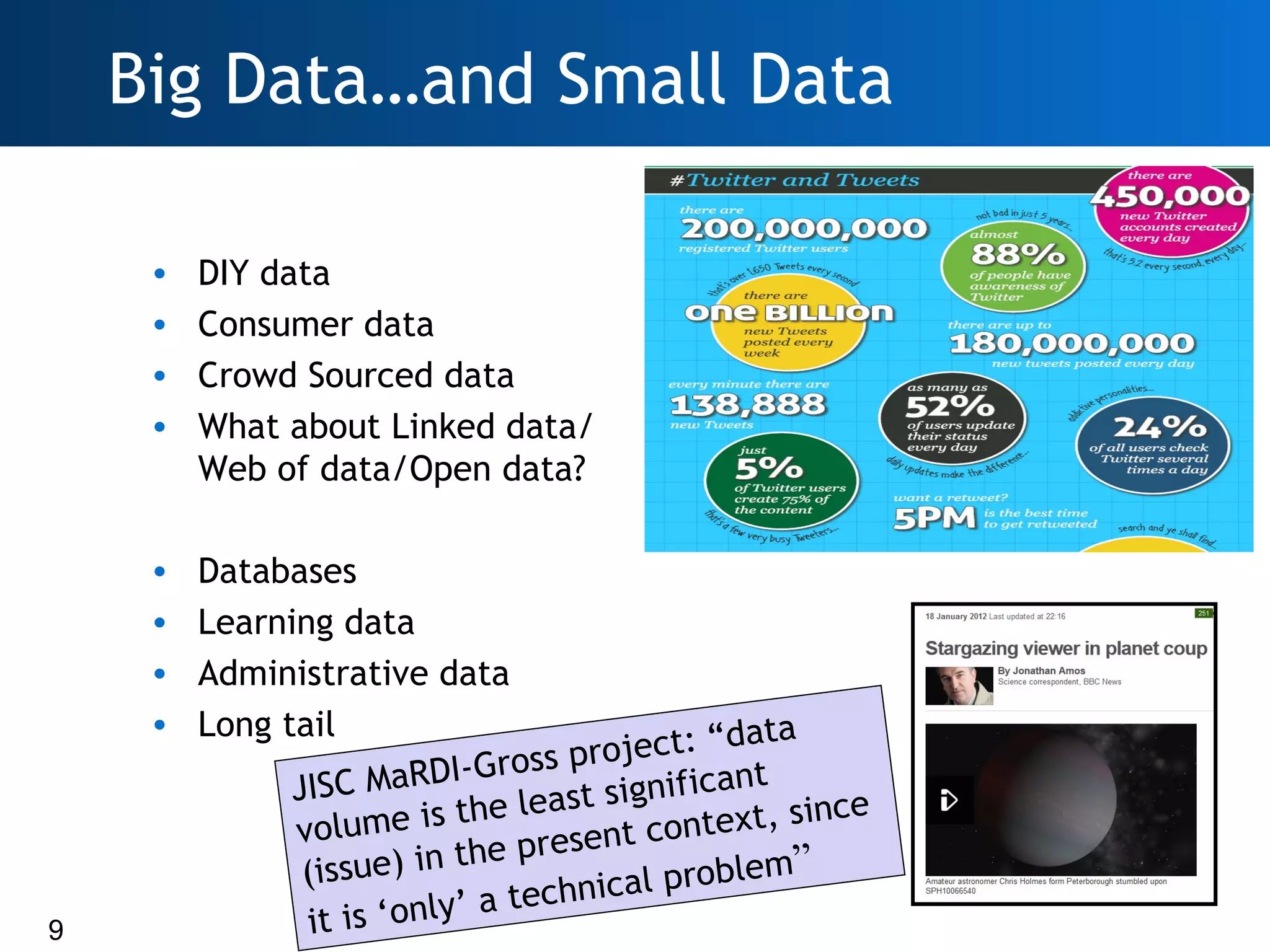
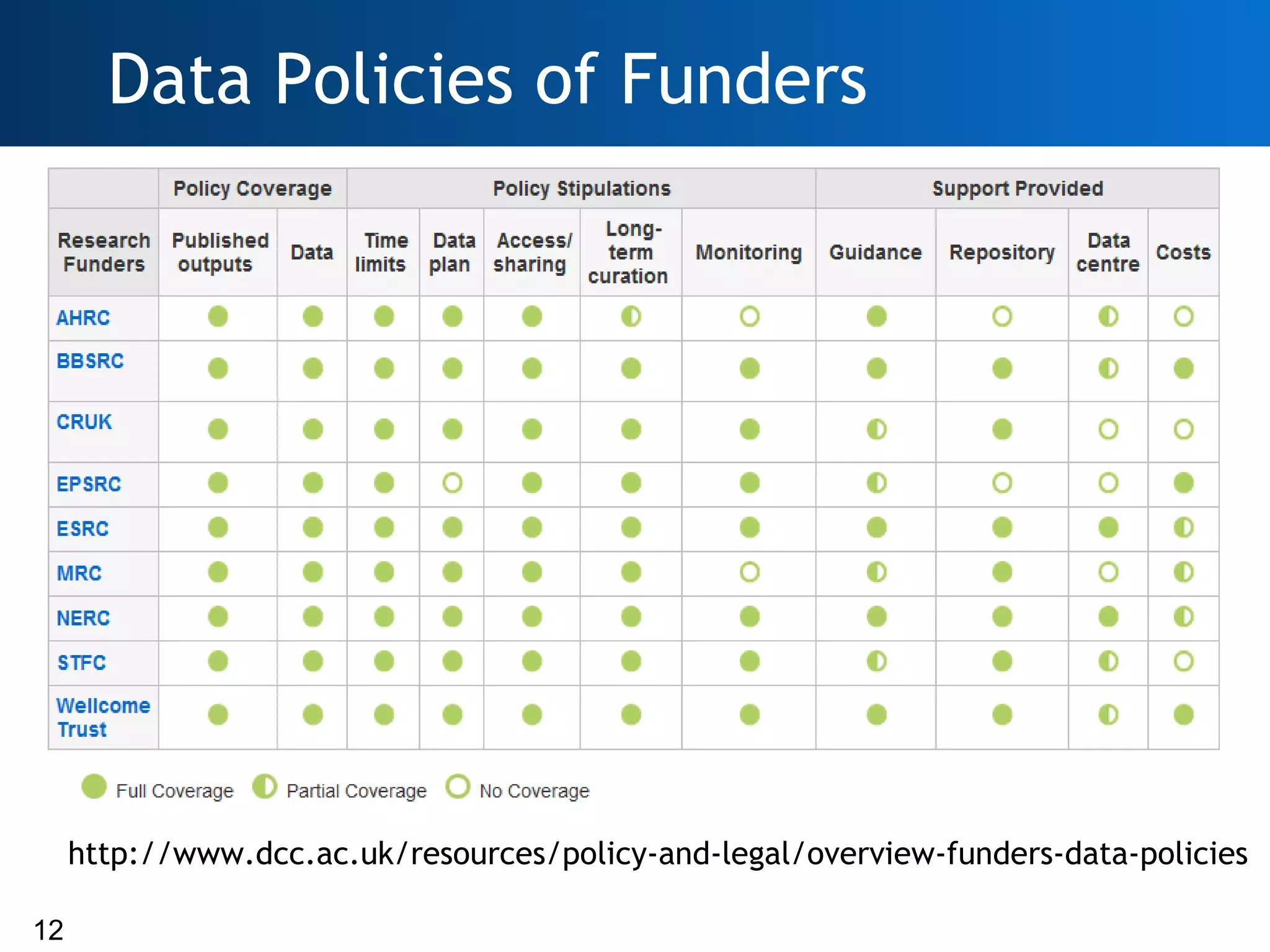
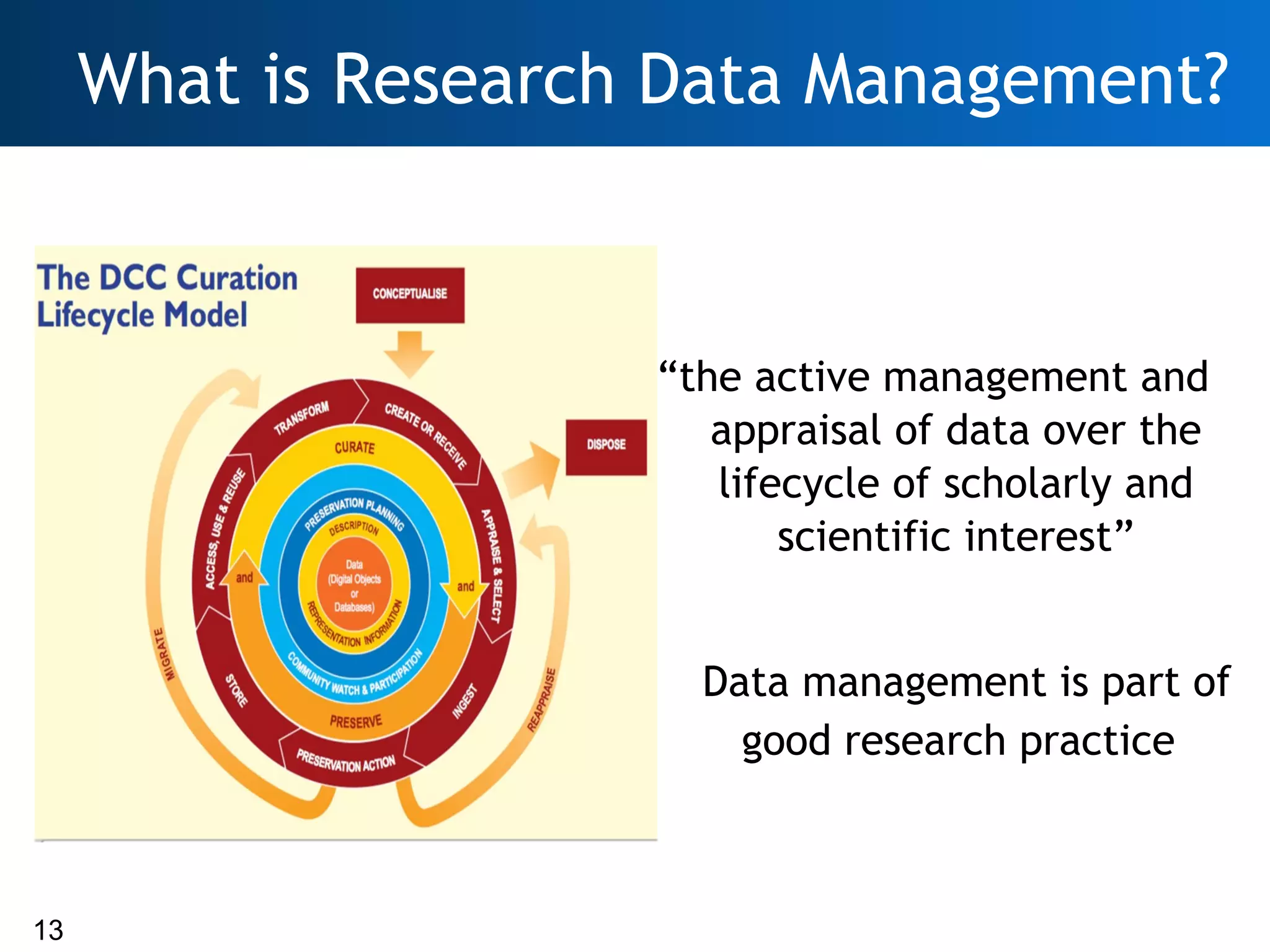
