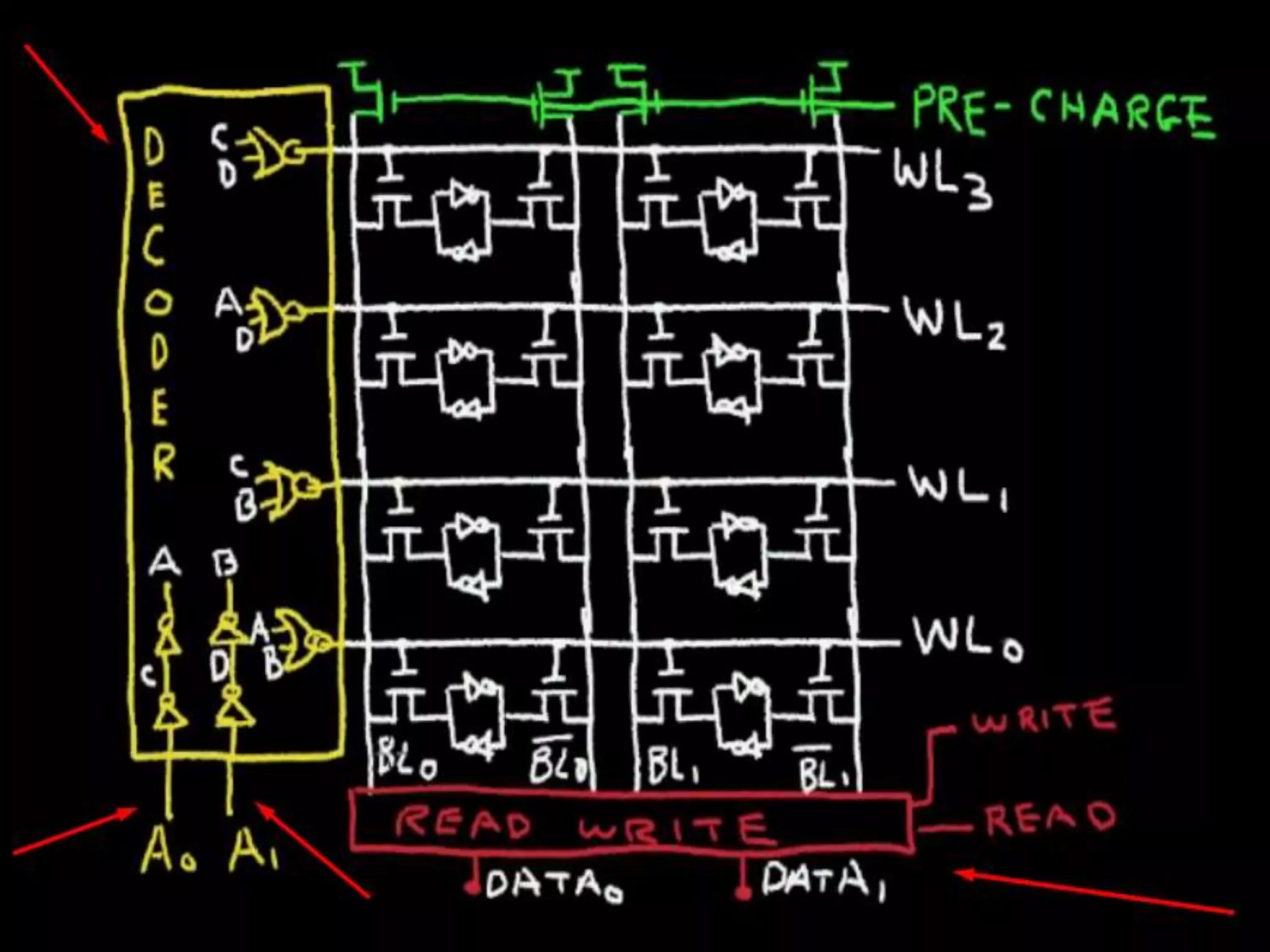
This document discusses RAM and ROM chips. It provides a brief history of RAM invention by Robert Dennard and others in the 1960s-1970s. It defines RAM as random access memory that allows data to be accessed randomly and is volatile, while ROM is read-only memory used for boot instructions and is non-volatile. The key difference is that RAM contents are lost when powered off, while ROM retains data. Advantages of RAM are silent and power-efficient operation, while disadvantages are volatility and limited space.