This document provides notes and model objective questions for the recruitment of Fisheries Administrators in Rajasthan. It begins with the author's views on preparing study material for this exam and acknowledging influences. It then includes the syllabus for Fisheries Development Officer provided by the Rajasthan Public Service Commission. Next, it covers notes on various topics from the syllabus like important fish species, indices, aquaculture techniques, government extension programs, objectives of fisheries development in Rajasthan, etc. It concludes by providing a solved paper from a previous Fisheries Development Officer exam. The overall document serves as a collection of relevant information to aid exam preparation.




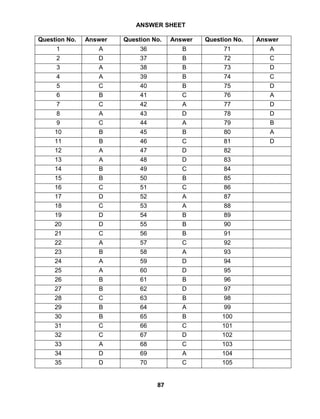
![i
euksgj yky vjksM+k fuokl & ch 116] glu [kka esokrh uxj]
lsokfuo`r lgk;d funs'kd] eRL;] vyoj & 301001 ¼jktLFkku½
eRL; foHkkx] jktLFkku ljdkj eksckbZy & 09414812756
bZesy& arora.manohar.54@gmail.com
ys[kd dk –f"Vdks.k
jktLFkku yksd lsok vk;ksx] vtesj }kjk eRL; vf/kdkfj;ksa ds fjDr
inksa ij HkrhZ ds fy, ekg tqykbZ 2019 es foKfIr tkjh dh xbZA dqN çR;kf'k;ksa us
flyscl vuqlkj esVsfj;y ds fy, lEidZ fd;kA tkudkjh yh x;h rks irk pyk fd
fjlpZ o Vhfpax ds fy, rks dbZ ykHknk;d iqLrdsa miyC/k gSA ysfdu fQ'kjht
,MfefuLVªsVj fo'ks"kdj vUrLFkyh; ekRl;dh ds jkT;ks ds fy, HkrhZ ds fy, vyx
ls dksbZ iqLrd miyC/k ugh gSA ,d fopkj vk;k fd OgkV~lvi xqIl ij fu;fer :i
ls gj jkst de ls de 10 vksCtsfDVo ç'uksa dh lhjht 'kq: dj dh tkus ij bl
ijh{kk ds çR;kf'k;ksa esa tks'k] mRlkg o meax cuk;k tk ldrk gSA bl fopkj dks
MkWñ ,yñ ,yñ 'kekZ lkgc iwoZ Mhu o çksQslj] dkyst vkWQ fQ'kjht] mn;iqj us
ilUn fd;kA bl çdkj flyscl vuqlkj uksV~l o vksCtsfDVo ç'uks dh lhjht
OgkV~lvi xqIl ij çkjEHk dh x;hA bl ckjs esa dbZ lq>ko Hkh çkIr gq, vkSj mlh ds
vuq:i lq/kkj Hkh fd;s x;sA
bl çdkj djhc nks ekg rd tks Hkh esVsfj;y lks'ky ehfM;k ds
ek/;e ls çR;kf'k;ksa dks Hkstk x;kA vc blh dks FkksM+k lk O;ofLFkr dj eheksxzkQ
Fishery Answers VkbZVy ds #i esa ih-Mh-,Q- QkbZy es çLrqr gSA blesa flyscl ds
lkFk dqN VkWfid ij laf{kIr uksV~l vkSj lgk;d eRL; fodkl vf/kdkjh ds flyscl
dks vk/kkj ekurs gq, 5 xzqIl esa ekWMy vksCtsfDVo ç'u&mŸkj fn;s x;s gSA eRL;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-5-320.jpg)
![ii
fodkl vf/kdkjh 2016 dh ijh{kk dk GK INDIA App ij miyC/k lksYoM isij Hkh
fn;k x;k gSA
bUgsa rS;kj djus ds fy, orZeku esa çpfyr o yksdfç; iqLrdksa vkSj
bUVjusV ij miyC; lkexzh dh enn yh x;h gSA oSls tSlk lkspk Fkk] ml ds
vuq:i DokfyVh vkbZVe ds #i esa Fishery Answers rS;kj ugh dh tk ldh gSA
blesa nh x;h lkexzh esa dqN dfe;k¡ o =qfV;k¡ jg tkuk LoHkkfod gSA vr% fdlh Hkh
izdkj dh HkzkfUr o la'k; gksus ij fo[;kr ys[kdksa dh iqLrdksa o bUVjusV ij miyC/k
lkexzh dk lgkjk fy, tkus dk fuosnu gSA
eheksxzkQ Fishery Answers dks rS;kj djus essa ftu iqLrdksa o
bUVjusV dh lkexzh dh lgk;rk yh x;h gS] muds ys[kdksa ds lkFk&lkFk çsj.kk
L=ksr MkWñ ,yñ ,yñ 'kekZ lkgc dk gkfnZd vkHkkj O;Dr fd;k tkrk gSA
fnukad 10 vDVwcj 2019
vyoj ¼jktLFkku½ euksgj yky vjksM+k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-6-320.jpg)











![4
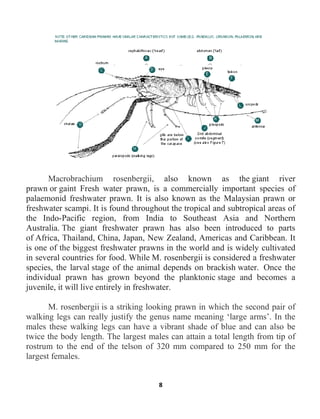
2. Mastacembelus armatus (Lacepede, 1800)
Kingdom : Animalia
Phylum : Chordata
Class : Actinopterygii
Order : Synbranchiformes
Family : Mastacembelidae
Genus : Mastacembelus
Species : Mastacembelus armatus
D1.33-38/ D2.64-94, P.21-25, D2
It is commonly known as tire-track spiny eel or zig-zag eel. It is
vernacularly known as baim/bami/baam in India. Mastacembelus armatus is
widely distributed in India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, Sumatra, Sri Lanka,
Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, Myanmar, Malaysia, Southern China and other
parts of South East Asia. It occurs in a variety of freshwater habitats in the
plains as well as in hills of India. It mainly inhabits rivers, canals, beels,
ponds and inundated fields. It also occurs in still waters, both in coastal
+A+ C.3/167-178.
