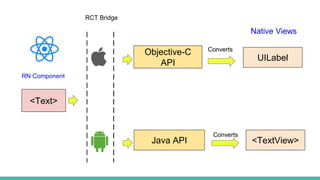
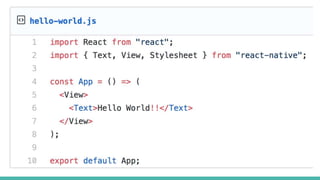
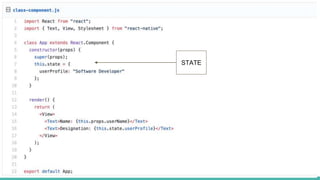
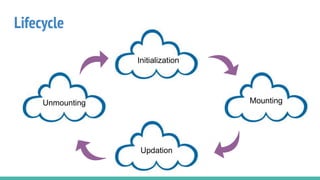
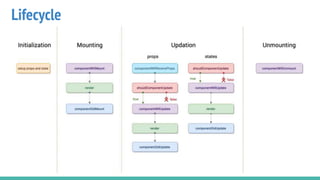
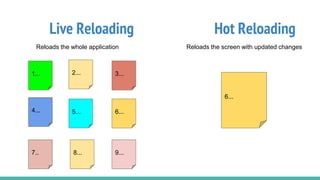
React Native is an open source framework for building mobile apps using React and JavaScript. It uses native components and allows building real mobile apps for Android and iOS. It works by using a virtual DOM layer that maps React components to native mobile components using Objective-C and Java APIs. Developers can get started using Expo or React Native CLI. Expo is easier for beginners while CLI allows more customization and third party libraries. Core concepts include components, JSX, state, props, and unidirectional data flow. React Native also includes tools like live reloading and hot reloading for faster development.