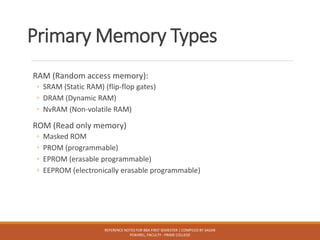
Primary memory includes various types of RAM and ROM. RAM is volatile and includes SRAM, DRAM, and NVRAM. ROM is non-volatile and includes masked ROM, PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM. RAM is used for temporary storage and active programs while ROM is used for permanent storage like BIOS.