Mastacembelus armatus is a common fish species of Indian
subcontinent. It belongs to the family Mastacembelidae under the order
Synbranchiformes. It is one of the most popular table fishes with delicious
flesh quality having a special flavor, characteristic texture and high protein,
oil and vitamin C content [1-3]; and thus has a good market demand. In
northern and eastern India, the fish is very popular when sold alive. It is also
popular as an aquarium fish due to its attractive color pattern and has high
demand among the aquarium fish hobbyists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-18-320.jpg)






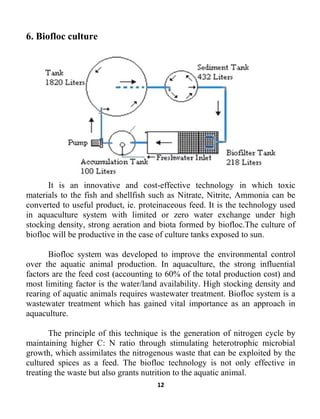

![14
feed. It reduces the pressure on capture fisheries ie., use of cheaper food fish
and trash fish for fish feed formulation.
Disadvantages of Biofloc Technology
Increased energy requirement for mixing and aeration. Reduced
response time because water respiration rates are elevated. Start-up period
required. Alkalinity supplementation required. Increased pollution potential
from nitrate accumulation. Inconsistent and seasonal performance for
sunlight-exposed systems
7. Gonadosomatic index
The Gonadosomatic index ( GSI), is the calculation of the gonad mass
as a proportion of the total body weight. It is represented by the formula –
GSI = [gonad weight / total tissue weight] × 100
The Gonadosomatic index measured as egg output per unit weight,
decreases interspecifically with female size in fishes (Sadovy, 1996). The
frequency of spawning also decreases with species size, with smaller species
much more likely to be daily spawners. One way to consider more periodic
spawning, whether it is restricted to a lunar period or a yearly period, is that
the benefits for spawning at a particular time of year outweigh two potential
costs: not surviving to the next reproductive period, and morphological
limitations on how many eggs can be developed at a given time. For larger
species, lower instantaneous mortality rates could lessen any costs of delaying
reproduction, tipping the balance in favor of seasonal reproduction.
8. Ponderal index
The Ponderal index (PI) or The Corpulence index (PI) is a weight-
height related parameter that is mainly used to assess the pattern of fetal
growth in small-for-gestational age infants. The PI was calculated by using
the following formula -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-28-320.jpg)






![21
iv) SHGs have significantly empowered poor people, especially women, in
rural areas.
v) SHGs have helped immensely in reducing the influence of informal
lenders in rural areas.
vi) Many big corporate houses are also promoting SHGs at many placesin
India.
vii) SHGs help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
Women can discuss their problem and find solutions for it.
