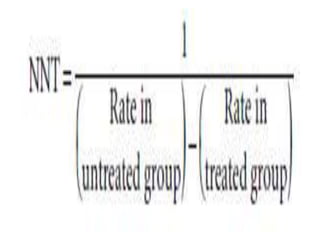
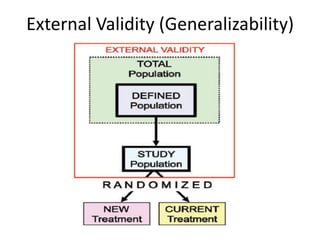
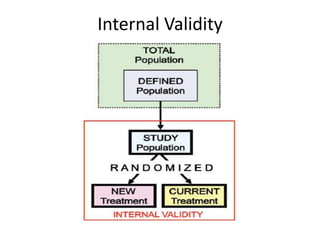
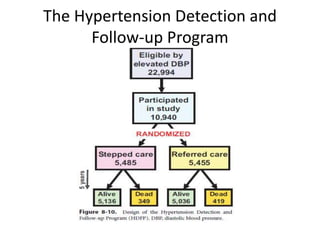
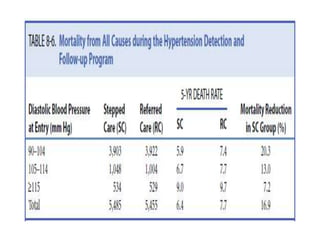
Randomized trials are important for evaluating the effectiveness of new medical treatments compared to existing options. Key considerations in randomized trials include sample size, type I and type II errors, power, and internal and external validity. Sample size calculations require estimates of expected outcomes under different treatments and specifications of acceptable error rates and desired power. Randomization helps reduce bias but poses ethical issues that must be addressed through informed consent and oversight. Registration of all clinical trials helps reduce publication bias.








![Estimate the Sample Size
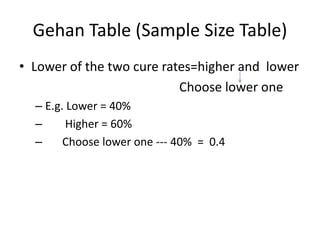
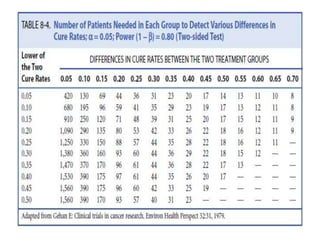
1. must specify the expected difference in response rate
• existing therapy cures- 40%
• expect new therapy cure-50%, 60%
• expect 10% or 20% better than current therapy
• A new therapy
– no prior experience
– to search data in human populations
– To search data from animal studies
– No way of producing such an estimate
– Can make a guess [estimate] --- bracket the estimate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/randomizedtrialsii-dr-170626082826/85/Randomized-trials-ii-dr-wah-17-320.jpg)