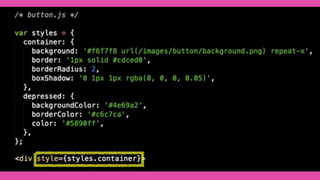
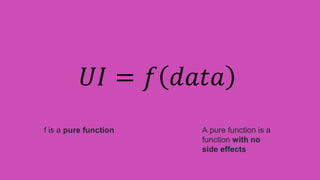
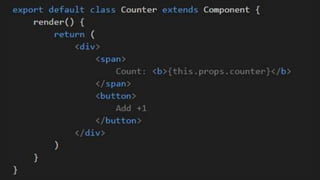
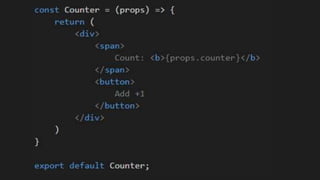
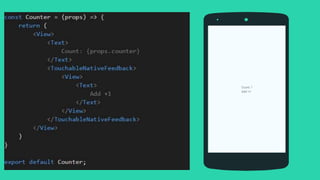
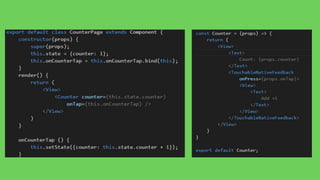
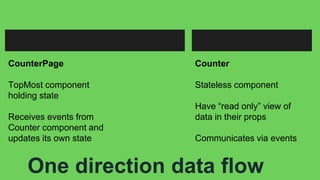
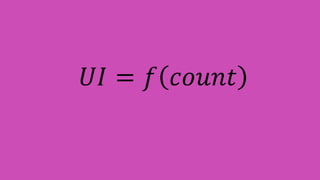This document summarizes a presentation about React Native, a library for building mobile apps using JavaScript and React. React Native allows building native mobile apps using the same tools and workflow as web development. It brings the "React way" of building UIs with reusable components to mobile and uses a single-direction data flow. While code can be shared between platforms, some UI components may not be fully reusable due to platform differences. The virtual DOM generated by components is translated to real native UI.