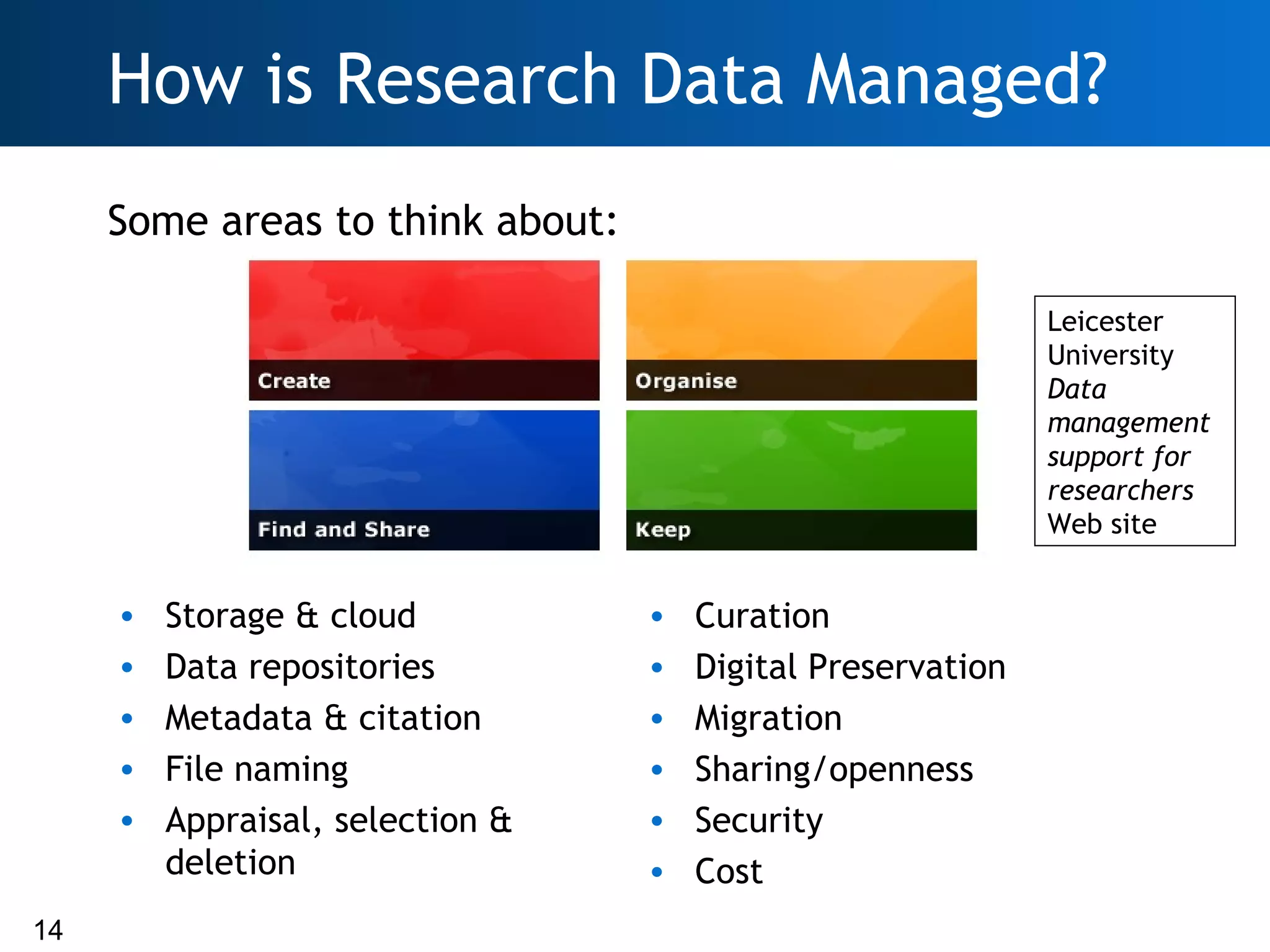
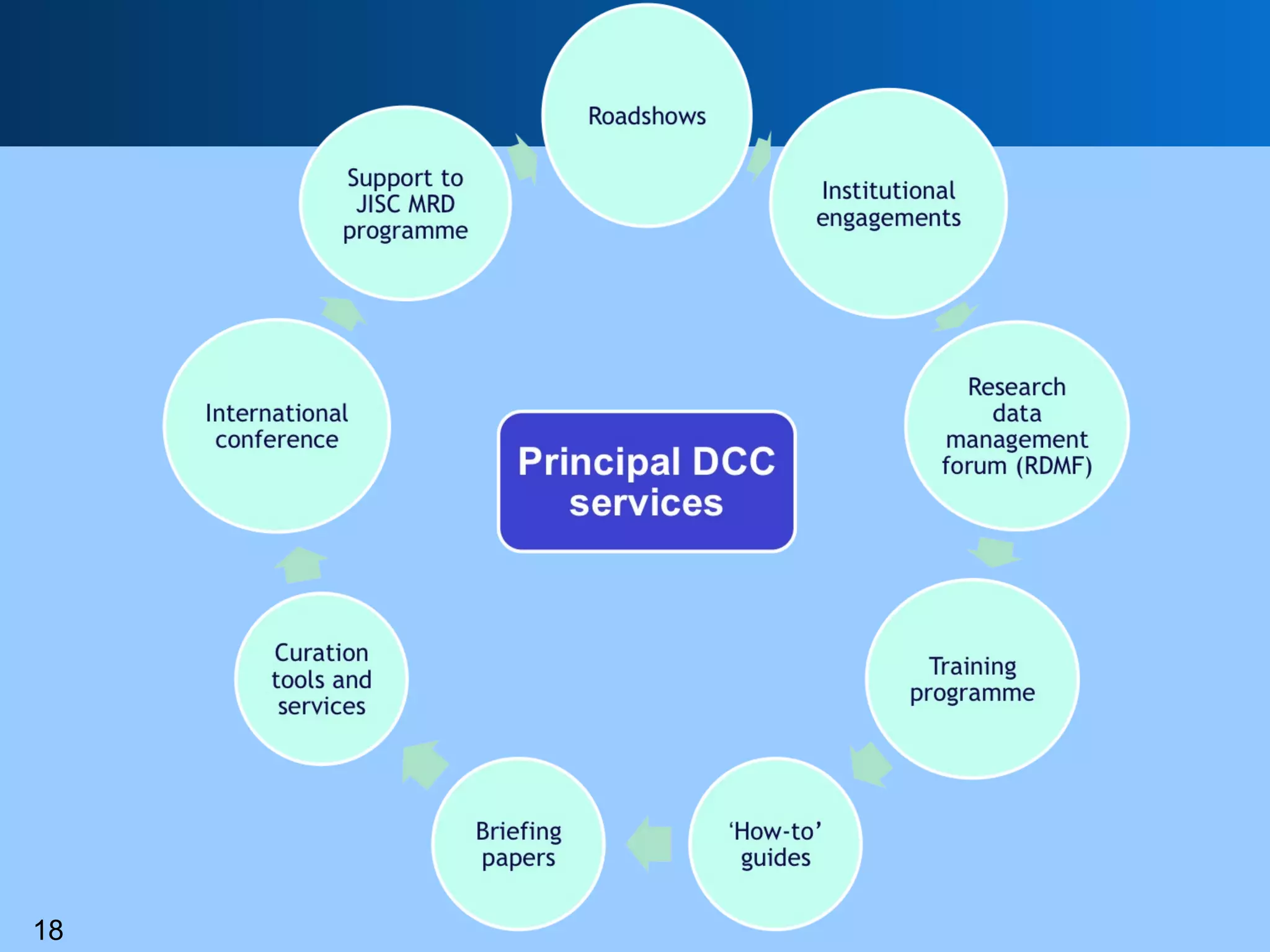
