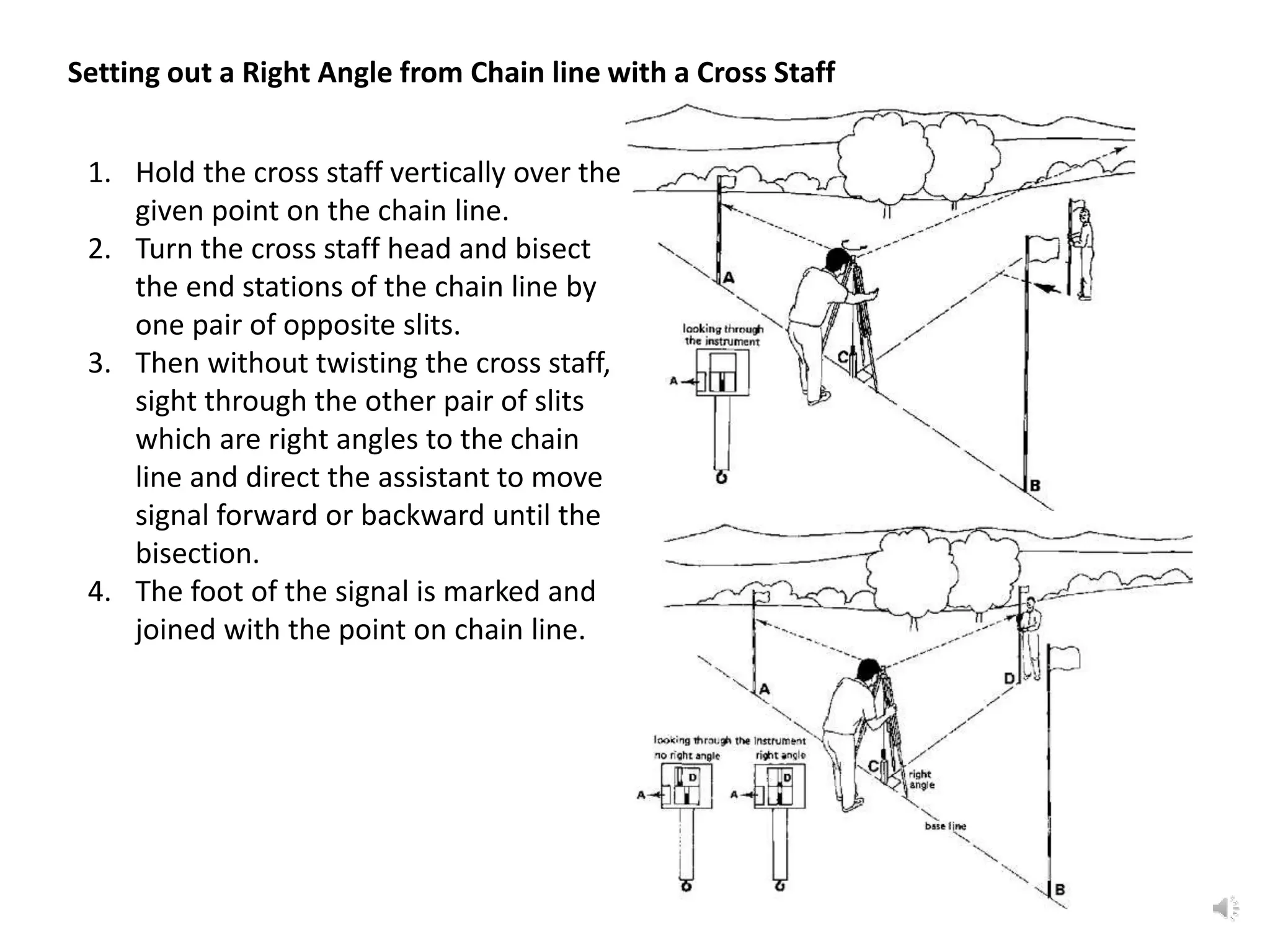
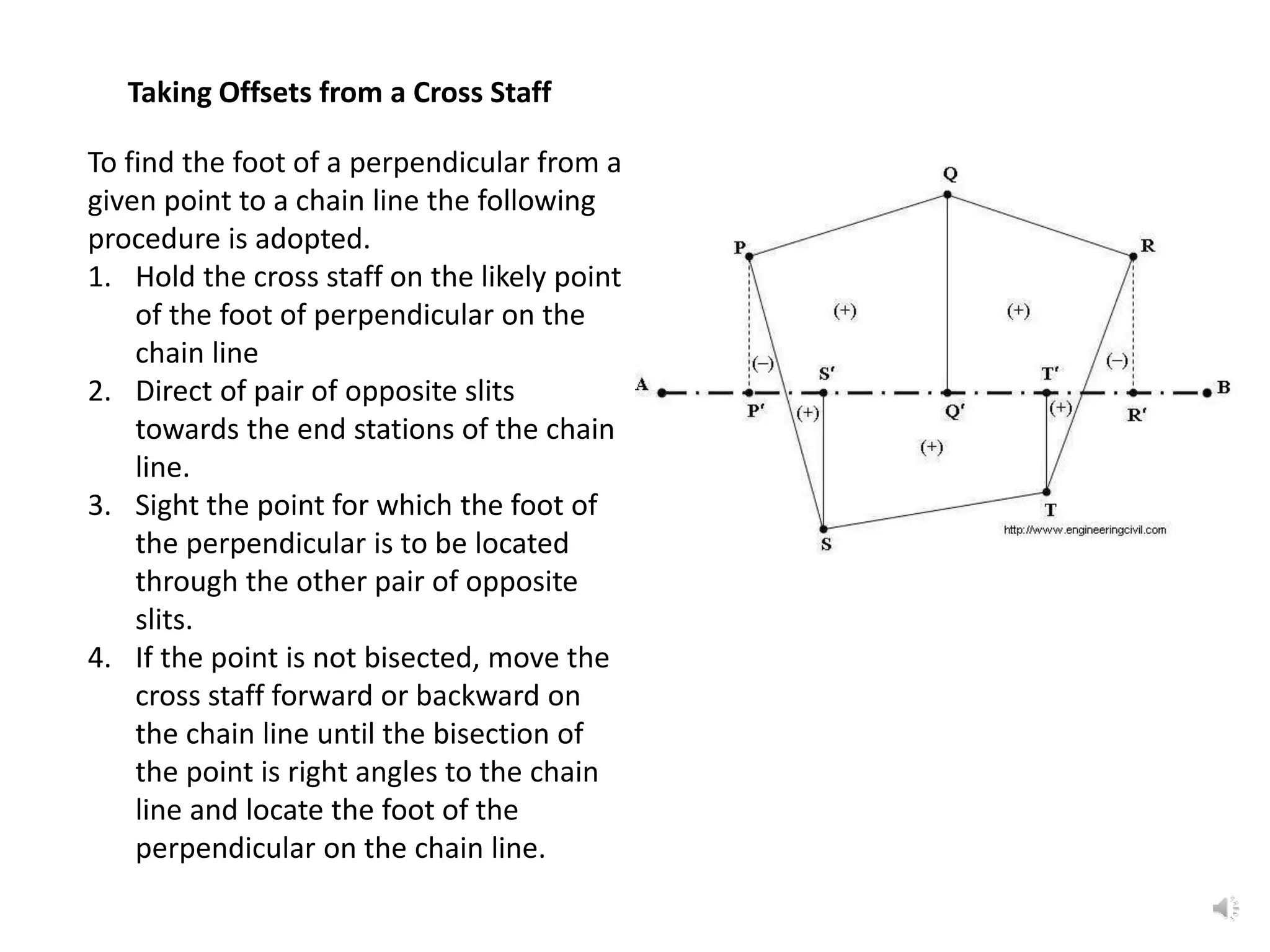
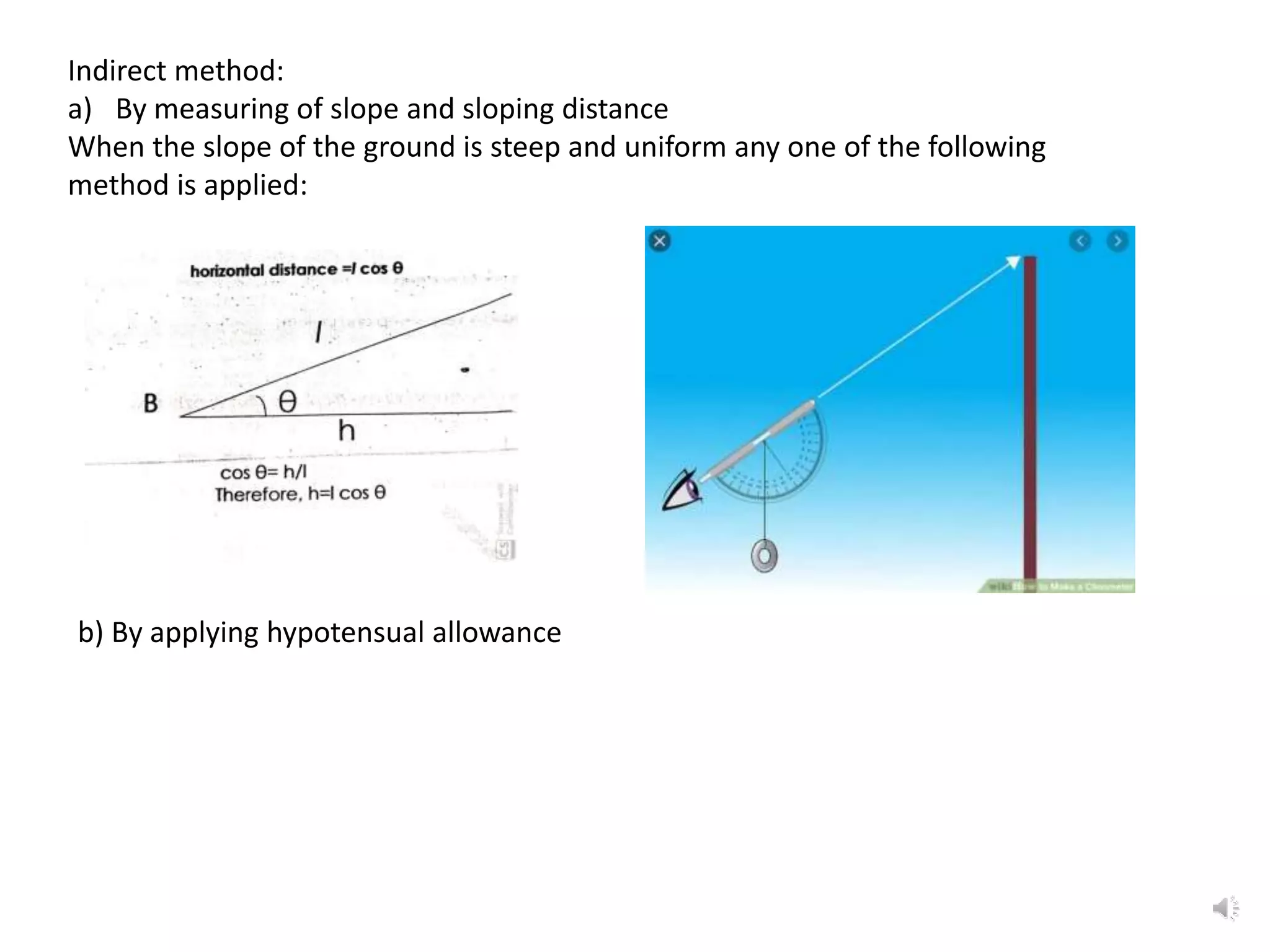