12- eNyh lM+us ds dkj.k vkSj fuokj.k
eNyh dks ikuh ds ckgj fudkyus ij dqN le; rd NViVkrh gS vkSj
vkDlhtu ugh feyus ij e`R;q dks çkIr gks tkrh gSA bl NViVkgV dh lekfIr ds
lkFk gh ejh gqbZ eNyh dk 'kjhj ,d fo'ks"k voLFkk esa ços'k djrk gSA bls fjxj
eksjfVl dgk tkrk gSA ftldk 'kkfCnd vFkZ gksrk gS & ejus ds ckn 'kjhj esa vkus
okyh dM+kgVA
okLro esa ;g voLFkk eNyh dh rktxh dk çrhd gSA tks vklikl ds
okrkoj.k] rkieku] 'kjhj esa mifLFkr inkFkZ bR;kfn ij fuHkZj djrh gSA bl voLFkk
esa eNyh ds 'kjhj esa fLFkr XykbZdkstu dk vkDlhtu dh vuqifLFkfr esa
XykbZdksykbfll gks dj ysfDVd ,flM dk fuekZ.k gksrk gSA 'kkjhfjd yphykiu
lekIr gksdj vLFkkbZ dBksjrk vk tkrh gSA bl dh lekfIr ij 'kkjhfjd ek¡l ueZ
gksdj <hyk o ckn esa fiyfiyk gks tkrk gSA
fjxj eksjfVl voLFkk esa 'kkjhfjd fo?kVu dh dqN ,Utkbfed fØ;k,¡a gksrh gSA
bu dh xfr Hkh dkQh /kheh gksrh gSSSA ijUrq bl voLFkk esa thok.kq fØ;k,¡ ugh gksrh
gSA bl voLFkk dh lekfIr ds lkFk gh e`r 'kjhj thok.kqvksa ds ;ksX; gks tkrk gS vkSj
budh xfrfof/k;k¡ rsth ls c<+ dj eNyh dks lM+k nsrh gSA ysfdu ,Utkbfed o
jklk;fud ifjorZu igys dh rjg /kheh xfr ls gh gksrs jgrs gSA
fjxj eksjfVl voLFkk dh lekfIr ij vxzfyf[kr fØ;k,¡ rsth ls gksdj eNyh
dks [kkus ;ksX; ugh jgus nsrh gS&
1. 'kkjhfjd ih-,p- eku vR;f/kd {kkjh; gks tkrk gSA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-35-320.jpg)
![22
2. cSDVhfj;k] ,Utkbfed o jklk;fud fØ;kvksa ls ukbVªkstu ;qDr inkFkksZ ds
fo[k.Mu ls veksfu;k] dkcZu MkbZ vkWDlkbM bR;kfn mRiUu gksrs gSA
3. lM+us dh fØ;k ds rhozrj gksus ls ?k`f.kr xa/k okys mRikn bUMksy o gkbMªkstu
lYQkbM mRiUu gksrs gSA
4. 'kjhj esa ekStwn pchZ esa vkDlhMs'ku gksdj nqxZU/k rst gks tkrh gS vkSj ek¡l dk
jax Hkwjk gks tkrk gSA
ejh gqbZ eNyh tc rd fjxj eksjfVl voLFkk es jgrh gS] rc rd ;g [kkus
;ksX; o rktk cuh jgrh gSA bl voLFkk dks vf/kd le; rd cuk;s j[kus ds fy,
vxzfyf[kr dk;Zokgh dh tkuh pkfg, & ¼d½ eRL;k[ksV ds le; eNfy;ksa dks de ls
de Fkdkuk pkfg,] rkfd bu ds 'kjhj esa Xykbdkstu dh ek=k vf/kd ls vf/kd tek
jgsA ¼[k½ eNfy;ksa dks fuEu rkieku ij j[kk tkuk pkfg,] rkfd fofHkUu fØ;kvksa dh
xfrfof/k;k¡ /kheh jgsA ¼x½ eNfy;ksa ds LdsYl] fQUl o vkUrfjd Hkkx vyx dj nsus
pkfg,A bUgha vaxksa ij cSDVhfj;k] ,Utkbfed o jklk;fud fØ;kk,¡ lcls igys o
rhozrk ls gksrh gSA
eRL; cktkj essa dVh gqbZ eNyh dh mi;ksfxrk o ek¡x de gksrh gSA vr%
O;kolkf;d n`f"Vdks.k ls 'kjhj esa Xykbdkstu dh ek=k ds cpr vkSj fuEure rkieku
ij j[ks tkus ds mik; gh ykHkdkjh jgrs gSA ;|fi miHkksäkvksa }kjk Hk.M+kj.k ds fy,
bu dh lQkbZ o dVkbZ fd;k tkuk Qk;nsean jgrk gSA
13- [kkus ;ksX; eNyh dh igpku
eNyh 'kh?kz lM+usa vkSj [kjkc gksus okyk inkFkZ gSA pw¡fd foØsrk dk ç;kl
jgrk gS fd ml dh lHkh eNfy;k¡ fcd tk,A vr% bl ds [kkus ;ksX; voLFk dh
igpku t#jh gSA lM+h vkSj [kkus ;ksX; eNyh dh igpku 'kkjhfjd vax] <k¡pk] xa/k]
fxYl] vk¡[ksa bR;kfn ds vk/kkj ij dh tkrh gSA ijUrq vke miHkksäk bl ds fxYl
ij gh T;knk /;ku nsrk gSA dbZ LFkkuksa ij rktk eNyh dk Òze cuk;s j[kus ds fy,
eNfy;ksa ds fxYl ij [kfM+;k feêh yxk nh tkrh gSA [kkus ;ksX; o lM+h eNyh dh
lgh igpku ds fy, fofHkUu ckgjh 'kkjhfjd vaxksa ds fuEukafdr y{k.kksa dh lgk;rk
