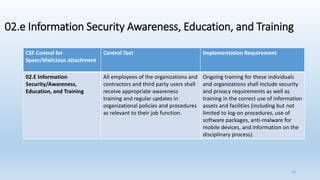
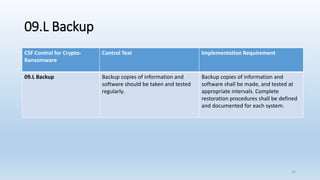
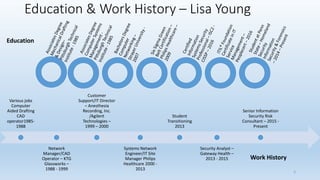
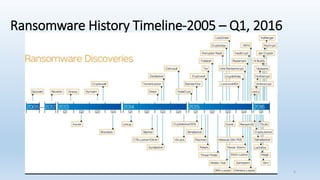
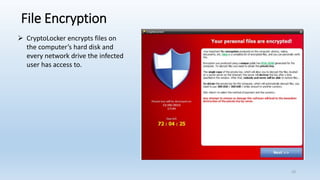
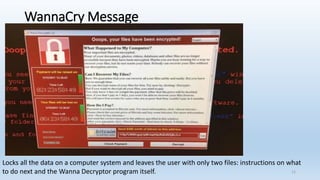
This document provides an overview of ransomware presented by Lisa Young. It begins with her background and experience in IT. The presentation defines ransomware, outlines its history from 2005, and provides statistics on its growth. It describes how ransomware works, common types like encryption and lock screen variants, and examples of major ransomware like Cryptolocker, Cryptowall, and WannaCry. Tips are provided on how to avoid ransomware through patching, backups, and security awareness training. Controls from the HITRUST framework are also mapped that relate to preventing and recovering from ransomware.













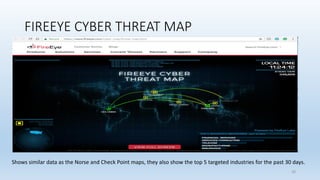
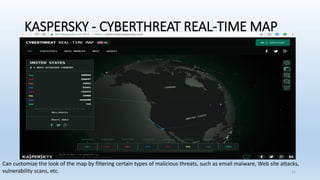
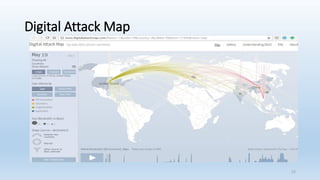
![Terms
• Sinkhole is basically a way of redirecting malicious Internet traffic so that it can be captured and analyzed
by security analysts. Sinkholes are most often used to seize control of botnets by interrupting the DNS names of the
botnet that is used by the malware.
• Malware – Malicious software program that is intended to damage or disable computers and computer systems.
• Trojan - Malicious computer program which is used to hack into a computer by misleading users of its true intent
• Worm - standalone malicious software that does not require a host program or human help to propagate.
• Virus - type of malicious software program ("malware") that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying
other computer programs and inserting its own code. Infected computer programs can include as well, data files, or the
"boot" sector of the hard drive.
• Botnet - a network of private computers infected with malicious software and controlled as a group without the owners'
knowledge, e.g., to send spam messages.
• Domain Name Servers (DNS) - The Internet's equivalent of a phone book. They maintain a directory of domain names and
translate them to Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
• Ransomware - Malicious software (malware) that locks a device, such as a computer, tablet or smartphone and then
demands a ransom to unlock it
• Bitcoin - a type of digital currency in which encryption techniques are used to regulate the generation of units of currency
and verify the transfer of funds, operating independently of a central bank.
• Drive-by-download attack – means two things, each concerning the unintended download of computer software from
the Internet: Downloads which a person authorized but without understanding the consequences (e.g. downloads which
install an unknown or counterfeit executable program, ActiveX component, or Java applet) automatically.
• Server Message Block (SMB), one version of which was also known as Common Internet File
System (CIFS, /ˈsɪfs/),[1][2] operates as an application-layer network protocol[3] mainly used for providing shared
access to files, printers, and serial ports and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides
an authenticated inter-process communication mechanism.
• Note: Definitions from wikipedia 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ransomwarely-170607103559/85/Ransomware-ly-23-320.jpg)