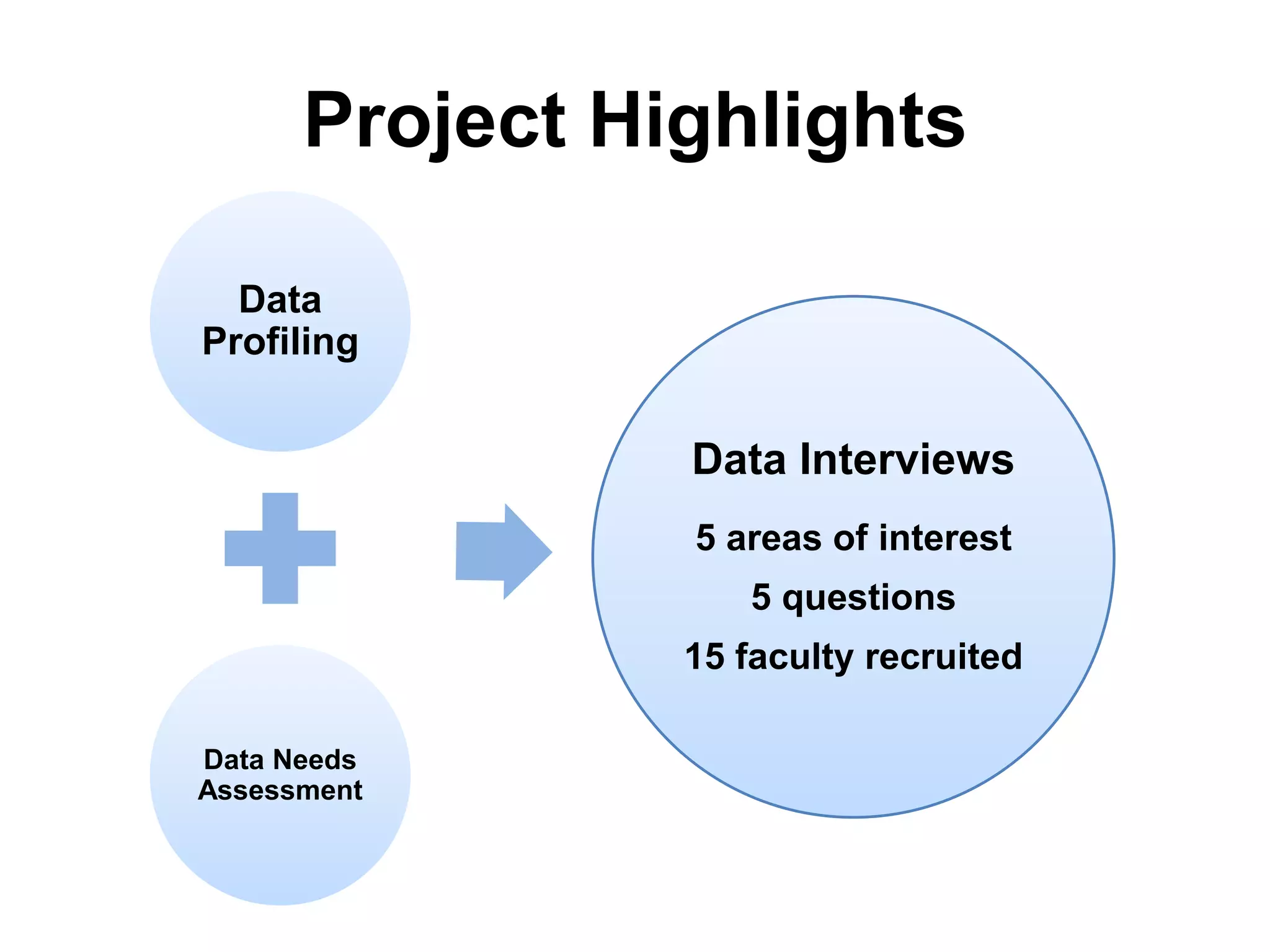
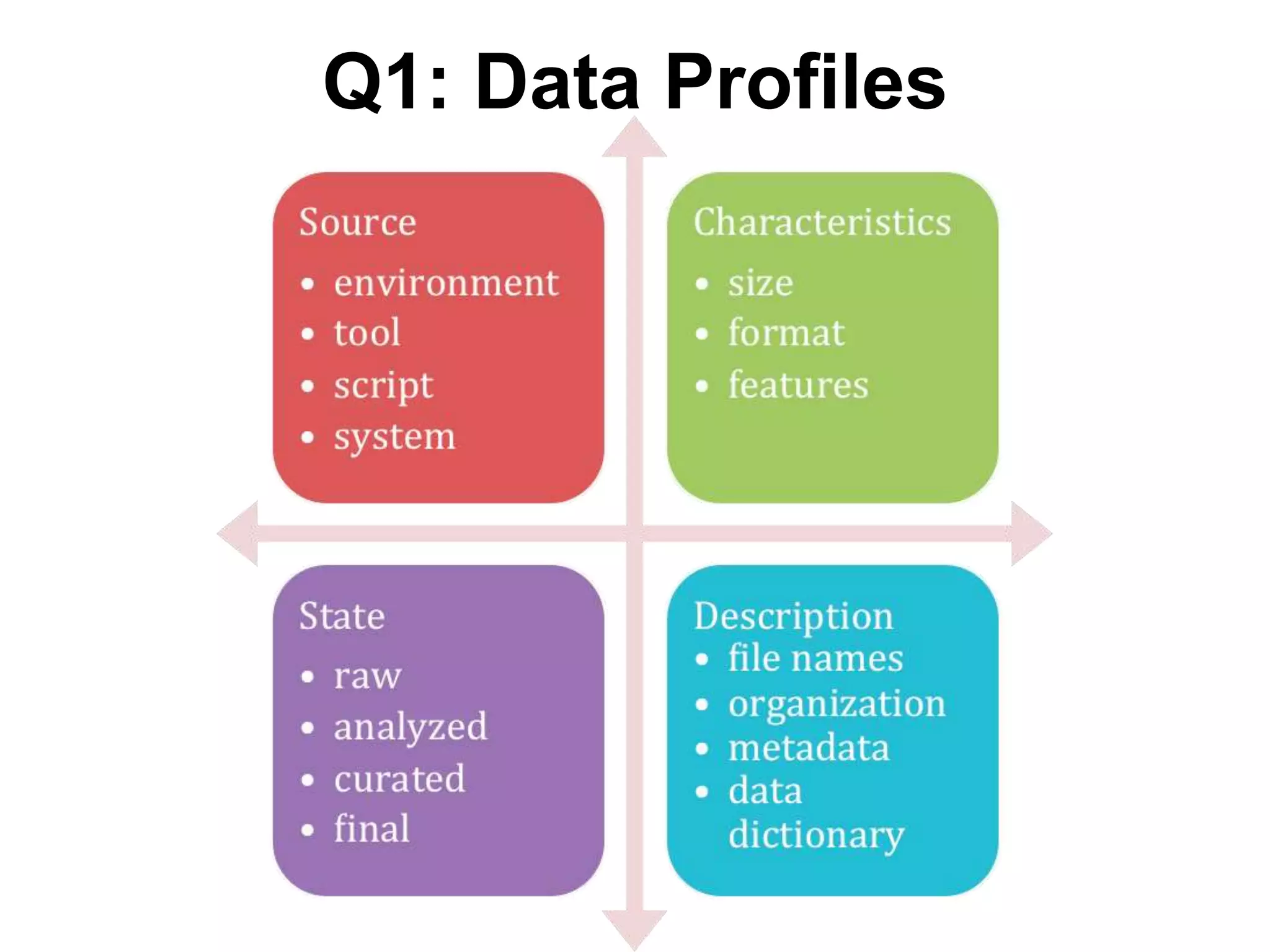
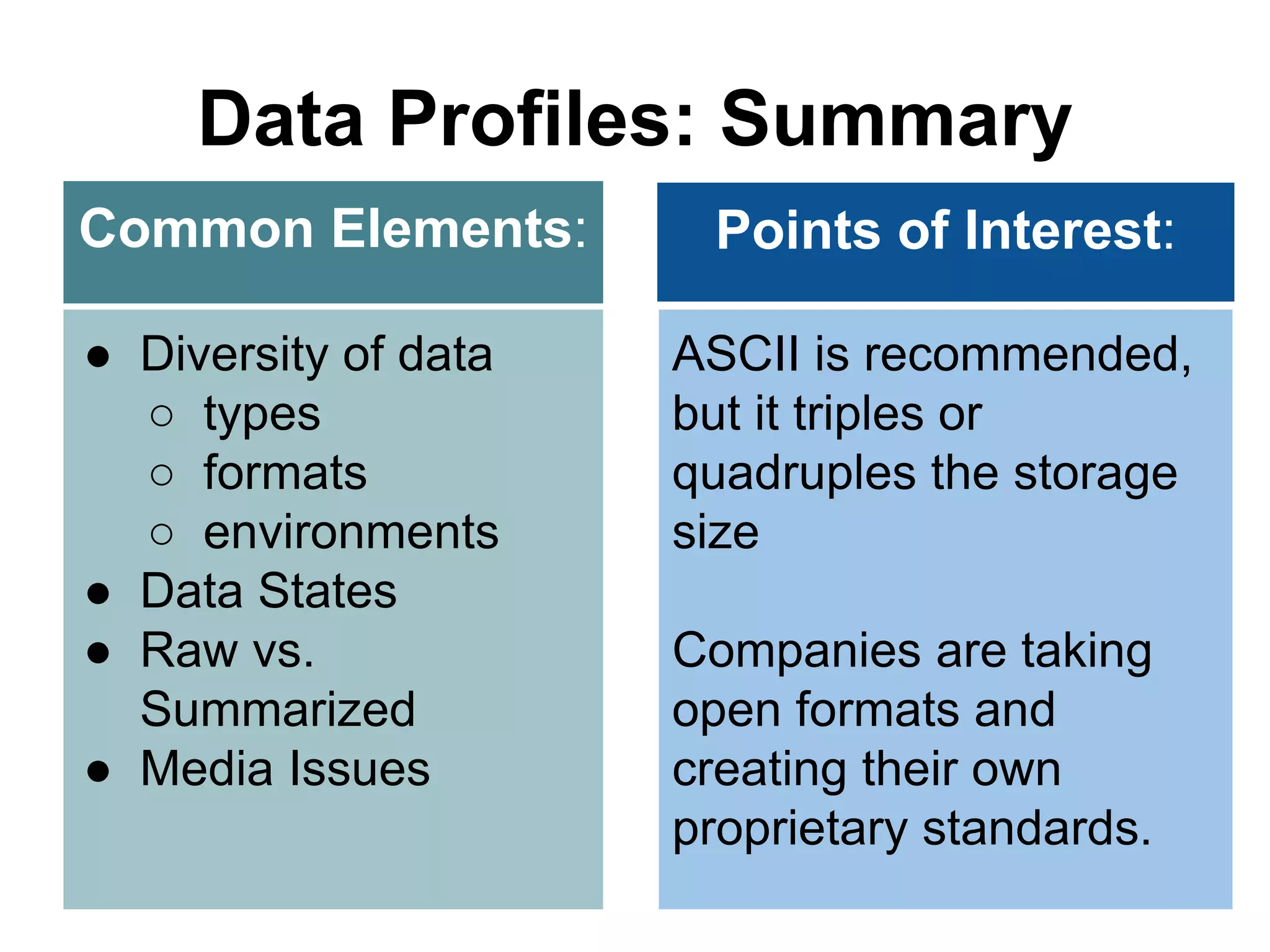