yh tkuh pkfg,A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-36-320.jpg)
![23
Ckkgjh 'kkjhfjd vax rktk o [kkus ;ksX; eNyh lM+h o [kkus ds v;ksX;
eNyh
'kkjhfjd jax
'kkjhfjd <k¡pk
vaxwBs ls nckus ij
'kkjhfjd xa/k
fxYl
vk¡[ksa
okLrfod fn[kkbZ nsrk gS] tks
/khjs&/khjs gYdk iM+rk tkrk
gSA
pednkj] Bksl] dBksj o fcuk
dqpyk gksrk gSA
ek¡l ij dksbZ fu'kku ;k xïk
ugh iM+rk gS vkSj vaaxwBk
gVkus ij ;g iwoZor lkekU;
voLFkk esa vk tkrh gSA
eNyh tSlh çkÑfrd o
rktxh;qä xa/k dk vuqHko
gksrk gSA
pedhys yky jax ds gksrs gS]
ftu ij lQsn æo yxk jgrk
gSA bu ls rktxh;qä eNyh
tSlh xa/k vkrh gSA
ns[kus esa lkekU;] pedhyh
vkSj iw.kZr% mUur gksrh gS
gYdk Hkwjk o eVeSyk gks
tkrk gSA
fcuk ped ds vkSj fiyfiyk
gksrk gSA
ek¡l ij fu'kku ;k xïk jg
tkrk gS vkSj vaaxwBk gVkus
ij okil lkekU; voLFkk
ugh vk ikrh gSA
?k`f.kr nqxZU/k dk vkHkkl
gksrk gSA
yky ;k Hkwjk jax tks gYdk
;k eSyk gks tkrk gSA lQsn
æo fylfylk gks tkrk gSA
bl ls ?k`f.kr nqxZU/k Hkh
vkrh gSA
uhps dks cSBh gqbZ] vikjn'khZ
vkSj QSyh gqbZ gksrh gSA
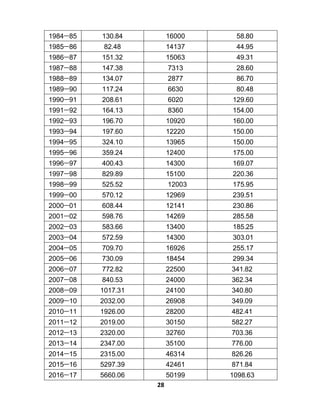
14- jktLFkku esa ekRL;dh fodkl ds miyC/k eRL; ty{ks=
Hkweh vkSj ty uked nks uSlfxZd ?kVdksa ls feydj cus tyh; ek/;e dks
ty{ks= dgk tkrk gSSA buds xq.kksa o fo'ks"krkvksa ij feÍh o ikuh ds fofHkUu xq.k&/keZ
vkSj tyok;q eq[; #i ls izHkko Mkyrh gSA ;g iz—fr dk fn;k ojnku gS] tks
lkekU;r% Hkweh dh lrg ij ik, tkus okys ty ij fuHkZj djrk gSA ;|fi Hkwehxr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-37-320.jpg)
![24
ty ds mi;ksx ls bu esa c<+ksrjh dh tk ldrh gSA ftl ty{ks= esa O;kolkf;d
vk/kkj ij eNyh mRiknu fd;k tkrk gS] mls eRL; ty{ks= dgk tkrk gSA ml
vuqdqyre ty {ks=Qy dks mRiknd ty {ks=Qy vFkok izHkkoh ty{ks=Qy ¼EWSA
= effective water spred area½ dgk tkrk gS] tks mRiknd dks eNyh ikyu ls
vko’;d vk; dh izkfIr djk dj o"kZ eas iw.kZ le; dk;Zjr j[k ldsA bldh
vko’;drk vkaoVu o yht fu/kkZj.k ds lkFk&lkFk eRL; mRikfnrk] ty ifj"dj.k
fØ;kvksa rFkk eRL; cht lap;u esa iM+rh gSA
jktLFkku es ekRL;dh fodkl ds fy, nks izdkj ds tyh; lalk/ku ekStwn gS&
lrgh ty vkSj Hkw&tyA buesa ty dh miyC/krk o"kkZ ij vk/kkfjr gksrh gSA
ekRL;dh fodkl eas lrgh ty dk mi;ksx fd;k tkrk gSA ekRL;dh lalk/kuksa ds
losZ{k.k] fodkl] lao/kZu o nksgu esa Hkh blh ty dks egŸo fn;k tkrk gSA dbZ
dkj.kksa ls Hkw&ty dk O;kid mi;ksx ekRL;dh fodkl esa vHkh rd ugh fd;k tk
ldk gSA
jklk;fud xq.kksa ds vk/kkj ij Hkh ekRL;dh fodkl esa mi;ksxh nks izdkj dk
ty ekStwn gS& ehBk ty vkSj [kkjk tyA [kkjk ty vR;f/kd lhfer ek=k esa lrgh
ty ds #i esa feyrk gSA ;|fi Hkw&ty ds #i es bldh fopkj.kh; ek=k ekStwn gSA
nynyh ty vR;f/kd lhfer ek=k esa fey tkrk gSA jkT; es tykuqfo} {ks=
¼water-loggeg area½ esa Hkh o`f} gqbZ gSA ehBs ikuh ds L=ksrksa esa ufn;ka] ukysa]
tyk'k;] rkykc] xzkeh.k iks[kj] ugjsa] dq,¡ bR;kfn 'kkfey fd, tkrs gSA ekRL;dh
fodkl es blh L=ksr dk lokZf/kd o O;kid Lrj ij mi;ksx fd;k tkdj bUgha ds
lao/kZu o fodkl dh vksj /;ku fn;k tkrk gSA
jkT; esa ekRL;dh L=ksrksa dk losZ{k.k iapo"khZ; ;kstukvksa es vkadM+ksa dh iwfrZ ds
fy, o"kZ 1974 esa fd;k x;kA blesa eNyh ikyu ds fy, ty{ks=Qy 3 yk[k gSDVj