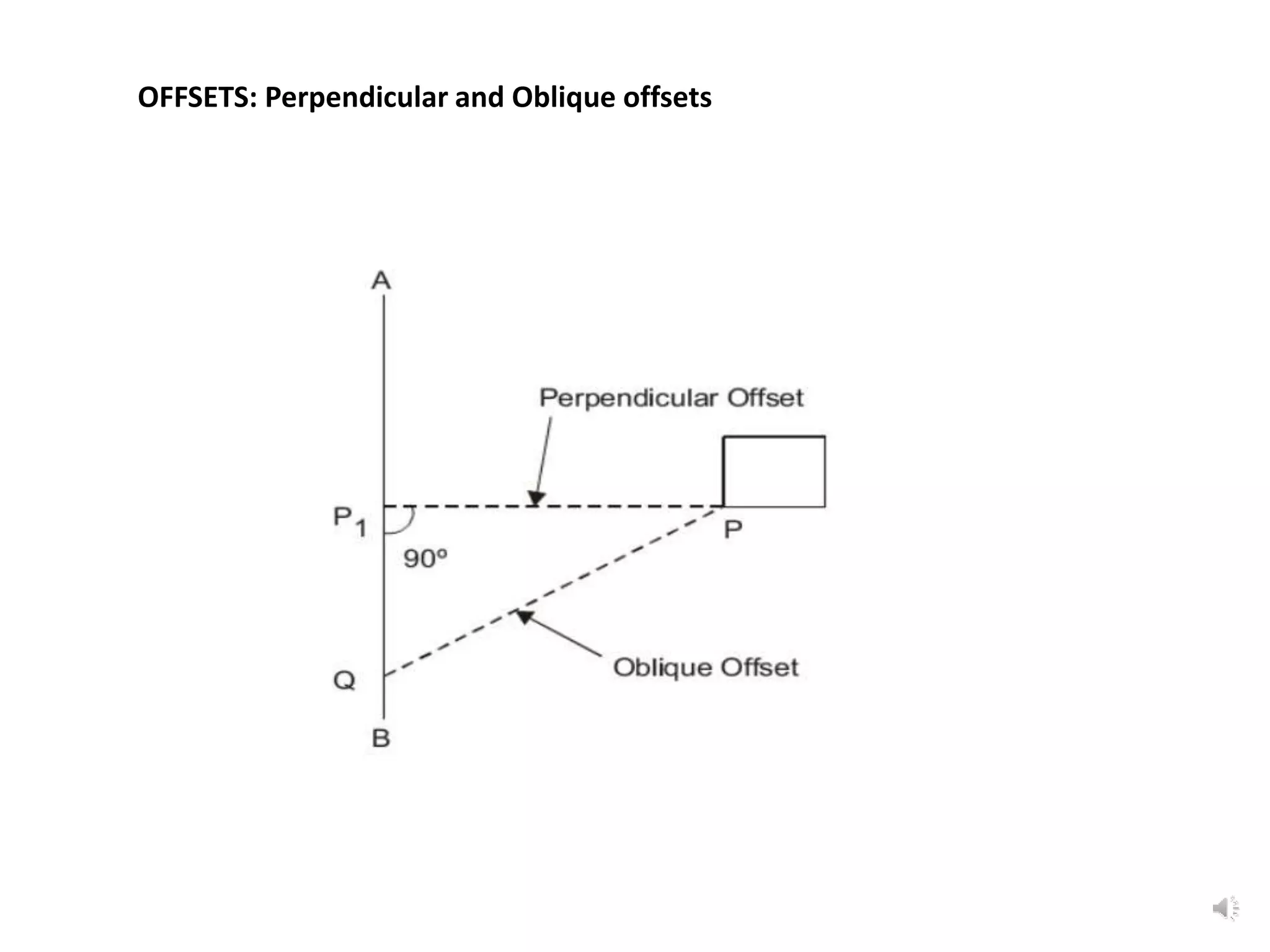
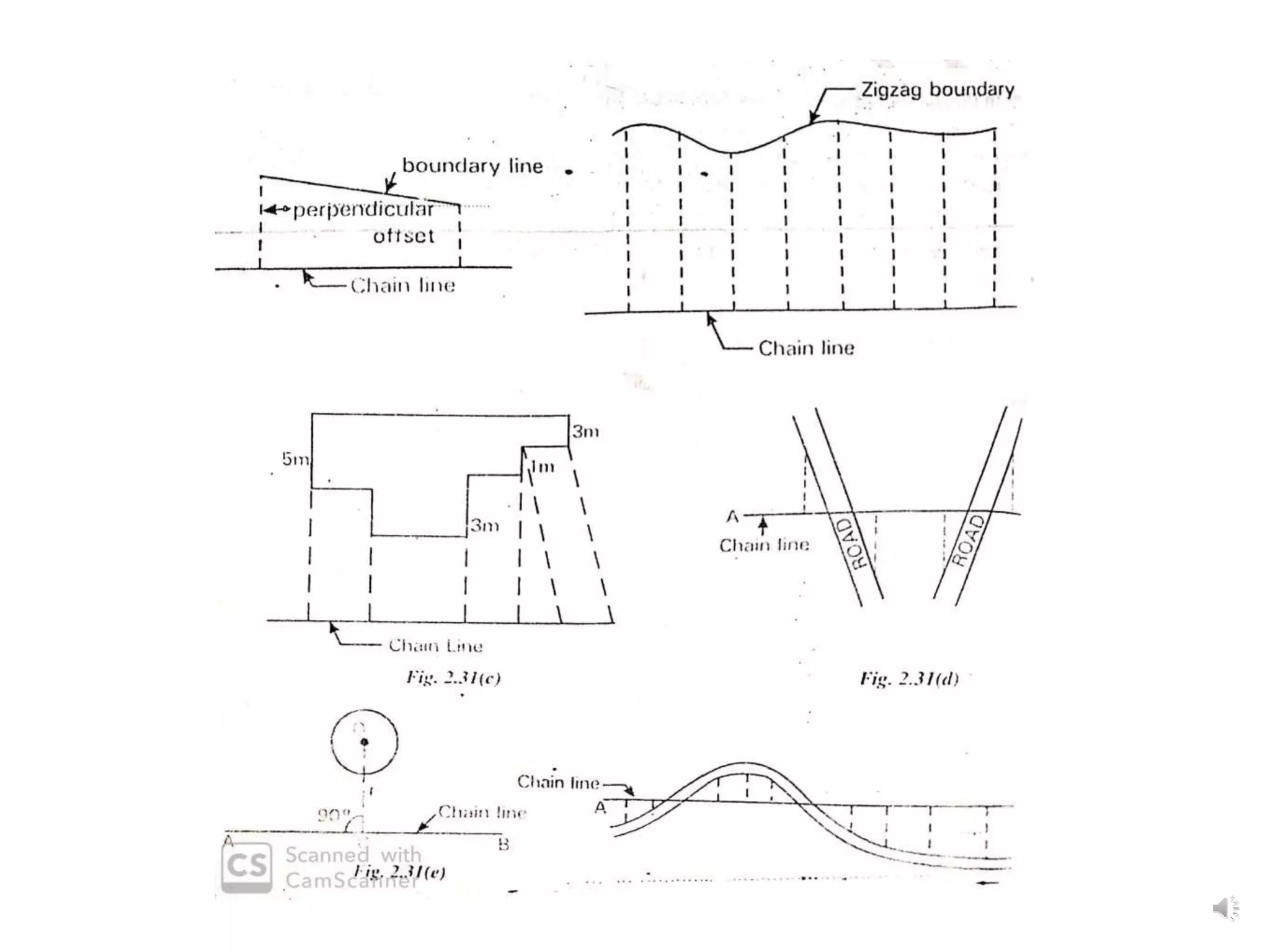
This document discusses various