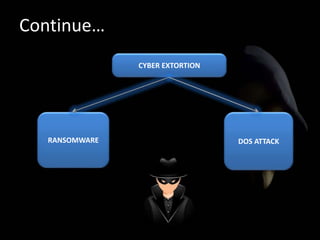
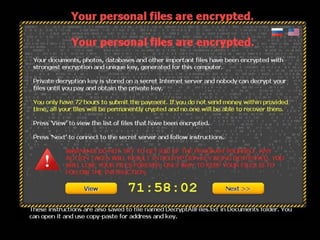
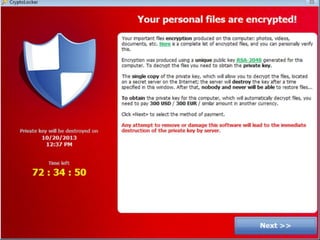
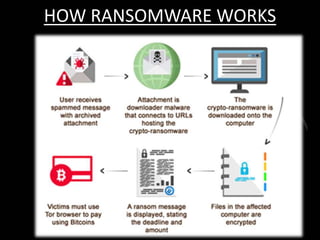
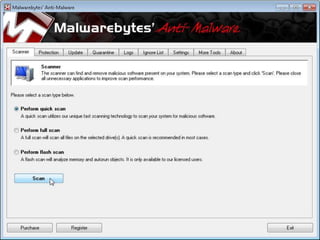
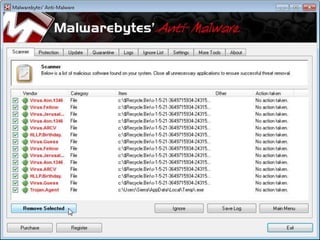
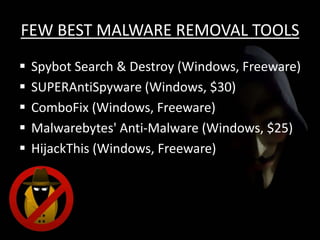
This document discusses cyber extortion and ransomware. It defines ransomware as malware that locks out a user's system and demands ransom in order to regain access. The document reviews the history of ransomware, describes famous ransomware like Reveton and CryptoLocker, and explains how ransomware works. It provides tips on how to prevent ransomware attacks and instructions for removing malware from Windows PCs.