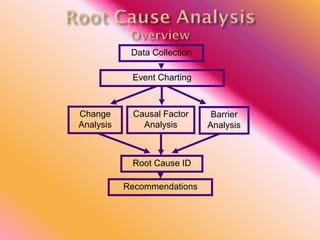
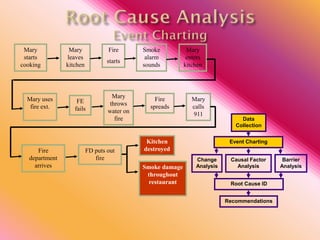
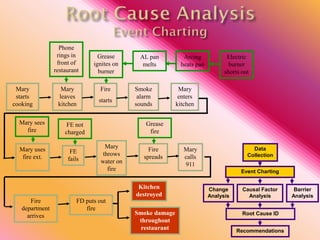
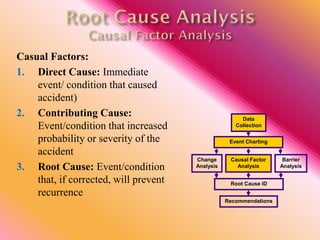
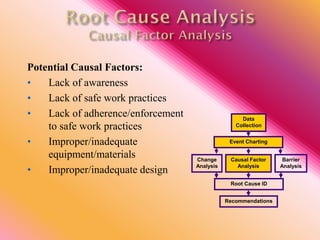
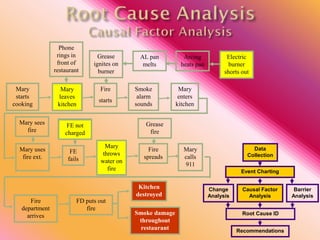
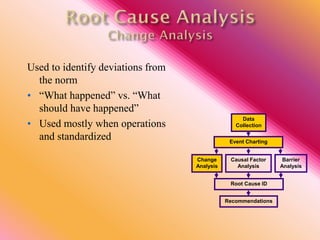
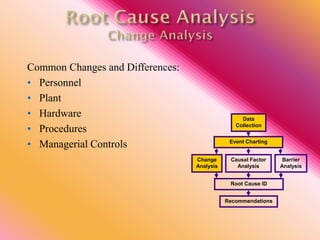
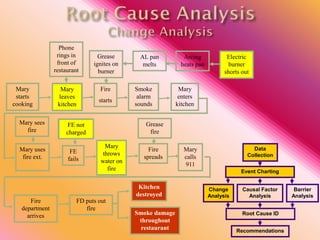
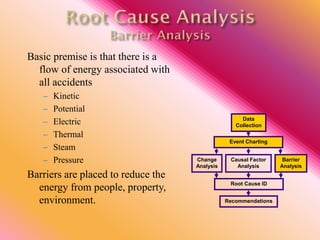
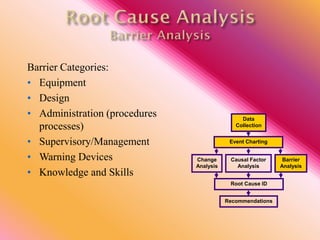
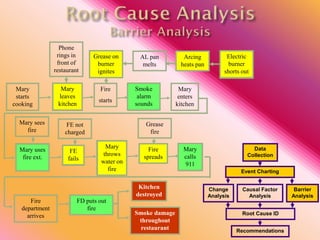
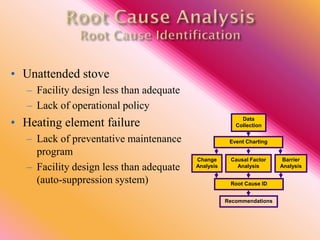
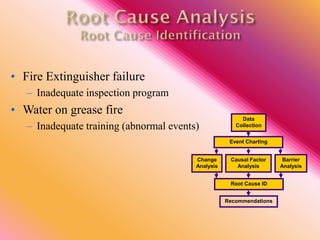
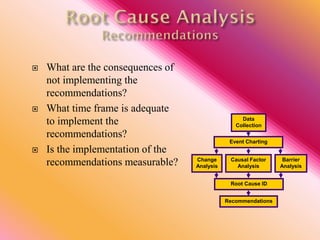
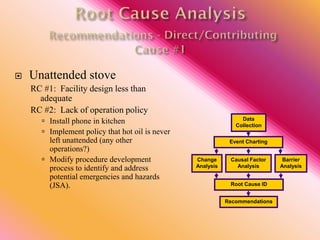
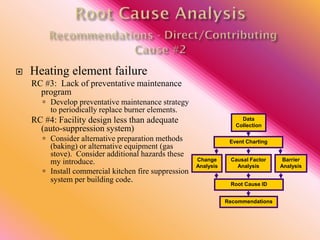
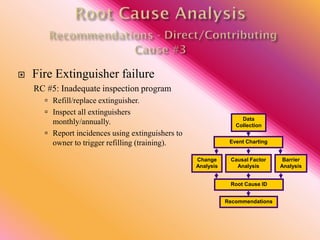
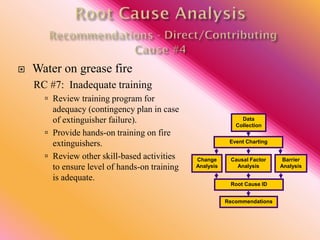
The document outlines three consistent approaches to investigating workplace accidents: data collection, event charting, and root cause identification. It then provides details on each approach and how to apply them to an investigation of a kitchen fire accident. Data collection involves gathering evidence like interviews, photos, and records. Event charting creates a timeline of the incident. Root cause identification determines the underlying causes that led to the accident through causal factor analysis, barrier analysis, and change analysis. The document uses the kitchen fire example to demonstrate how to apply these approaches to identify root causes and make recommendations to prevent future occurrences.