ekuk x;kA bls 0-40 yk[k gSDVj esa l?ku eNyh ikyu] 1-40 yk[k gSDVj esa
ikjEifjd eNyh ikyu vkSj 1-20 yk[k gSDVj esa tyk'k; fodkl ls eNyh ikyu es
oxhZ—r fd;k x;kA rRi’pkr bl ty{ks=Qy dks 3-30 yk[k gSdVj ekuk tkus yxkA
buesa ls djhc 1-20 yk[k gSDVj ty'k;ksa] 1-80 yk[k gSDVj y?kq ck¡/kksa] xzkeh.k
rkykcksa] ekSleh iks[kjksa o nynyh {ks=ksa vkSj 'ks"k 0-30 yk[k gSDVj ugjksa o ufn;ksa ds
#i esa ekuk x;kA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-38-320.jpg)
![25
Hkkjr ljdkj }kjk tkjh *gS.M+ cqd vkWu fQ'kjht LVsfVfLVd 2018* esa Hkkjr esa
vUr%LFkyh; ekRL;dh {ks= dk dqy ty {ks=Qy 8246662-17 gSDVj ekuk x;k gSA
blesa jktLFkku essa dqy ty{ks=Qy 4]30]780 gSDVj ekurs gq, fuEuçdkj ls foHkkftr
fd;k x;k gS &
1- ufn;k¡ vkSj ugjsa - & 5]290 fdyksehVj
2- o`gn] e/;e o lhekUr tyk'k; & 3]36]871 gSDVj ¼la[;k 394½
3- rkykc o iks[kj & 93]909 gSDVj
o"kZ 2010 dsfUnz; ekRL;dh f'k{kk laLFkku] eqEcbZ us jktLFkku esa ekRL;dh
fodkl dh lEHkkoukvksa ij losZ fd;kA bl laLFkku us vf/kdre tyHkjko {ks=Qy
(FTL= full tank level) ds vk/kkj jkT; ds fofHkUu izdkj ds ty{ks=ksa esa fuEu izdkj
ls oxhZ—r fd;k x;k gS&
ty{ks= dk oxhZdj.k
ty{ks=Qy ds vk/kkj ij
ty{ks=ksa
dh
la[;k
ty{ks= dk
vf/kdre Hkjko
yk[k gSDVj es
1- y?kq rkykc o iks[kj 1-0 gS- ls de 6913 0-0475
2- e/;e rkykc o iks[kj 1-1 ls 10-0 gS- 6207 0-255
3 foLr`r rkykc o iks[kj 10-1 ls 100-0 gS- 2047 0-636
4- y?kq tyk'k; 101 ls 1000 gS- 346 0-824
5- e/;e tyk'k; 1001 ls 5000 gS- 35 0-641
6- foLr`r tyk'k; 5001 ls vf/kd 12 1-833
7- ufn;ka o ugjsa & 0-300
8- tykuqfo} & 0-800
9- yo.kh; ty{ks= & 1-800
buesa lsa vf/kdre tyHkjko ij 5-17 yk[k gSDVj ty{ks=Qy dks ekRL;dh
fodkl ds fy, mi;qZDr ekuk x;k gSA tks 3-36 yk[k gSDVj foLr`r o e/;e
tyk'k;ksa] 0-94 yk[k gSDVj y?kq tyk'k;ksa o rkykcksa vkSj 0-87 yk[k gSDVj
ufn;ksa]ugjksa o tykuqfo} ds :i es miyC/k gSA pwafd ekulwu i’pkr ty{ks=ksaa dk
tyQSyko vf/kd gksrk gSA ijUrq flapkbZ ds fy, flapkbZ o isaVk dk’r ds fy, ty
fudklh] is;ty dh vkiwfrZ] ok’ihdj.k bR;kfn dkj.kksa ls bues tyQSyko ?kVrk
jgrk gSA vfu;fer o fc[kjh o"kkZ ds dkj.k tyk'k;ksa esa vf/kdre tyHkjko ij](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-39-320.jpg)
![26
vksoj¶yksa vkSj ufn;ksa esa iw.kZ {kerk ls tycgko dh fLFkfr rhu&pkj o"kksZ ds vUrjky
ij vk ikrh gSA vr% eRL; cht lap;u] eRL; mRiknu o ekRL;dh ds vU; fodkl
lEcU/kh v/;;u ds fy, bu ty{ks=ksa es vkSlru ty{ks=Qy ds fy, izHkkoh
ty{ks=Qy dk vkadyu fd;k tkrk gSA orZeku esa jkT; ds ekRL;dh {ks= esa izHkkoh
ty{ks=Qy 2-15 yk[k gSDVj ekuk x;k gS] tks vf/kdre ty{ks=Qy 5-17 yk[k
gSDVj dk yxHkx vk/ks ls Hkh de gSSA jkT; es dqy ty{ks=ksa dh la[;k 16 gtkj ds
djhc gSA ijUrq eRL;k[ksV ds fy, yht ij nsus ds fy, o"kZ 2014&15 dh Bsdk lwph
es ek= 2210 ty{ks= vkSj 2017&18 esa 2161 ty{ks= gh j[ks x,A fofnr jgs fd o"kZ
1990&91 es Bsdk lwph es 1008 ty{ks= gh j[ks x,A
15- jktLFkku esa ekRL;dh fodkl ds vk/kkjHkwr y{;
jktLFkku es o"kZ 1958 ls izkjEHk dh xbZ ekRL;dh fodkl dh ;kstuk ds
izkjfEHkd izk#i es eq[;r% nks izeq[k y{;& eRL; mRiknu vkSj ljdkjh dks"k esa