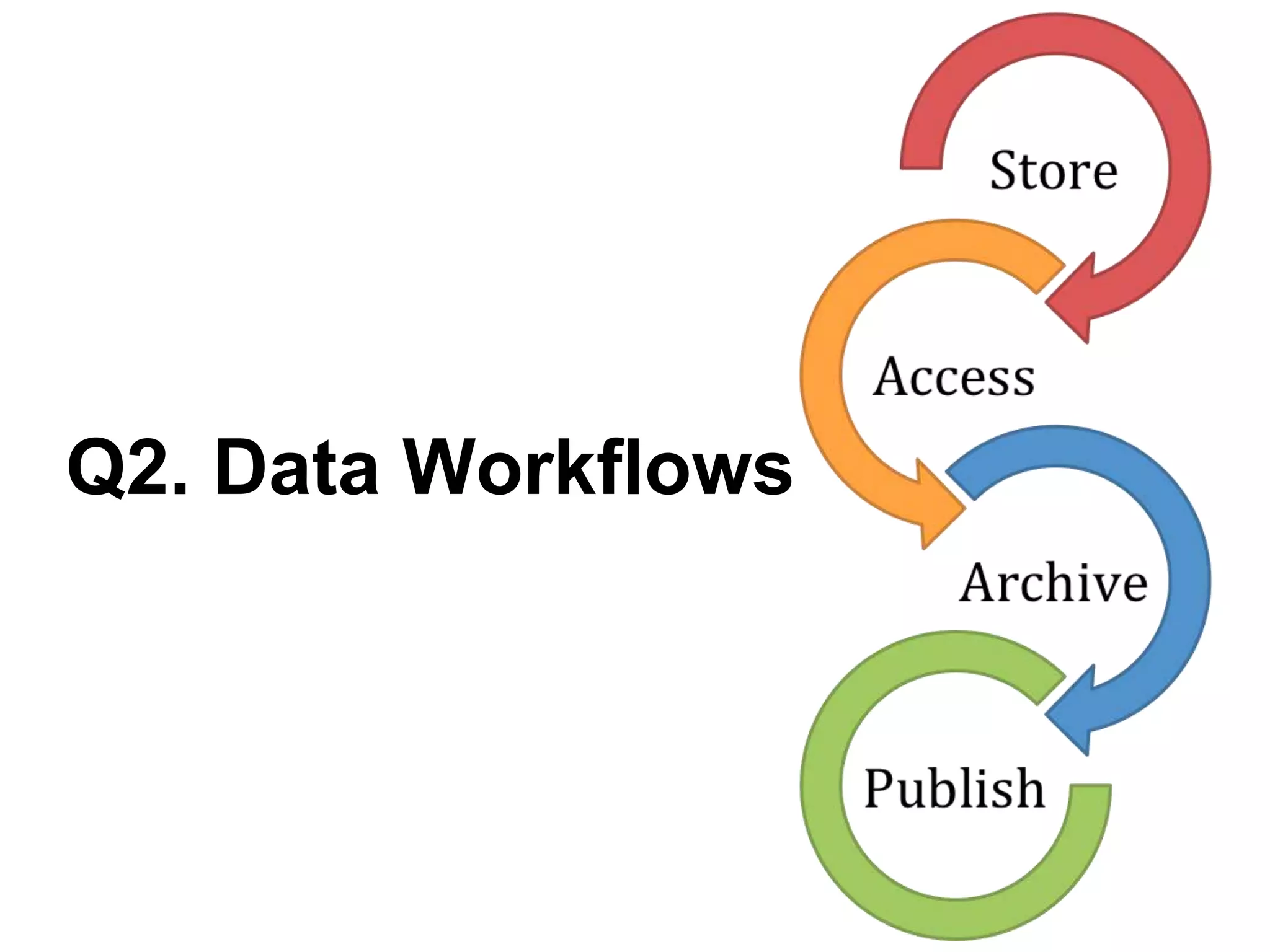
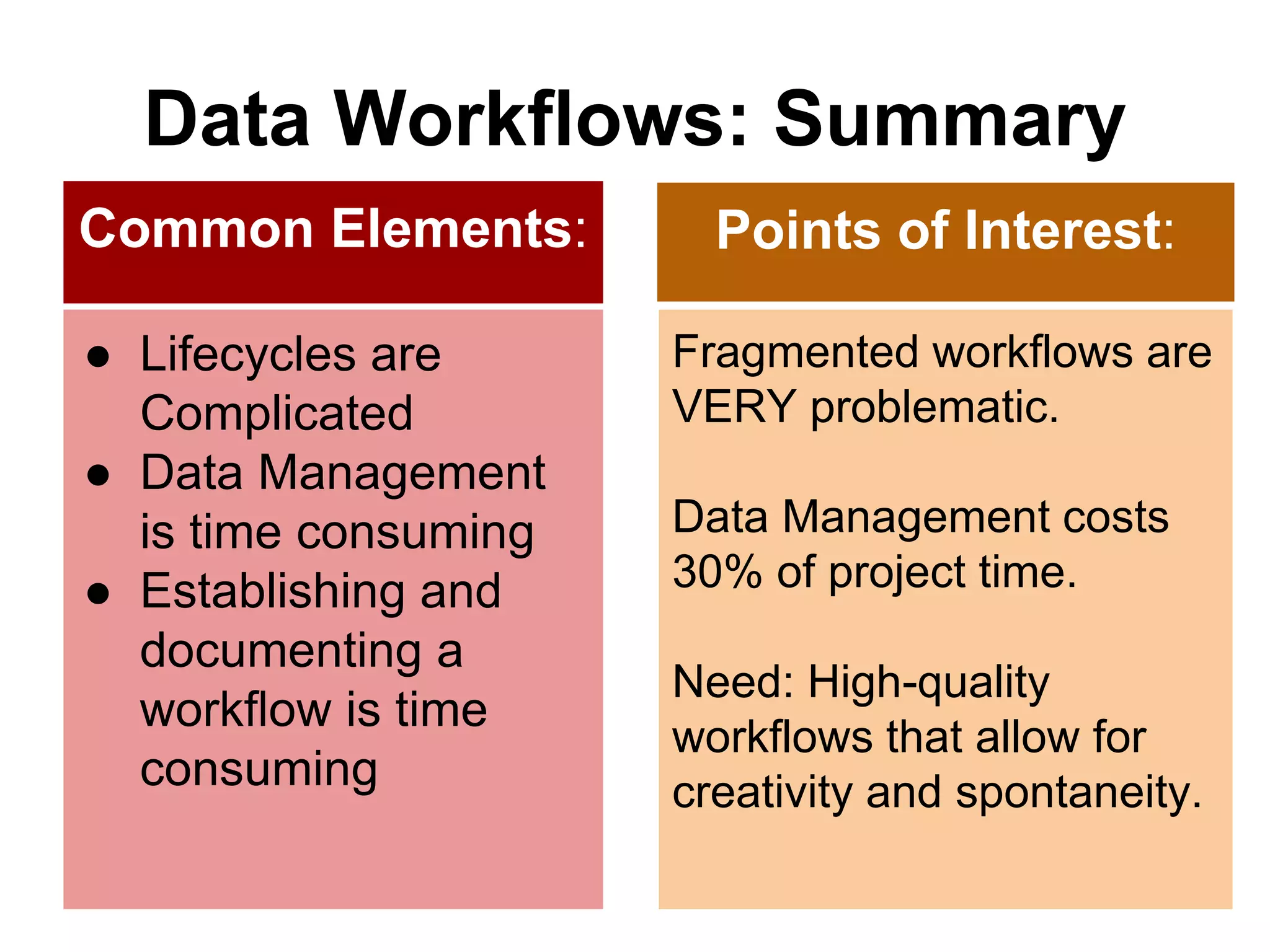
