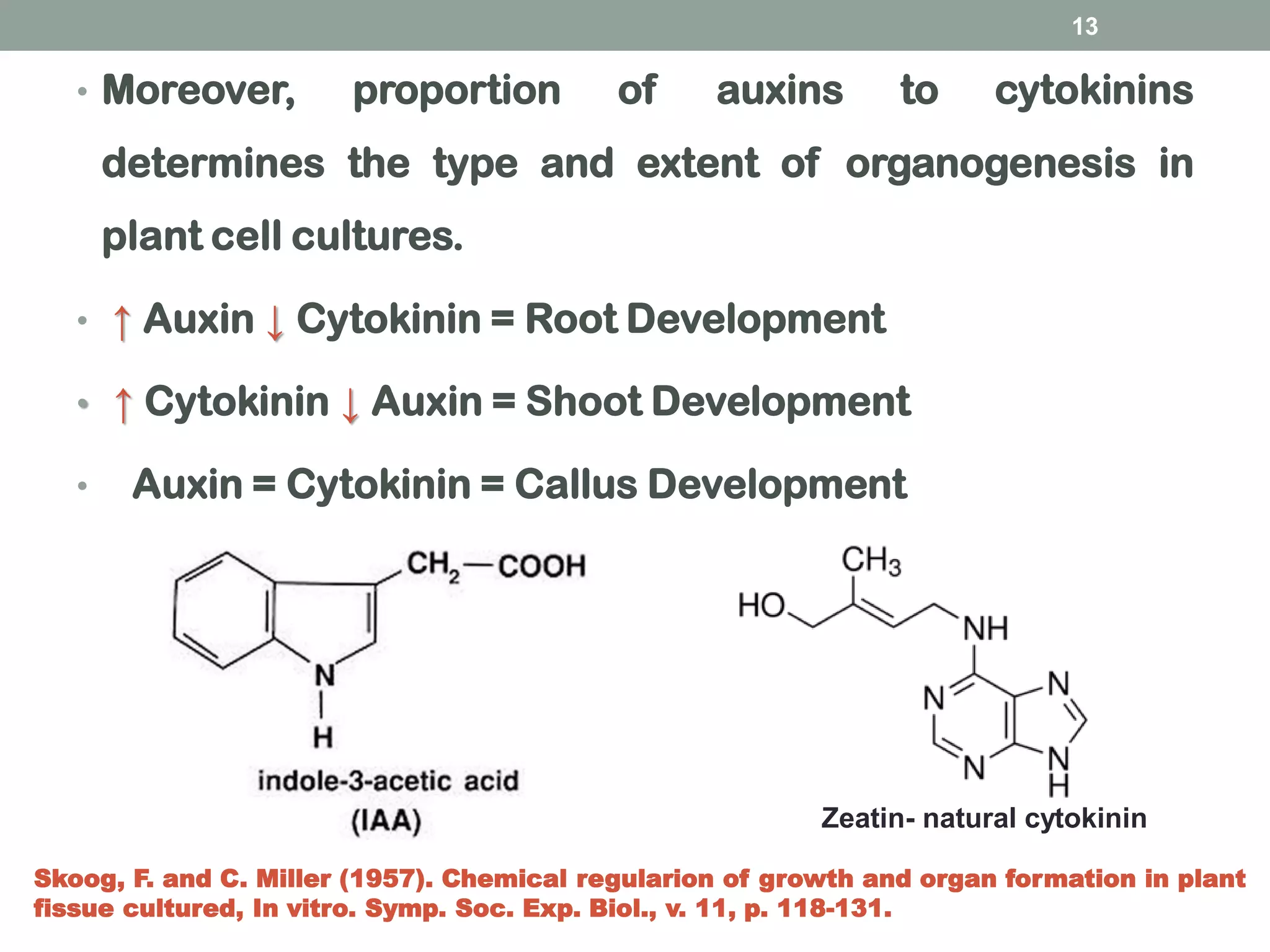
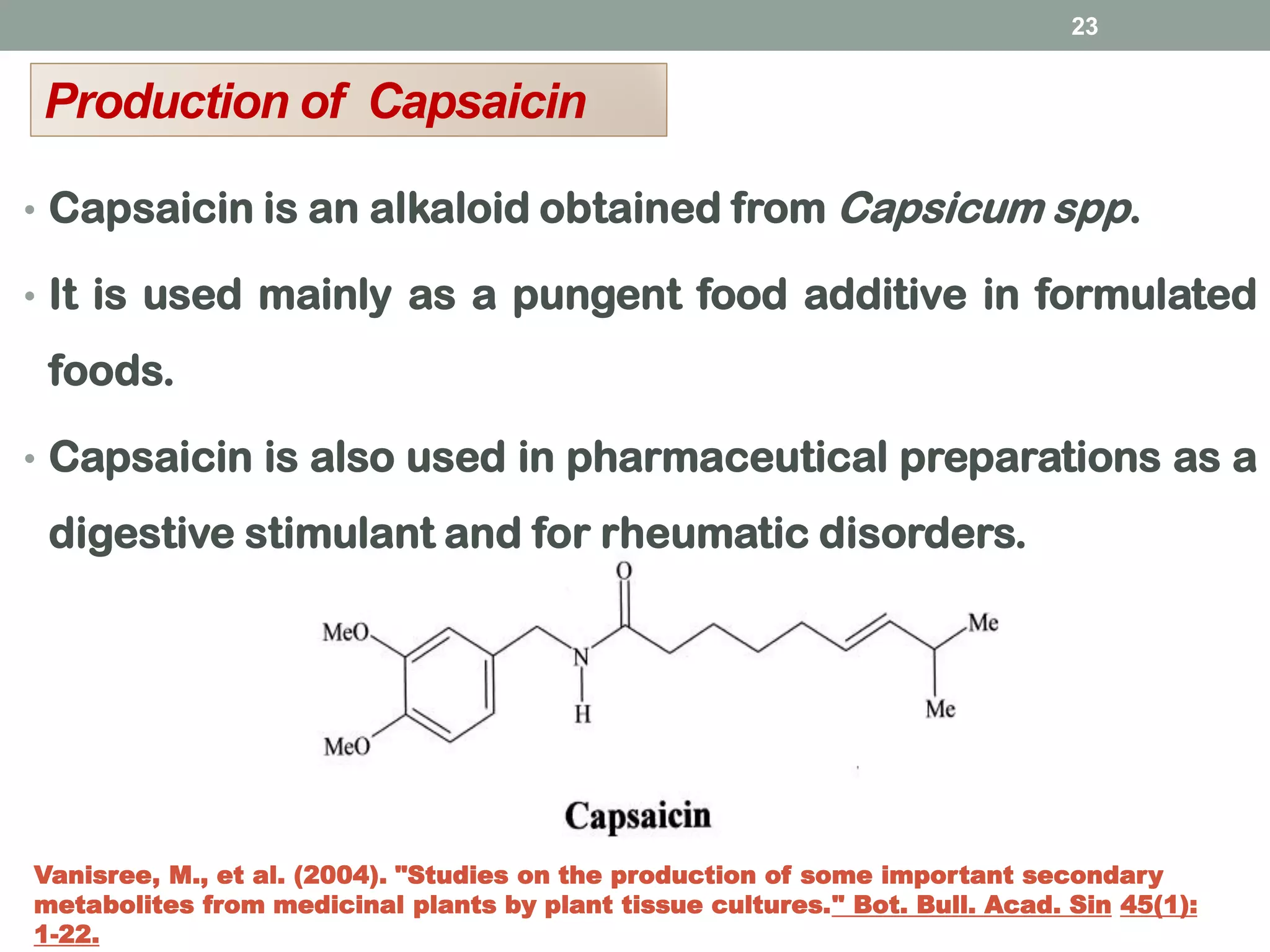
Plant tissue culture is the process of growing plant cells, tissues or organs in vitro under sterile conditions on a nutrient medium. The father of plant tissue culture was Haberlandt who first conceived of culturing plant cells aseptically in 1902. There are two main types of growth in tissue culture - organized growth where structure is preserved, and unorganized growth like callus or cell suspension cultures which lack structure. Key steps in establishing tissue cultures include selecting an explant, surface sterilization, and culturing on solid or liquid media. Plant growth regulators like auxins and cytokinins are important for directing growth. Tissue cultures are used to produce valuable secondary metabolites like taxol through optimization of culture conditions and addition of elic