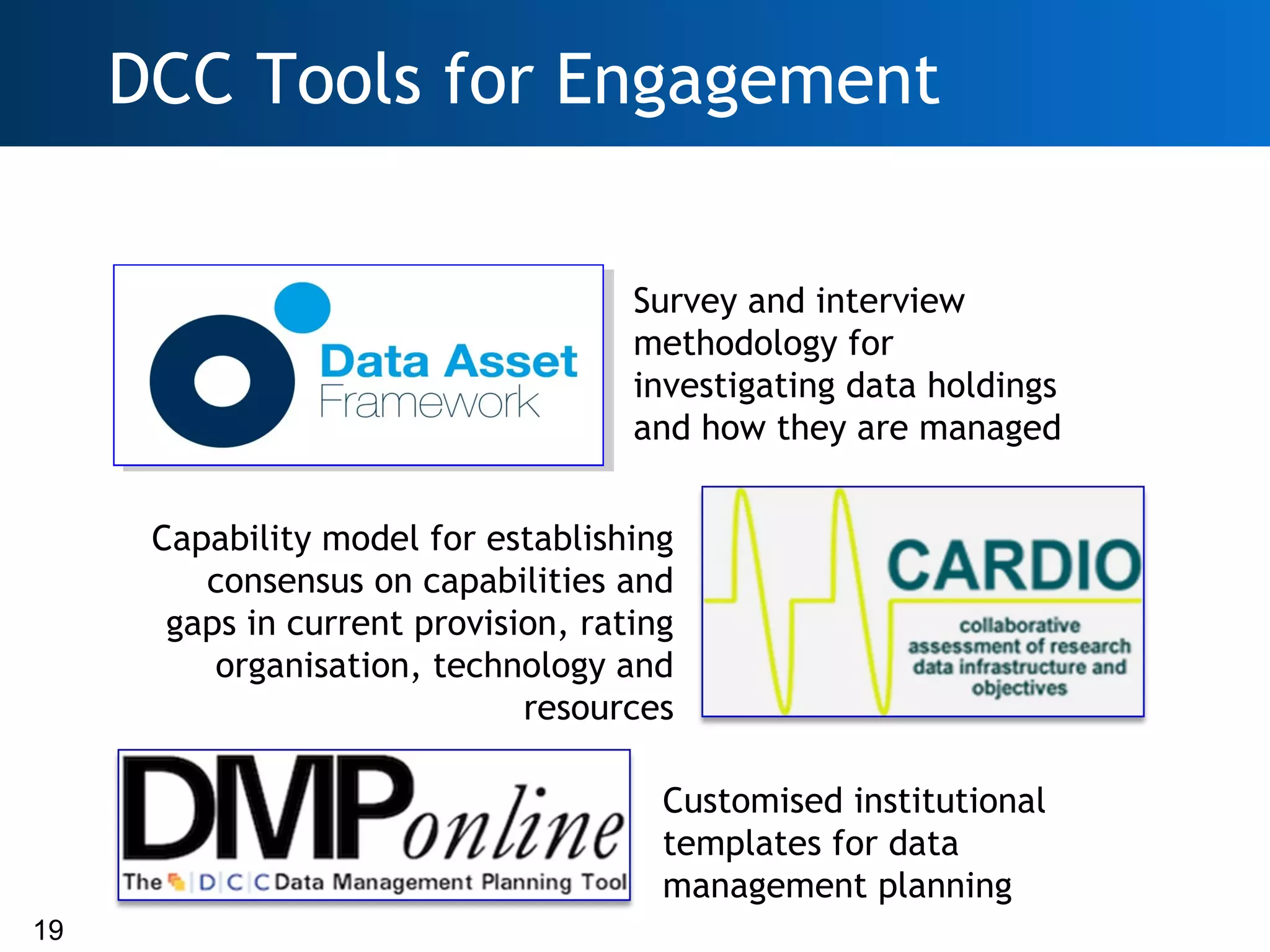
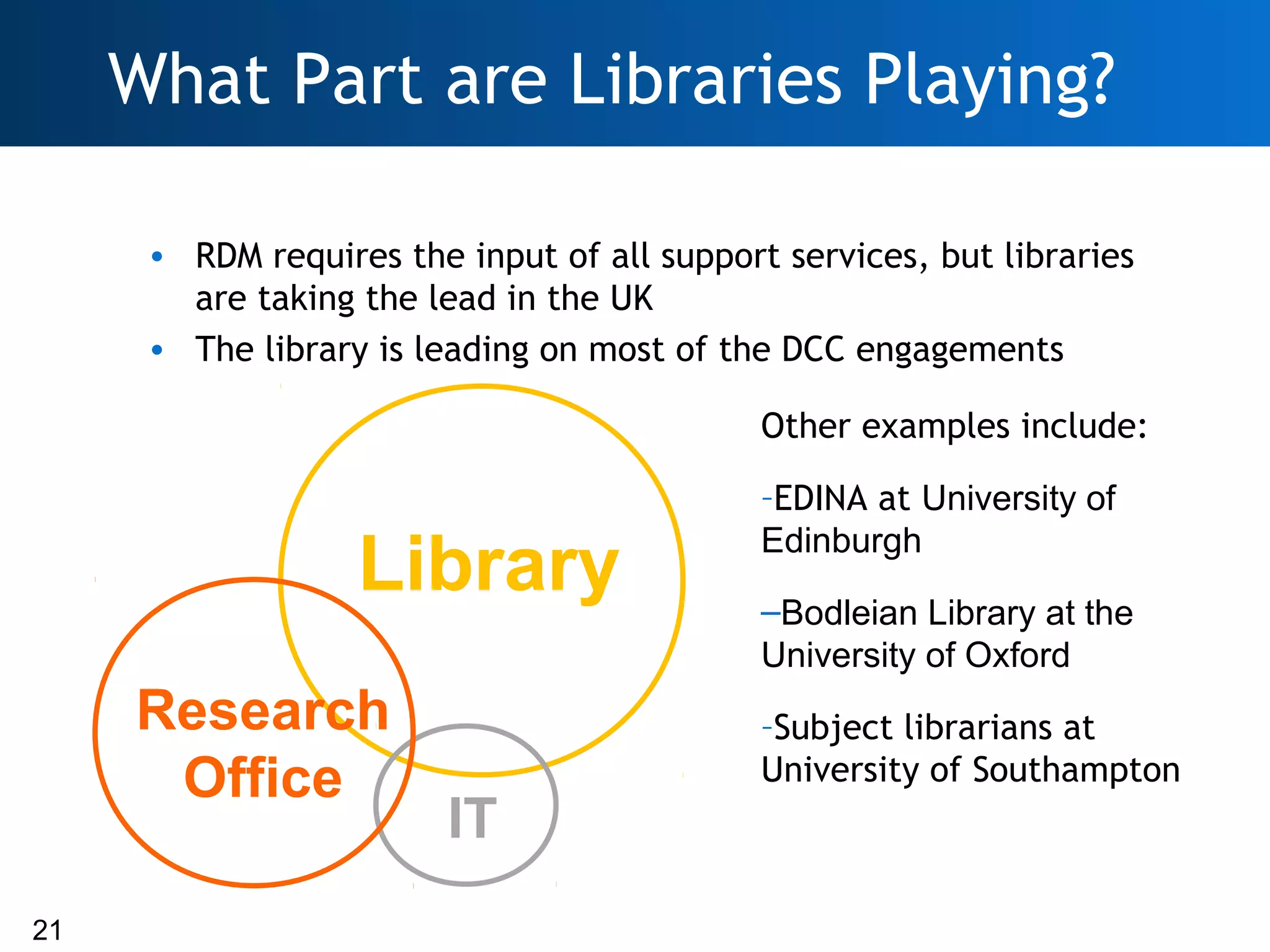
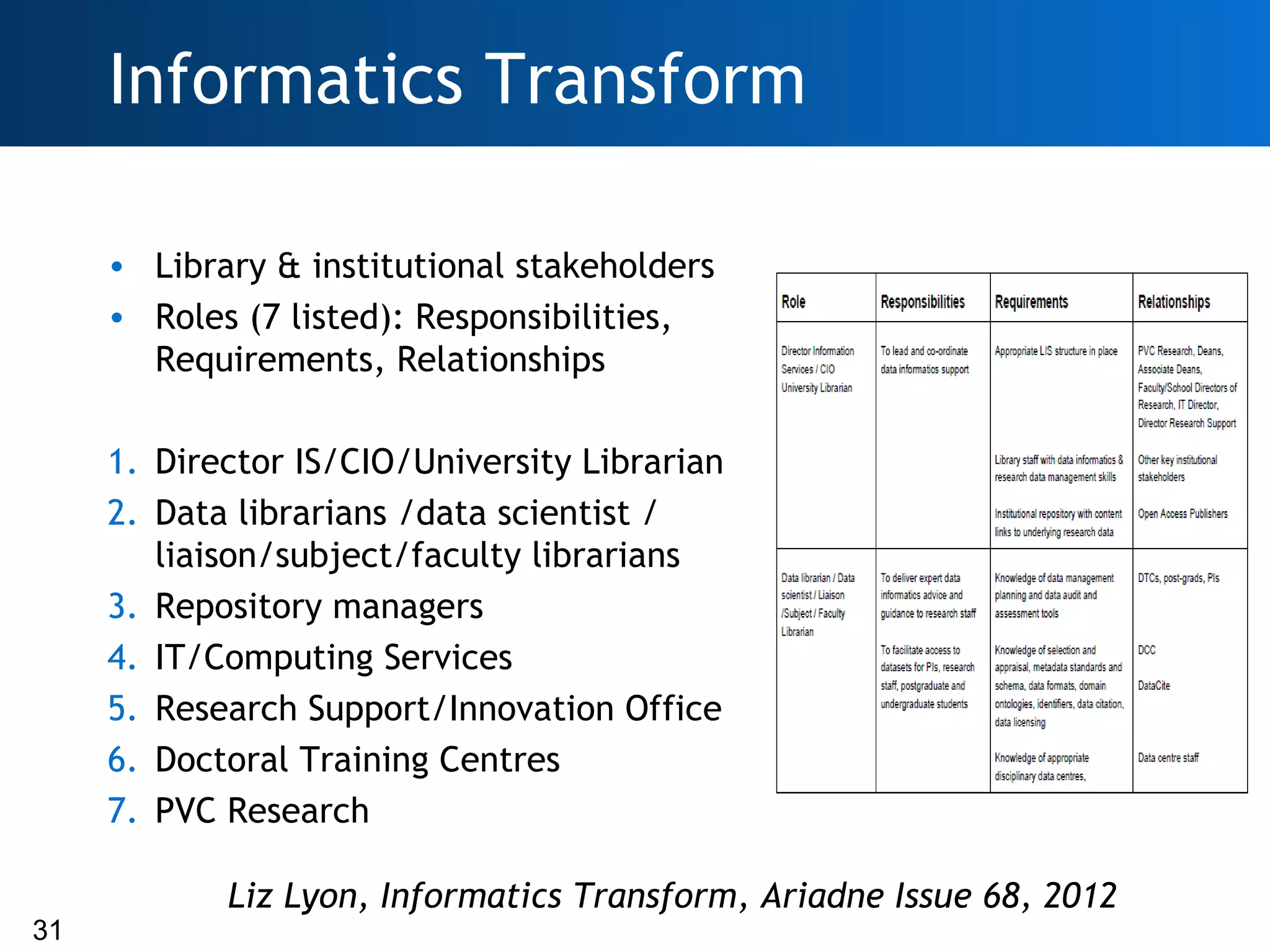