jktLo izkfIr & j[ks x;sA ckn esa bu y{;kas dh izkfIr ds fy, egŸoiw.kZ le>s tkus
okys izeq[k buiqV vFkkZr eRL; cht mRiknu ,oa lap;u dks Hkh 'kkfey dj fy;k
x;kA bu y{;ksa es LFkkuh; jkstxkj vkSj tudY;k.k dk dksbZ ftØ gh ugh fd;k
x;kA bu y{;ksa esa LFkkuh; jkstxkkj dks o"kZ 1973&74 es *gkQ , fefy;u tkWc
dk;ZØe* ls j[kk tkus yxkA Hkys gh iz'kklfud –f"V ls jkT; dh ekRL;dh dks
i'kqikyu O;olk; dh Js.kh es j[kk x;k gksA ijUrq ewy #i ls vkt Hkh vkfFkZd i{k
ls lEcfU/kr bUgh ekin.M+ks ij izxfr dk vkadyu fd;k tk jgk gSA
o"kZ 1950&51 ls 2017&18 rd dh vof/k eas izkIr dh xbZ bu rhuks vk/kkjHkwr
y{;ksa dh miyfC/k fuEu rkfydk es izLrqr gS A tks ;g n'kkZrh gS fd jkT; es [kk|
leL;k ds gy es eRL; mRiknu] jktdh; dk;ksZ ds fy, vko’;d jktLo izkfIr vkSj
bu nksuks y{;ks dh izkfIr es egŸiiw.kZ fuHkkus okys izeq[k buiqV eRL; cht mRiknu
es o"kZ nj o"kZ fujUrj c<+ksrjh gh gksrh jgh gSA ekRL;dh fodkl ds vk/kkjHkwr y{;ksa
dh fujUrj çkIr dh tk jgh bl miyfC/k ls Li"Vr% fu"d"kZ fudkyk tk ldrk gS
fd jktLFkku dh vFkZO;oLFkk ds fodkl ess ekRL;dh fodkl dh Hkh ,d fu.kkZ;d o
egÙoiw.kZ ;ksxnku jgrk gSA
o"kZ jktLo izkfIr
¼#i;k yk[kks es½
eRL; mRiknu
¼eSfVªd Vu ½
eRL; cht mRiknu
¼QzkbZ fefy;u es½
1950&51 2-21 & &](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-40-320.jpg)
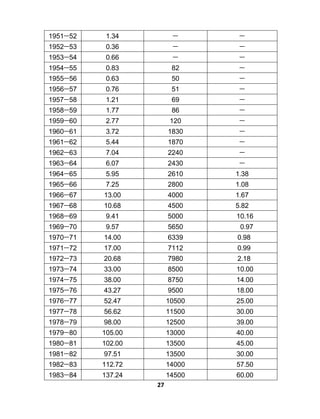
![29
2017&18 6116-39 54035 1094-01
16- jktLFkku esa ekRL;dh fodkl dh yhftax ikfylh vkSj jktLo vtZu
jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV 1953 dh /kkjk 2 esa *izkbZosV okVj* dh ifjHkk"kk nh
xbZ gSA *izkbZosV okVj* dks NksM+dj vU; ty{ks=ksa esa eRL; fodkl] lao/kZu o nksgu ds
fy, jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl 1958 ykxw fd, x, gSSA blds fu;e 5 ds vUrxZr
lqLi"V yhftax ikfylh dk fuekZ.k fd;k x;k gSA bl izdkj jkT; esa oS/kkfud :i ls
nks izdkj ds ty{ks= gS& ,d og ty{ks= gS] ftu ij jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl
1958 ykxw gksrs gSA bUgsa vf/klwfpr ty{ks= dgk tkrk gSA blesa jktdh; ty{ks=
lEefyr fd;s tkrs gSA nwljs og ty{ks= gS] tks *izkbZosV okVj* dh ifjHkk"kk es vkrs
gS vkSj jkT; ljdkj us jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV 1953 dh /kkjk 5¼2½ dk mi;ksx dj
bu ty{ks=ksa dks jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl 1958 ds vUrxZr ykus dk xtV
uksfVfQds'ku tkjh ugh fd;k gSA bUgsa v&vf/klwfpr ty{ks= dgk tkrk gS vkSj bl
Js.kh es xzkeh.k iks[kj] lkoZtfud laLFkkuksa o Lo;a dh Hkweh ij cus iks[kj vkrs gSA
jktLFkku iapk;rh jkt fu;e 1996 ds vUrxZr 50 ,dM+ flapkbZ {kerk ds
xzkeh.k iks[kj LFkkuh; xzke iapk;r ds lqiqnZ fd;k x;k gS vkSj buesa eNyh ds Bsds
nsus dk vf/kdkj lEcfU/kr ftyk ifj'kn dks fn;k x;k gSA ysfdu ;g iks[kj
jktLFkku eRL; vf/kfu;e 1953 es nh xbZ *izkbZosV okVj* okVj dh ifjHkk"kk es vkrs
gSA bl izdkj xzke iapk;r ds LokfeRo ds 50 ,dM+ flpkbZ {kerk ds Lo;a ds xzkeh.k
iks[kjksa es eRL;k[ksV Bsds nsus dk dk;Z iapk;rh jkt fu;e 1996 ds vUrxZr gh fd;k
tkrk gSA xzke iapk;r ds Lo;a ds vf/kdkj ds bu iks[kjksa ij eRL; foHkkx ls
iapk;rh jkt laLFkkvksa dks gLrkukUrfjr tyk'k;ksa ds fu;e ykxw Hkh ugh gks ikrs gSA
