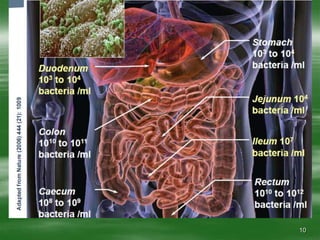
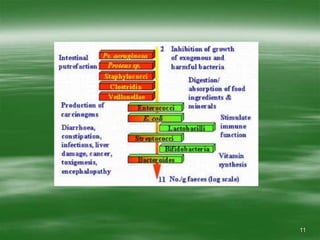
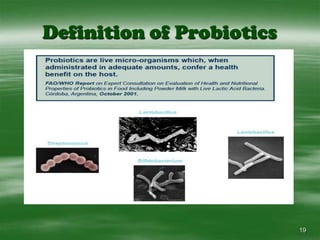
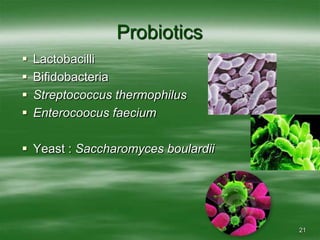
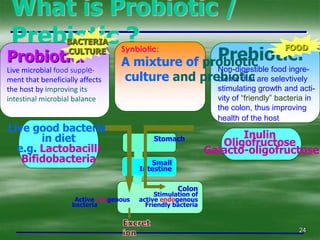
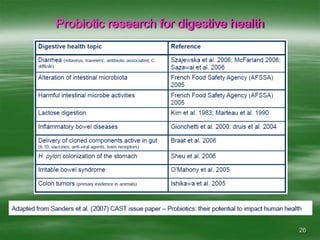
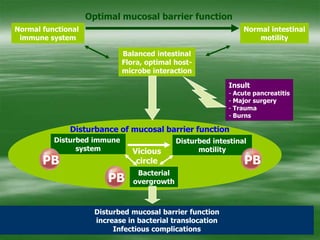
The document discusses digestive well-being and probiotics. It begins with an introduction to the topic, noting that one-third to one-half of the population suffers from digestive illnesses related to diet and lifestyle. It then covers the roles of probiotics and normal gut flora in supporting metabolic processes, epithelial cell differentiation, and pathogen protection. Probiotics, including lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, are live microorganisms that can beneficially affect the host by improving gut microbial balance. Prebiotics are non-digestible foods that stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria. Clinical studies have shown probiotics may help maintain optimal mucosal barrier function and balance intestinal flora.