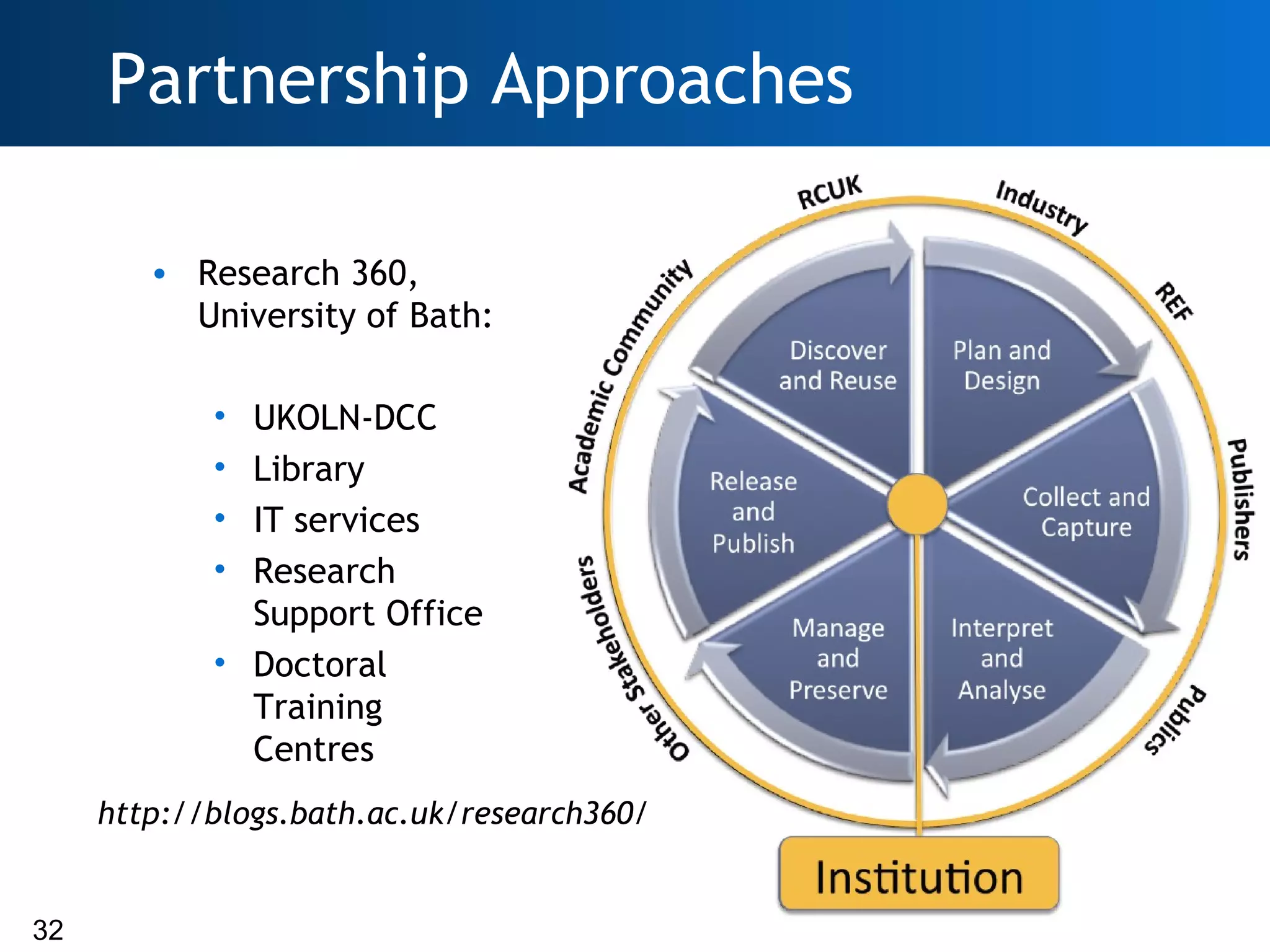
The document discusses the importance of research data management (RDM) and the evolving role of libraries in supporting institutions with their data needs. It highlights the challenges of managing research data, including quality, preservation, and compliance with funding mandates, while emphasizing the necessity for libraries to enhance their skills in this area. The Digital Curation Centre plays a crucial role in providing support and resources for improving RDM capabilities across higher education institutions.