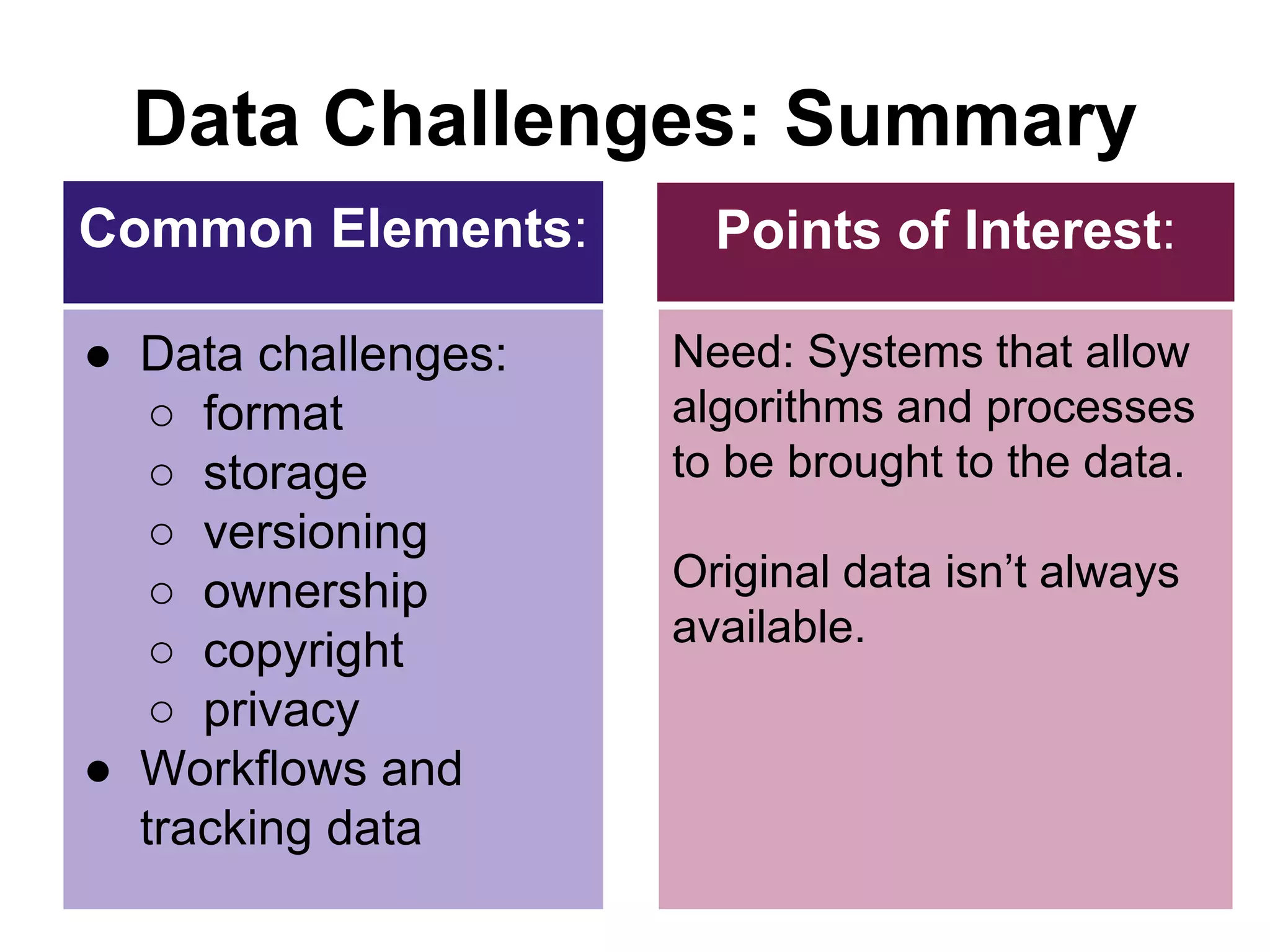
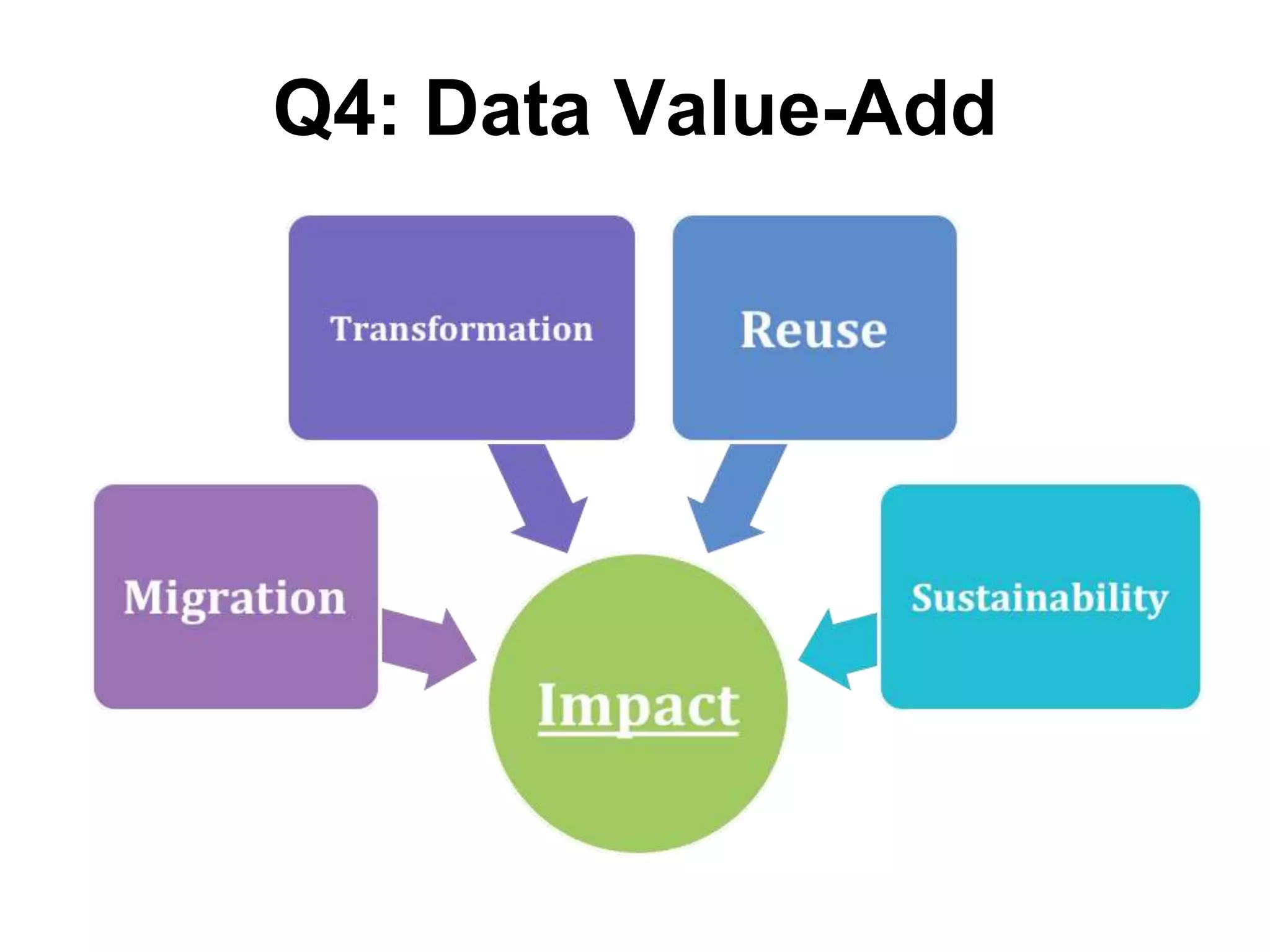
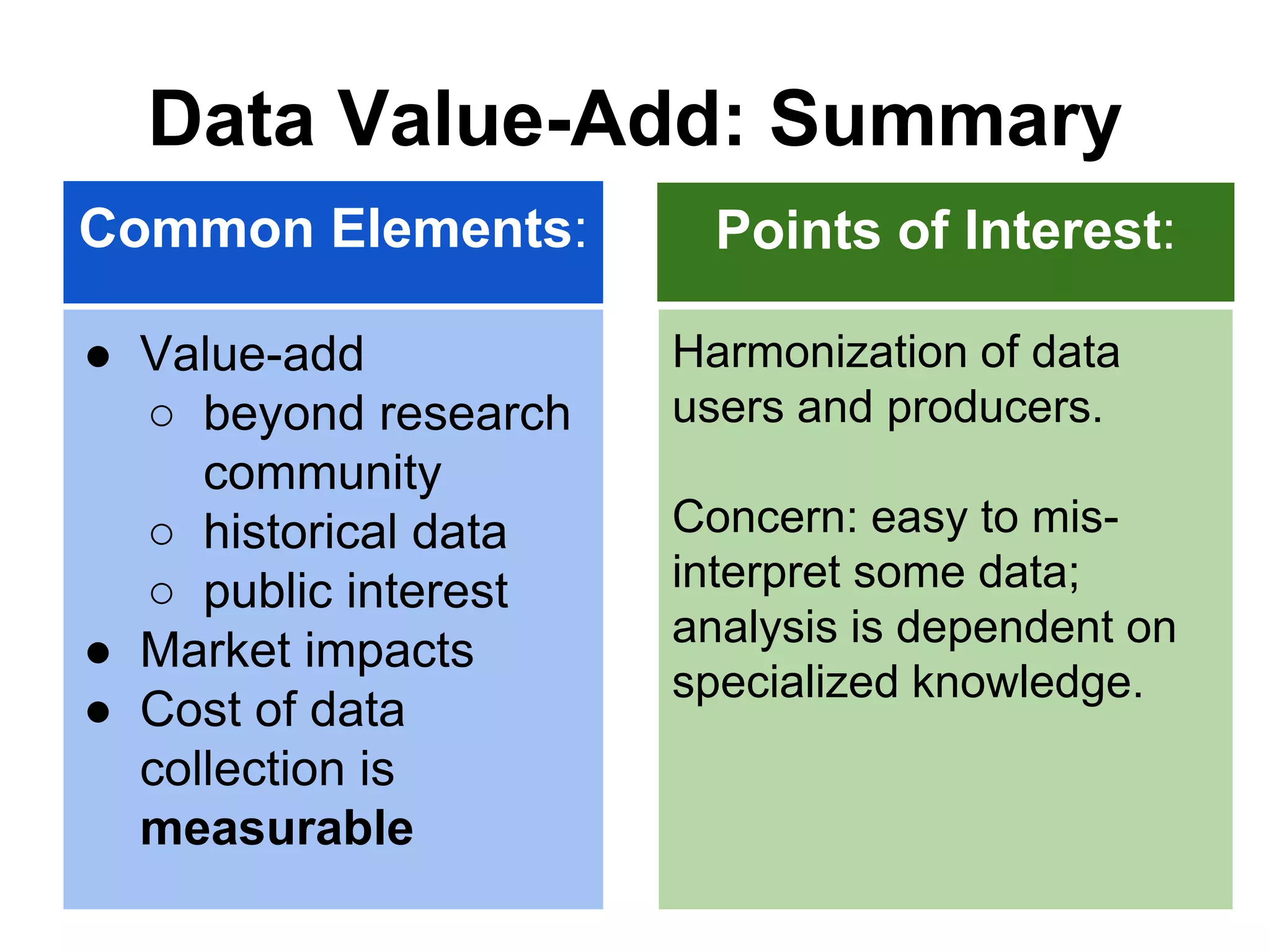
