The document discusses rate-controlled drug delivery systems (DDS), highlighting the need for these systems to achieve consistent drug levels, reduce dosing frequency, and improve patient compliance. It covers advantages and disadvantages, classifications based on technical sophistication, and mechanisms of action such as osmotic and feedback-controlled systems. Furthermore, it outlines specific applications and emphasizes the potential for significant advancements in targeted drug delivery and therapeutic effectiveness.
![RATE CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY
SYSTEM
Presented by-
Miss Khade S.B
M.Pharm-1 [pharmaceutics department]
RCP , Kasegaon
10/09/2019 1Rate controlled DDS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ratecontrolleddrugdeliverysystemsbk-copy-191001060755/75/Rate-controlled-drug-delivery-system-1-2048.jpg)


![Controlled Release system[Mechanism]
Controlled
release system
Dissolution
controlled
Diffusion
controlled
Chemically
controlled
Ion –
exchange
resin Hydrogel
Water
penetration
controlled
Diffusion
and
dissolution
Matrix
Encapsulation
Matrix
Reservoir
Reservoir
and
monolithic
Osmotic
pressure
controlled
system
10/09/2019 6Rate controlled DDS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ratecontrolleddrugdeliverysystemsbk-copy-191001060755/85/Rate-controlled-drug-delivery-system-6-320.jpg)

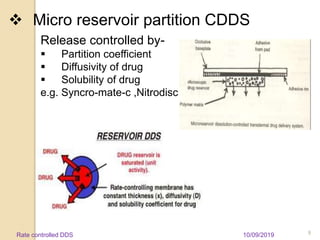



![ Effect of system parameters-
Physiological properties
Polymer solubility
solution solubility
Partition coefficient
Polymer diffusivity
Solution diffusivity
Thickness of polymer diffusional path
Thickness of hydrodynamic diffusional layer
Molecular size [400 Dalton] ,Drug pKa
Drug stability , Protein binding
Biological factors-Absorption ,Half life[2-3hrs]
Dose size, Therapeutic and Absorption window,
patient physiology
10/09/2019 13Rate controlled DDS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ratecontrolleddrugdeliverysystemsbk-copy-191001060755/85/Rate-controlled-drug-delivery-system-13-320.jpg)