surveying techniques for setting out perpendiculars, offsets, and angles using ranging, theodolites, cross-staffs, optical squares, and prism squares.
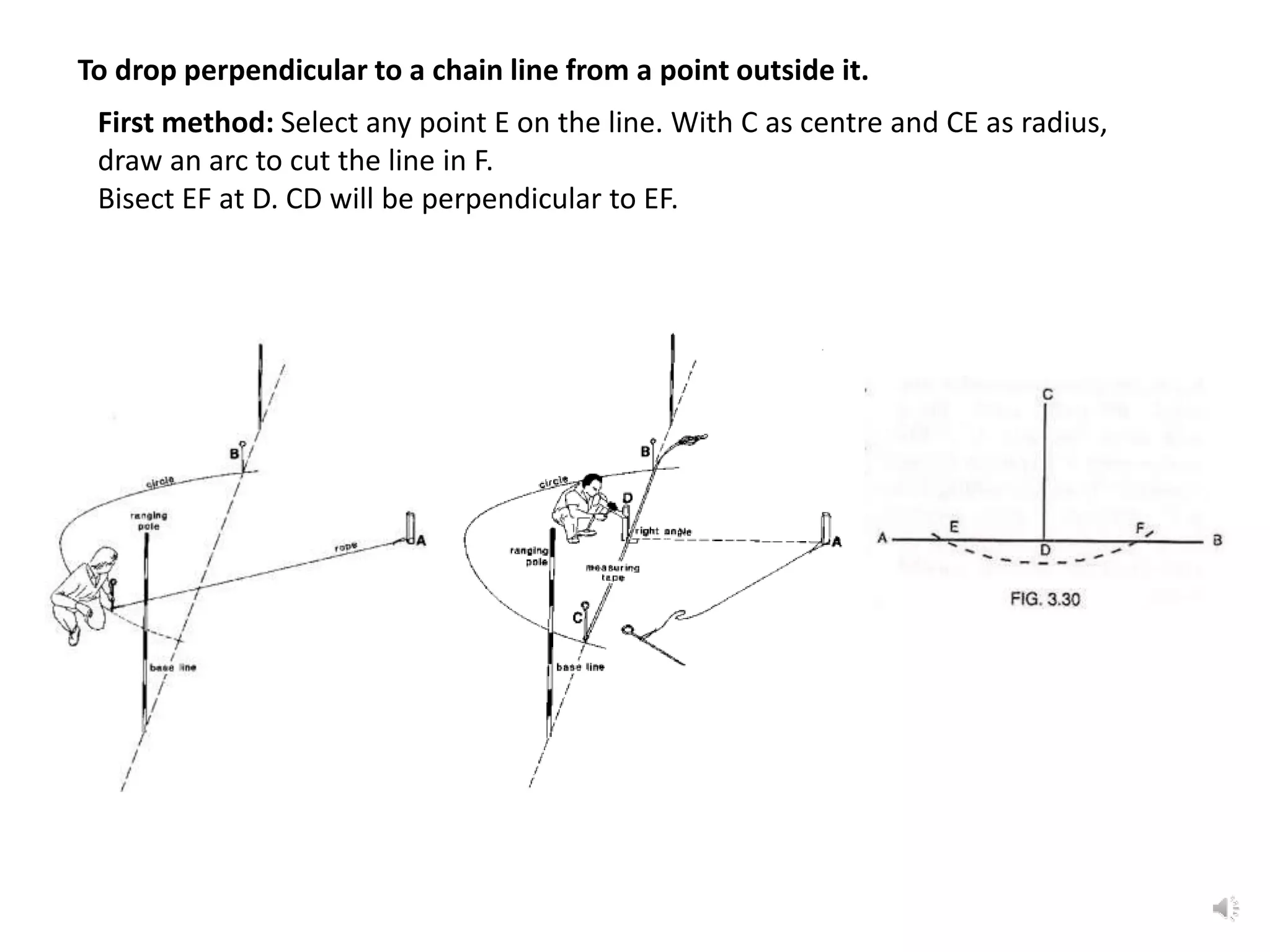
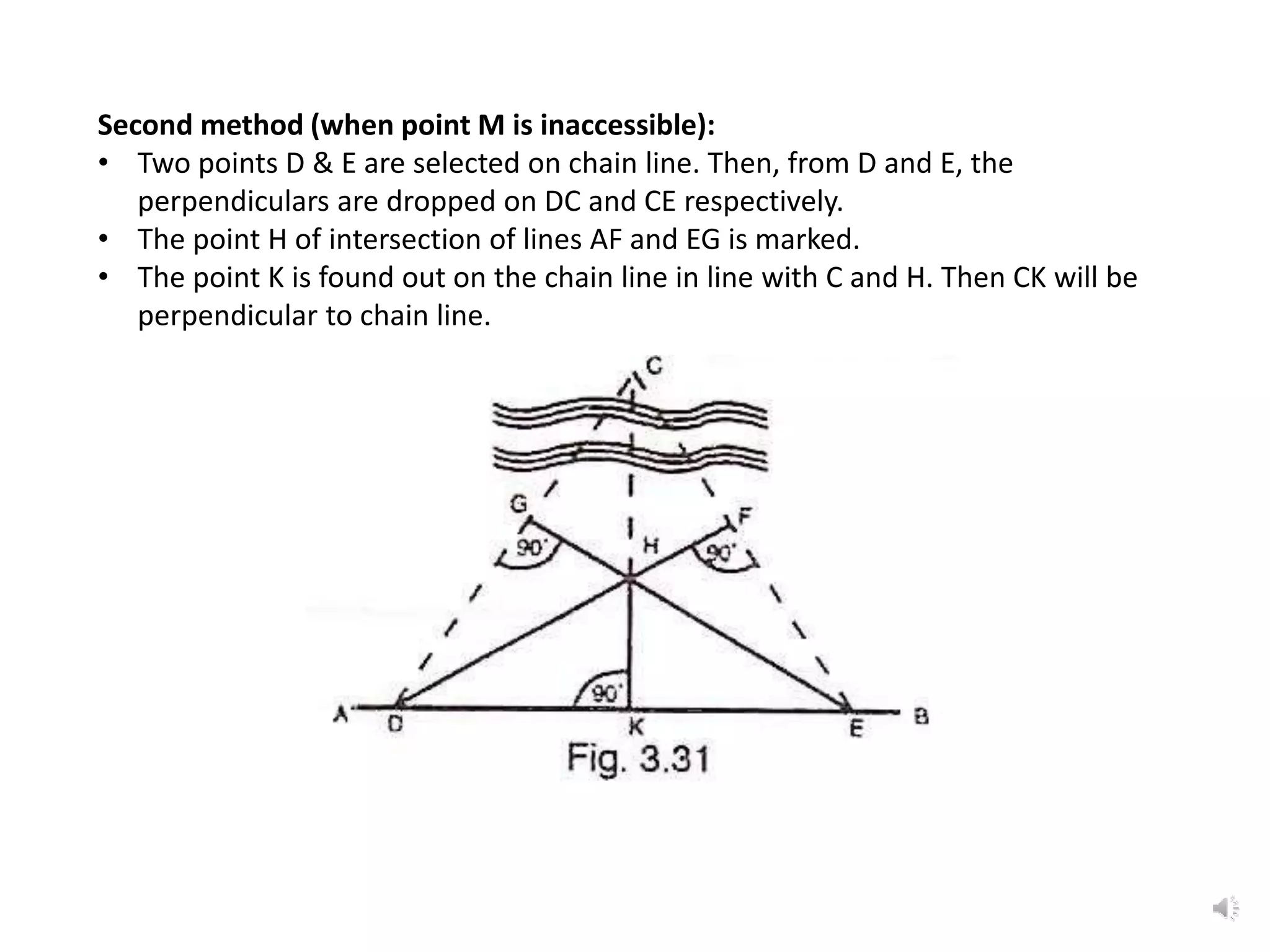
