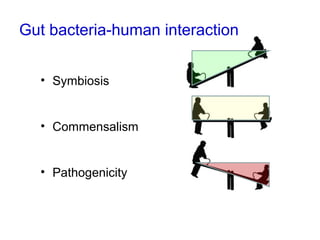
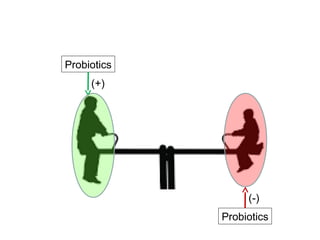
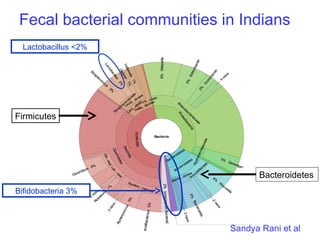
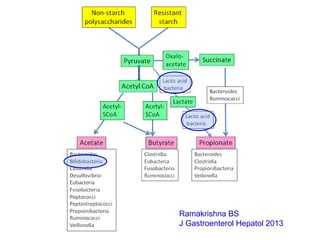
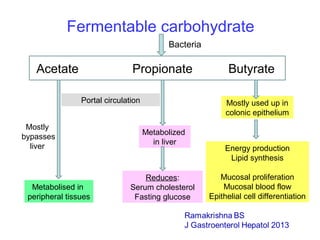
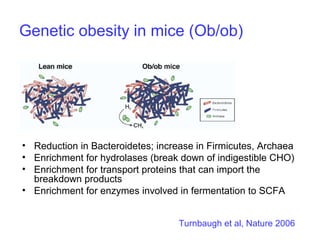
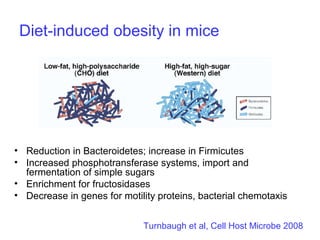
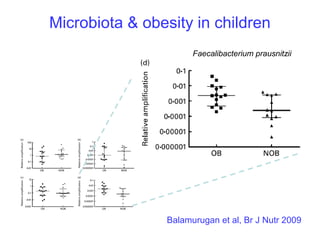
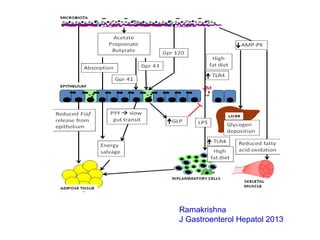
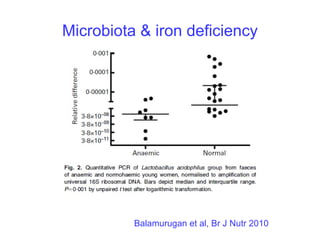
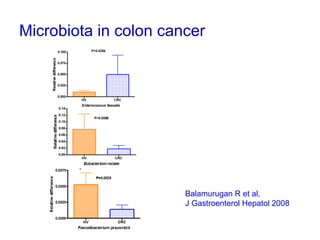
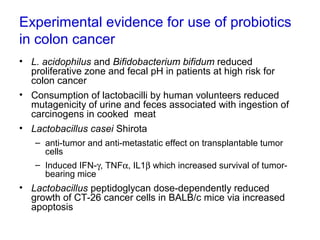
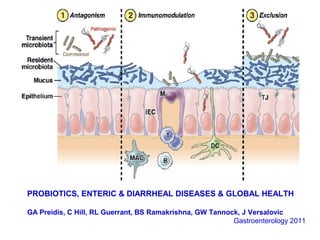
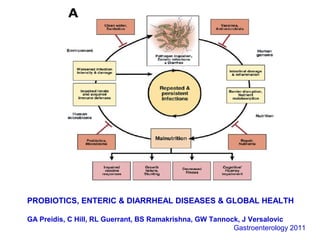
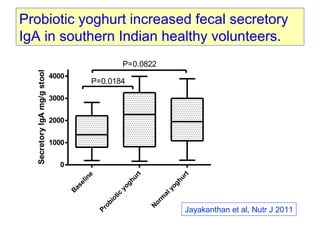
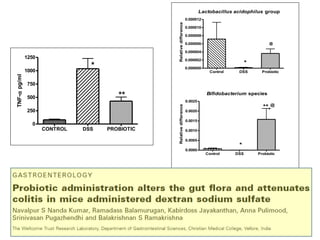
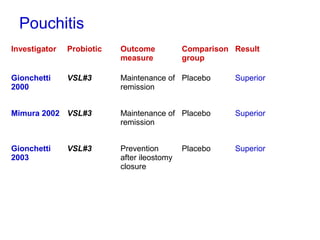
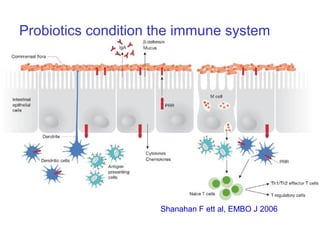
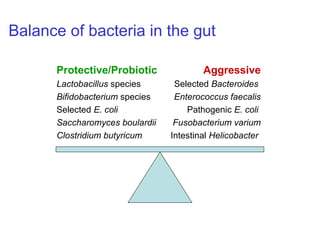
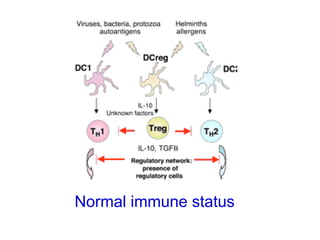
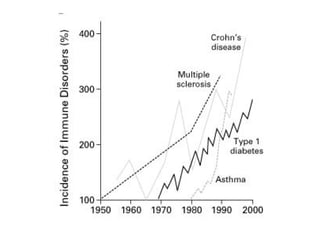
This document discusses the relationship between gut bacteria and human health. It covers how probiotics can promote intestinal and overall health by maintaining symbiosis with commensal gut bacteria. Probiotics are shown to enhance colonic health, maintain body weight, improve iron absorption, reduce pathogenicity, and reduce inflammation. Clinical evidence supports the use of certain probiotics to induce and maintain remission of ulcerative colitis and pouchitis. However, evidence for treating Crohn's disease or managing obesity with probiotics is limited. In conclusion, probiotics can interact with and condition the immune system to promote overall health.