oSls jkT; ljdkj pkgsa rks jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV 1953 dh /kkjk 5¼2½ es nh xbZ
“kfDr;ksa dk mi;ksx dj xzke iapk;r dh Lo;a ds bu iks[kjksa ij Hkh jktLFkku
fQ'kjht #Yl 1958 ykxw dj ldrh gSA ijUrq vHkh rd jkT; ljdkj us bl ckjs es
dksbZ xtV uksfVfQds'ku tkjh ugh fd;k gSA
o"kZ 2000 es jkT; ljdkj us flapkbZ foHkkx ds vf/kuLFk 80 gSDVj flapkbZ
{kerk ds tyk'k; LFkkuh; xzke iapk;r vkSj fQj 2003 es 80 ls 300 gSDVj flapkbZ
{kerk ds tyk'k; LFkkuh; iapk;r lfefr dks gLrkukUrfjr fd, gSA iapk;rh
laLFkkvksa dks lq–<+hdj.k ds mÌs’; ls flapkbZ foHkkx ls iapk;rh jkt laLFkkvksa dks
gLrkukUrfjr bu tyk'k;ksa ls flapkbZ dj] flapkbZ ds vfŸkfjDr ty fcØh]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-43-320.jpg)
![30
?kkl&ikr&ikiM+h] flaxkM+k mit] xkn] lw[ks {ks= dh uhykeh] bR;kfn ls izkIr jktLo
lEcfU/kr iapk;rh jkt laLFkk dks lkSik x;k gSaA ijUrq buesa eRL; ikyu dk vf/kdkj
bUgsa ugh fn;k x;k gSA ;g vf/kdkj eRL; foHkkx ds ikl gh j[kk x;k gSA
oSls rks jktLFkku ds ty{ks=ksa esa eRL;k[ksV Bsdk nsus dh dksbZ vf/k—r yhftax
ikfylh ugh gSA ysfdu jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV o #Yl ds vUrxZr vkus okys
vf/klwfpr ty{ks=ksa es eRL;k[ksV ds Bsds fn, ls izkIr gksus okys eRL; jktLo es
fujUrjrk cuh jgsA blds fy, jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl ds fu;e 5 ds vUrxZr
O;ofLFkr izko/kku fd;s x;s gSA okLro esa vf/klwfpr ty{ks=ksa ds vkaoVu o Bsdk fn;s
tkus ds ;gh izko/kku gh yhftax ikfylh dgs tkrs gSA jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV o
#Yl ds vUrxZr izfro"kZ eRL;k[ksV ds Bsds fn, tkus gsrq jkT; ds vf/klwfpr
ty{ks=ksa dk oxhZdj.k fd;k tkrk gSA ,d le;c) dk;ZØe ds vUrxZr dk;Zokgh
djrs gq, vf/klwfpr ty{ks=ksa dk oxhZdj.k xr 3 o"kksZ dh vkSlr jktLo vk; ds
vk/kkj ij fd;k tkrk gSA
o"kZ 2017&18 dh eRL; Bsdk lwph es lEefyr fd;s x;s fofHkUu izdkj ds
ty{ks=ksa esa jktLo vtZu dk fooj.k uhps fn;k tk jgk gS&
1. foHkkx ds ikl miyC/k *,* Js.kh ds 178 tyk'k;ksa esa ls 156 tyk'k;ksa dks Bsds
ij fn;s tkus ls dqy #i;s 5651 yk[k dh jktLo vk; çkIr gqbZA
2. foHkkx ds ikl miyC/k *ch*] *lh* vkSj *Mh* Js.kh ds 39 tyk'k;ksa vkSj 16
ufn;ksa esa ls 45 ty{ks=ksaa dks Bsds ij fn;s tkus ls dqy #i;s 75-50 yk[k dh
jktLo vk; çkIr gqbZA
3. iapk;r jkt laLFkkvksa dks LFkkukUrfjr foHkkxh; tyk'k;ksa esa dqy 610-94 yk[k
dh jktLo vk; çkIr gqbZA
jkT; dh eRL; Bsdk lwph esa 52 ty{ks= ,sls Hkh gS] ftUgsa /kkfeZd Hkkoukvksa]
ou o oU;tho foHkkx dh vkifŸk rFkk vU; dkj.kksa ls eRL;k[ksV ds fy, Bsds ij
ugh fn;k tkrk gSA eRL;k[ksV ds vf/kdkj ysus ds izLrko cUn Vs.M+j ;k [kqyh cksyh
ls izkIr fd;s tkrs gSA o"kZ 1991 ls , Js.kh ds ty{ks=ksa dks 3 o"khZ; yht vkSj vU;
Js.kh ds ty{ks=ksa dks 5 o"khZ; yht ij nsus dh O;oLFkk dh xbZA ysfdu o"kZ 2003 ls
lHkh Js.kh ds ty{ks=ksa dks 5 o"khZ; yht ij vkoaVu dk izko/kku fd;k x;k gSA
tyk'k;ksa esa vkaxqfyd voLFkk ds cht dh vko';drk dks /;ku es j[krs gq, *,* o
*ch* Js.kh ds iÍk/kkfj;ksa dks vkjf{kr nj ij fudVorhZ *lh* o *Mh* Js.kh ds tyk'k;ksa
ds vkoaaVu dh O;oLFkk Hkh dh xbZ gSA *lh* o *Mh* Js.kh ds tyk'k;ksa dks eRL; ikyd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-44-320.jpg)