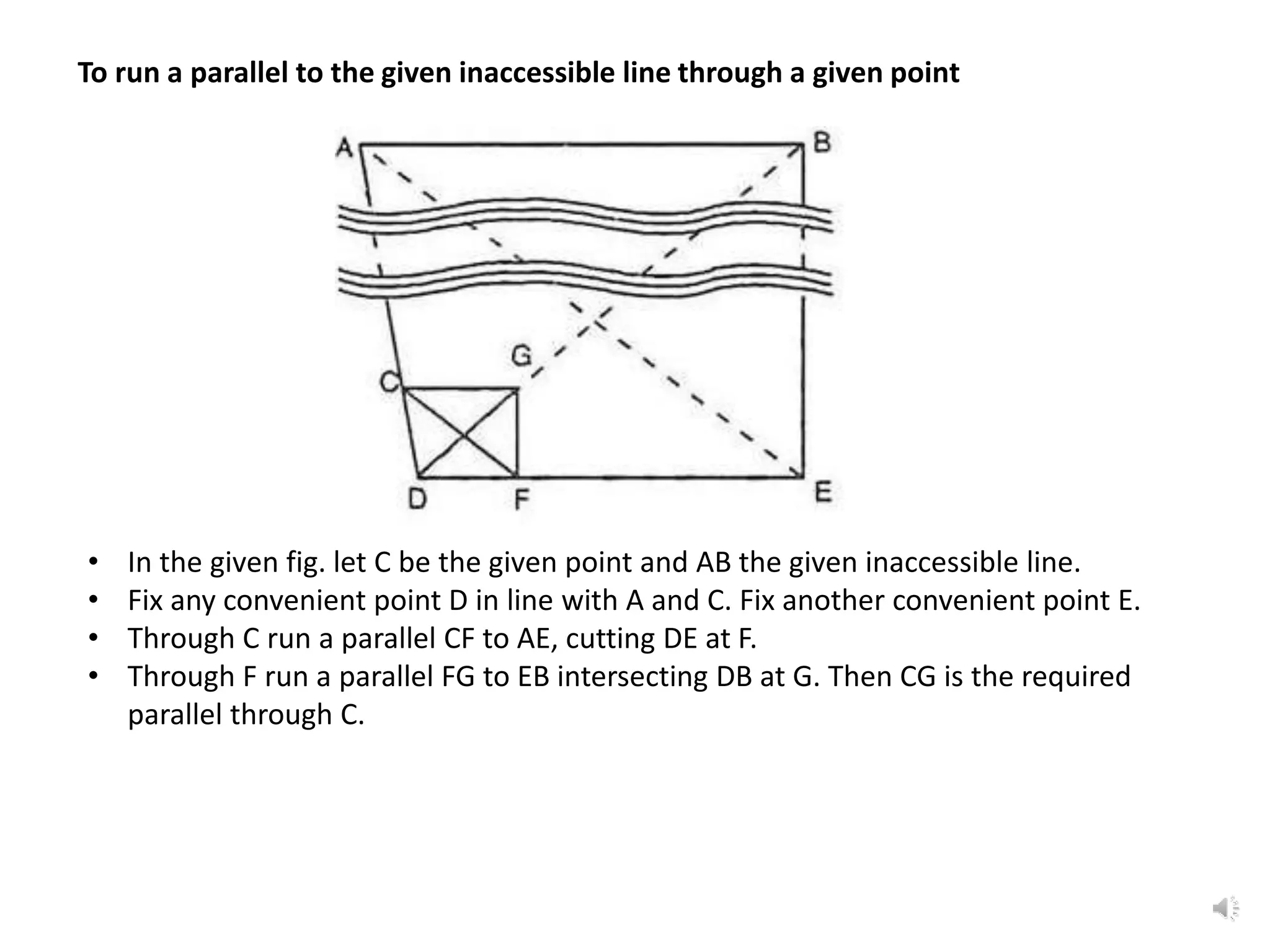
It describes how to use ranging by line ranger or theodolite to fix intermediate points on a line. It also explains different methods for setting out right angles using chains, offsets, bisection, and known lengths. Techniques are provided for dropping perpendiculars to accessible and inaccessible lines.
