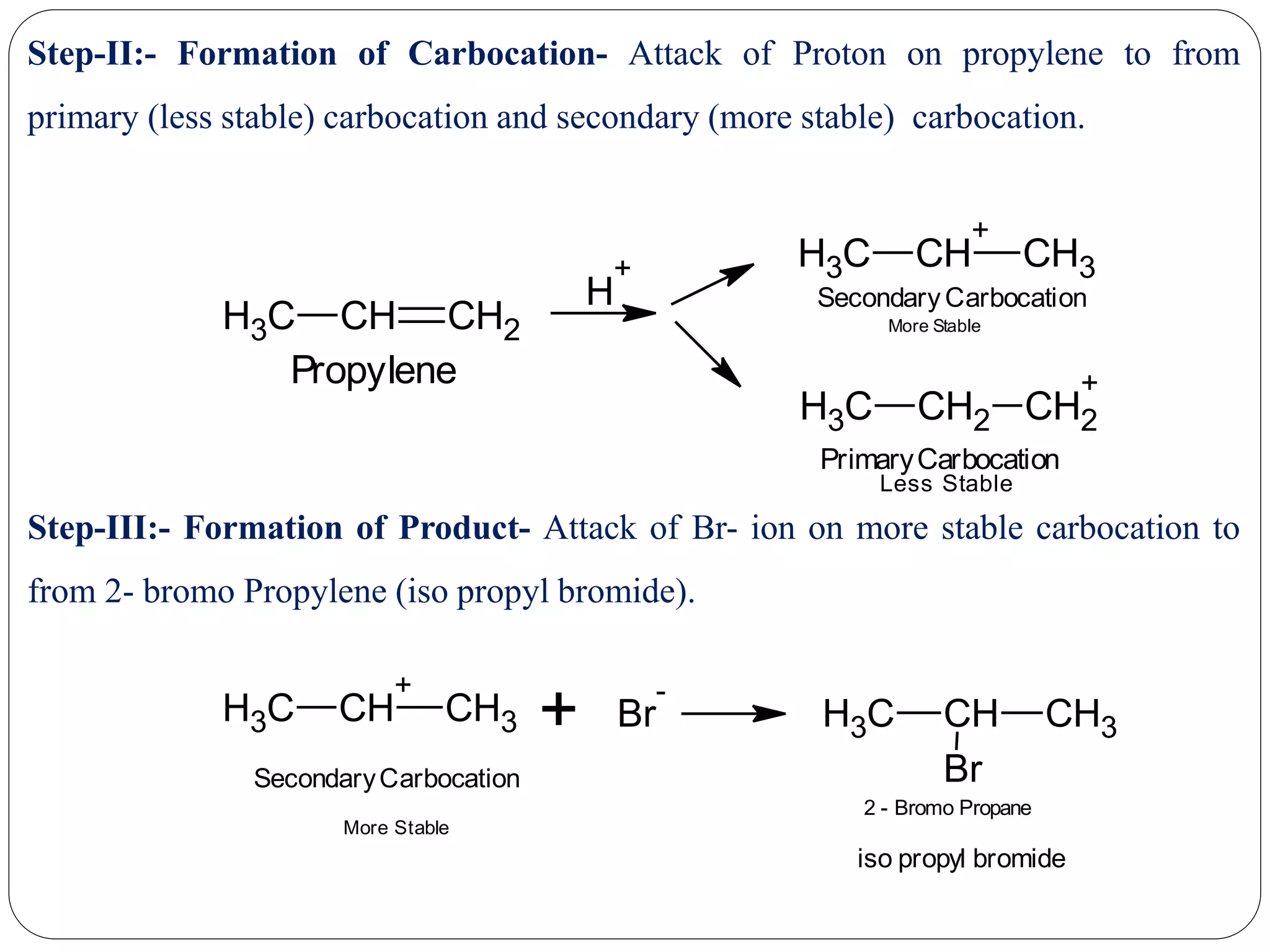
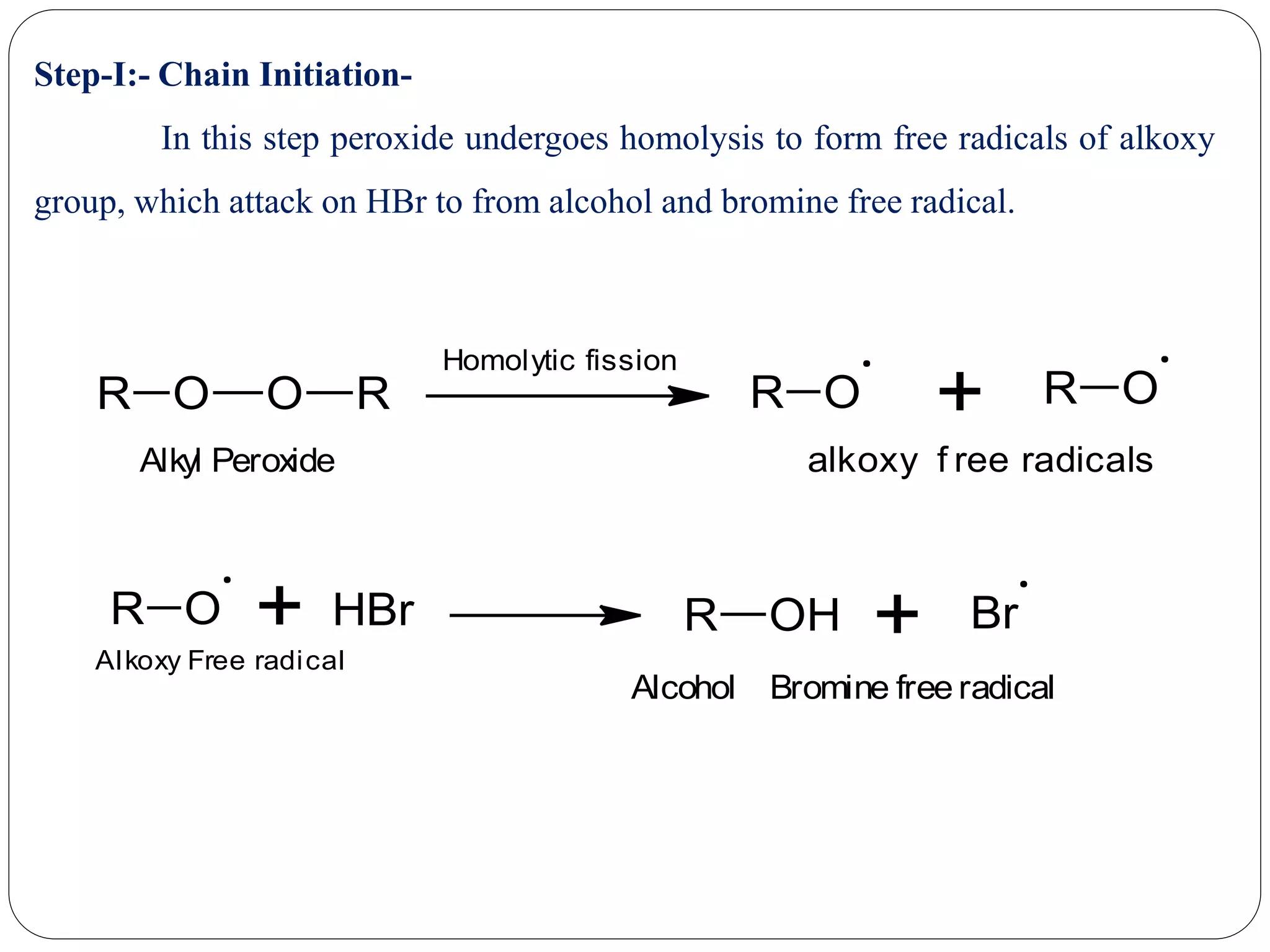
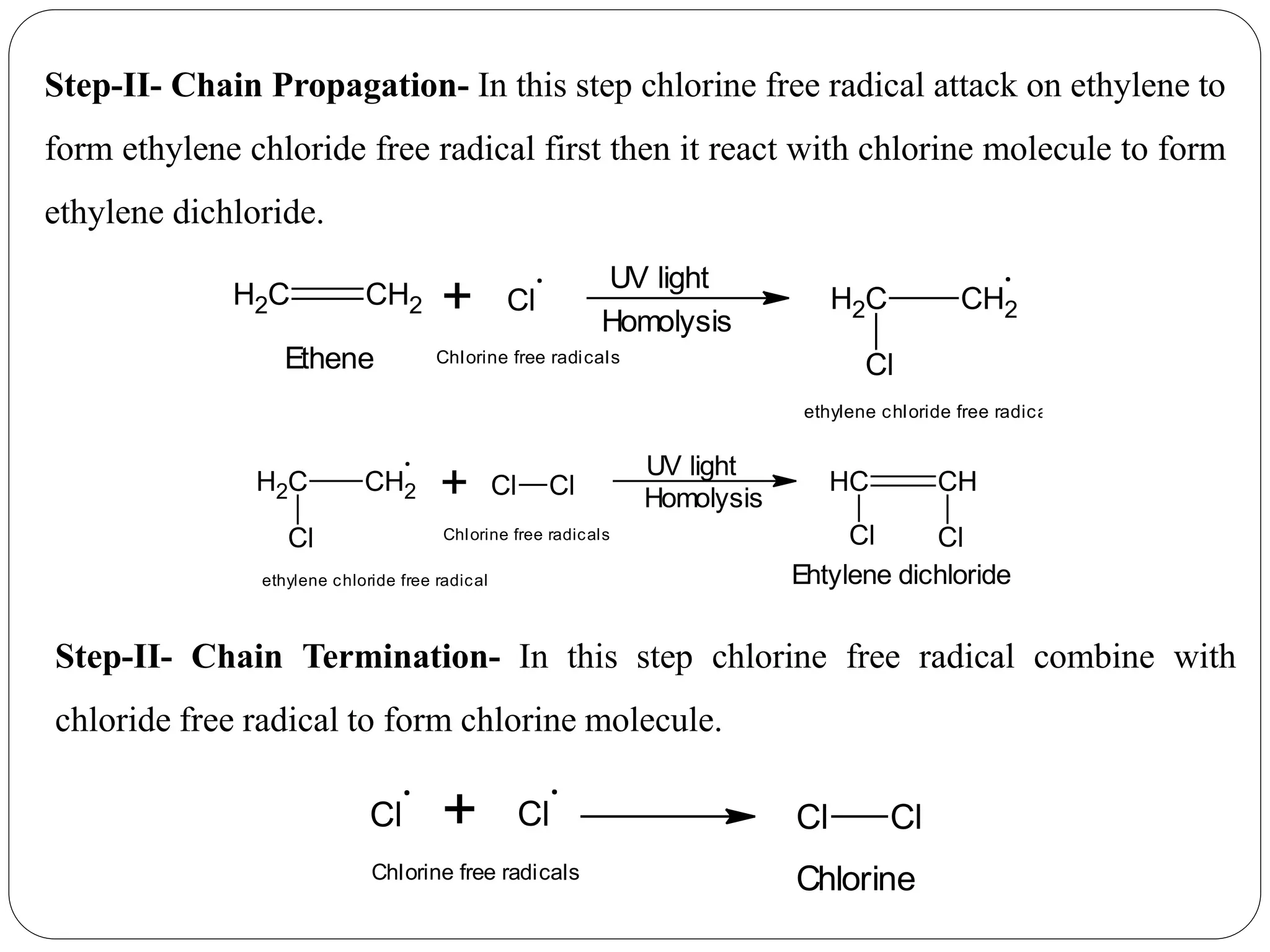
The document provides an overview of aliphatic hydrocarbons, particularly focusing on alkanes and alkenes, detailing their definitions, structures, methods of formation, and chemical reactions. It introduces the concept of hydrocarbon functional groups, explains the mechanisms of various reactions such as halogenation and elimination reactions, and discusses the Markownikoff's rule and peroxide effect. Additionally, it outlines specific examples, reactions, and conditions related to the synthesis and transformations of these compounds.