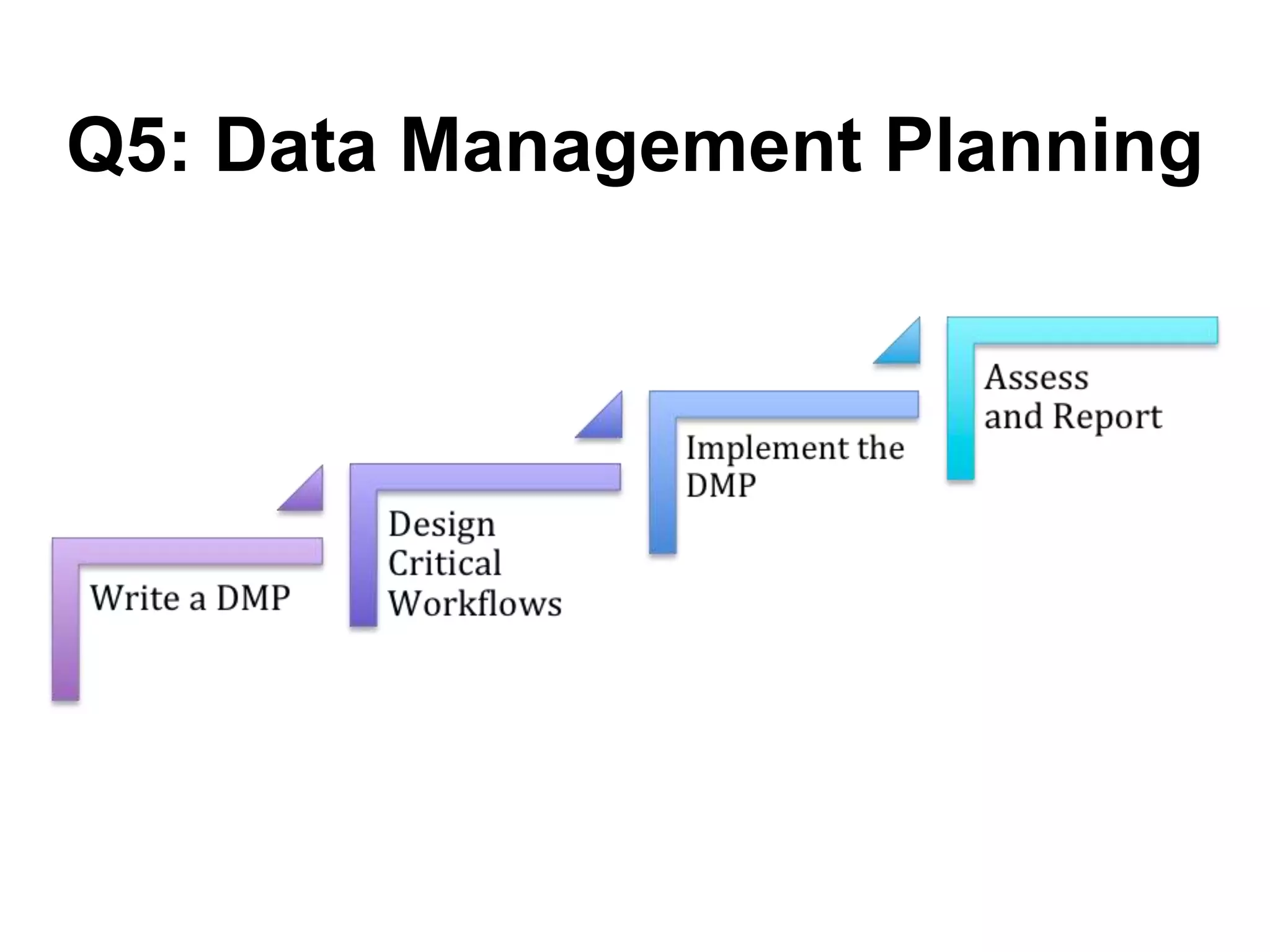
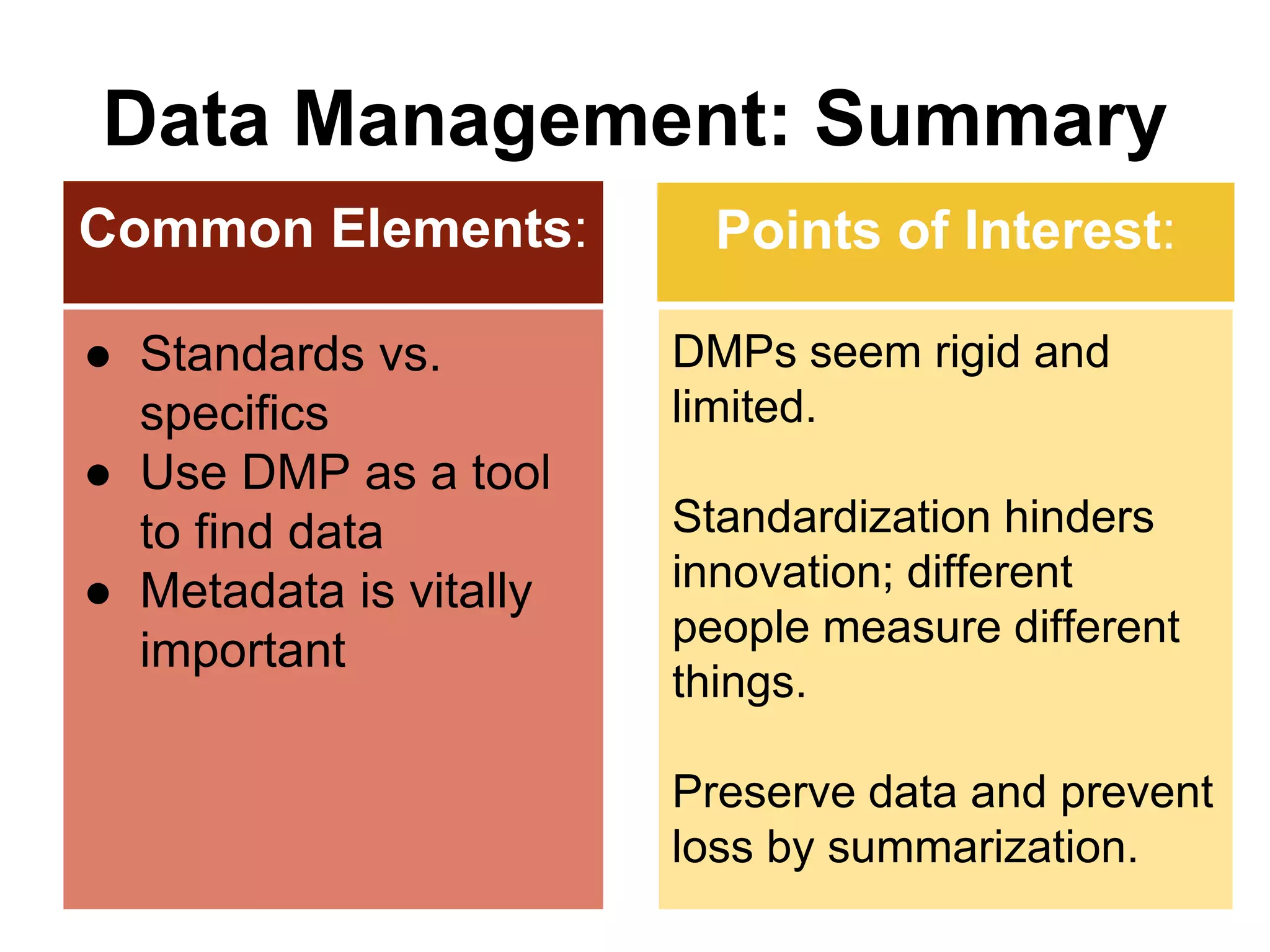
Virginia Tech's pilot program aims to enhance research data services for the College of Natural Resources and Environment. It identifies challenges in data workflows, management, and standardization while emphasizing the need for high-quality data management practices and training. The project fosters partnerships and conversations to improve research data access and preservation within the university community.