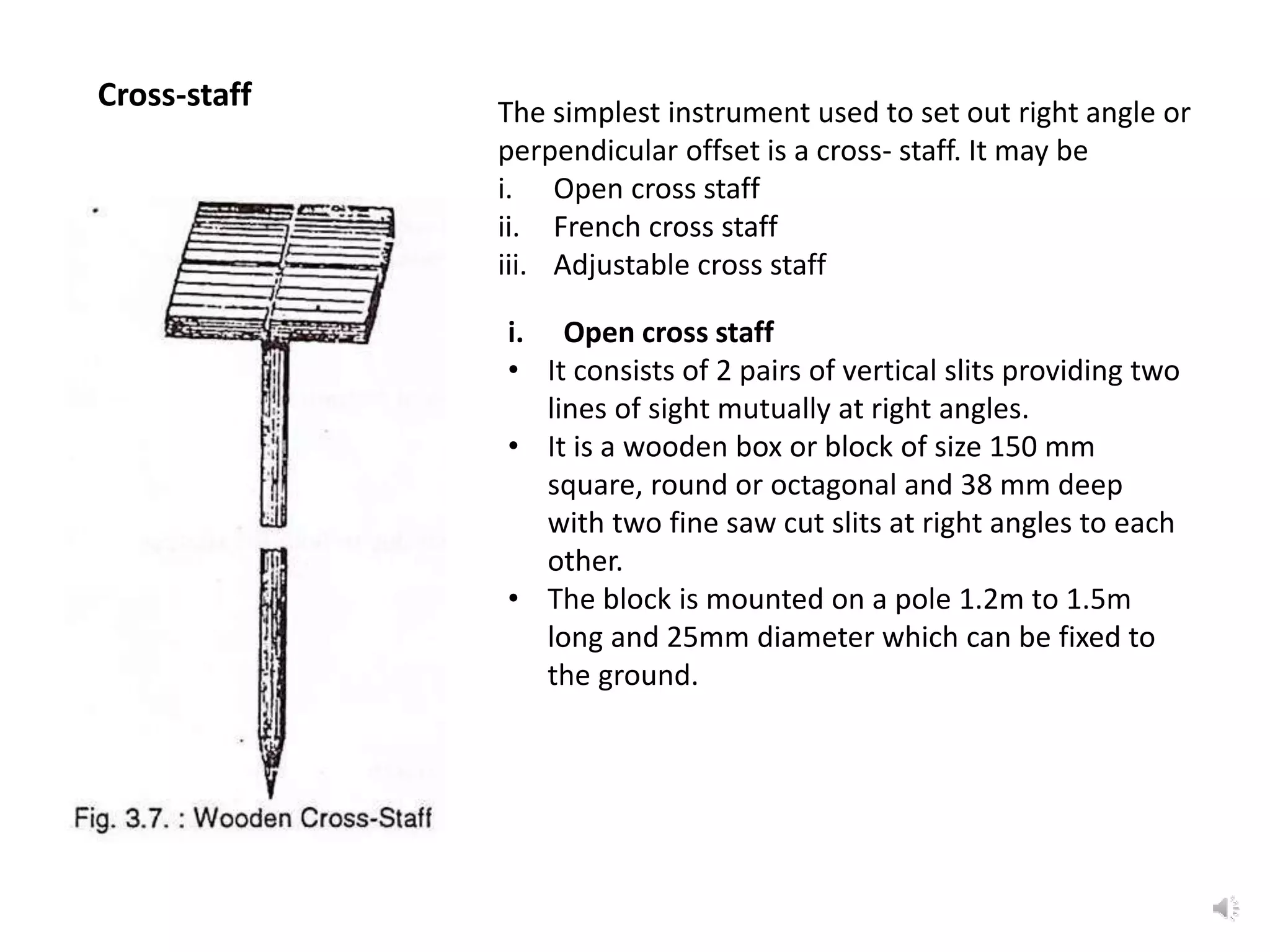
The document outlines the use of various manual instruments like cross-staffs, optical squares, and prism squares to take perpendicular and oblique offsets from chain lines and set out angles. It also discusses measuring horizontal distances