![31
fodkl vfHkdj.k ds ek/;e ls izf'kf{kr eRL; —"kdksa dks 10 o"khZ; yht vof/k ds
fy, vkoaVu dk izko/kku Hkh gSA jktLFkku tutkfr {ksf=; fodkl lgdkjh la?k
fyfeVsM] mn;iqj dks Hkh yht ij ty{ks= vkoaVu dh O;oLFkk gSA jktLFkku ljdkj
us o"kZ 2000 esa *Mh* Js.kh ds tyk'k;ksa vkSj 2003 es *ch* o *lh* Js.kh ds tyk'k;ksa dks
iapk;rh jkt laLFkkvksa dks gLrkukUrj.k dk iz'kklfud fu.kZ; fy;k x;kA ;|fi o"kZ
2010 es jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl 1958 esa vko’;d la'kks/ku dj ds bl fu.kZ; dks
oS/kkfud ekUa;rk iznku dj nh x;hA
ty{ks=ksa esa nh?kZ vof/k ds fy, eRL;k[ksV ds vf/kdkj izfro"kZ yht c<+ksrjh ds
izko/kku ds lkFk LykbZfMax i)fr ls fn, tkrs gSA blds vUrxZr eRL;k[ksV vf/kdkj
dh jkf'k es xr o"kZ dh yht jkf'k es fuEu izdkj ls izfr o"kZ c<+ksrjh dh tkrh gS &
1. o"kZ 1991 es *,* Js.kh ds ty{ks=ksa esa yht vof/k ds nwljs o rhljs o"kZ xr o"kZ
dh yht jkf'k dk Øe'k% 12-5% o 15% vf/kd tek djkus vkSj ch o lh
Js.kh ds ty{ks=ksa es nwljs] rhljs] pkSFks o ikapos o"kZ xr o"kZ dh jkf'k dk
Øe'k% 12-5%] 15%] 17-5% o 20% c<+kus dk izko/kku fd;k x;kA ysfdu o"kZ
2003 es izR;sd o"kZ c<+kbZ tkus okyh fofHkUu njksa dks lekIr dj lHkh Js.kh ds
ty{ks=ksa esa xr o"kZ dh yht jkf'k dk 12% vf/kd tek djus dk izko/kku
fd;k x;kA
2. eRL; ikyd fodkl vfHkdj.kksa dks vkoafVr *lh* Js.kh ds ty{ks=ksa esa vkaofVr
jkf'k ds vk/kkj ij xr o"kZ dh jkf'k es 10% dh o`f} gj o"kZ dh tkrh gSA
*Mh* Js.kh ds ty{ks= 400 :i;s izfr gSDVj izfr o"kZ ds vk/kkj ij vkaofVr
dj xr o"kZ dh jkf'k es 10% c<+ksrjh dh tkrh gSA
3. eRL; foHkkx ls iapk;rh jkt laLFkkvksa dks gLrkukUrfjr *ch*] *lh* o *Mh* Js.kh
ds tyk'k;ksa es okf"kZd yht fu/kkZj.k dk vf/kdkj lEcfU/kr iapk;rh jkt
laLFkk Øe'k% ftyk ifj"kn] iapk;r lfefr o xzke iapk;r dks fn;k x;k gSA
ty{ks= es eRL;k[ksV dh vof/k ykbZlsUl tkjh gksus dh frfFk ls vkxkeh 31
ekpZ rd gksrh gSA bl vof/k es fu"ks/k _rq esa eRL;k[ksV fd;k tkuk oftZr jgrk gSA
bl uhfr ls ykbZlsUlh dks fu"ks/k _rq ls iwoZ ykbZlsUl ysdj o"kkZdky esa eRL; cht
lap;u dh O;oLFkk] izk—frd eRL; iztuu dsUnzksa dh pkSdlh vkSj eRL; lEink dh
lqj{kk es lqfo/kk jgrh gSA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-45-320.jpg)
![32
17- jktLFkku esa eRL; mRiknu esa fofHkUu eRL; tkfr;ksa dk ;ksxnku
Lok/khurk feyus rd jktLFkku ds ty{ks=ksa es izk—frd :i ls ekStwn
eNfy;ksa dh Hkjekj FkhA O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV ij izfrcU/k Fkk vkSj tuekul es
eNfy;ksa ds izfr :ph ugh FkhA lks'ky iqfyflax ds ek/;e ls eRL; lfgr leLr
tSo fofo/krk dks dBksjrk ls laj{k.k fn;k tkrk FkkA eNfy;ksa dk izk—frd eRL;
iztuu fuckZ/k gksrk FkkA QyLo:i eRL; ty{ks=ksa es eNfy;ksa dh la[;kRed o
xq.kkRed mifLFkfr cuh jgrh FkhA ekRL;dh fodkl ds 'kq:vkrh dky esa ekRL;dh
LFkyu (capture fisheries) ij tksj fn;k x;kA ty{ks=ksa esa izk—frd eRL; lEink
ds O;kolkf;d nksgu dks ekRL;dh LFkyu dgk tkrk gSA blesa eNfy;ksa dk
LoHkkfod mRiknu fd;k tkrk gSA ;g ekuo Je ij vk/kfjr O;olk; gSA blesa
U;wure fuos'k djrs gq, gq, izk—frd eRL; L=ksrksa dk eRL;k[ksV fØ;k ls nksgu
fd;k tkrk gSA ;g fuos'k Hkh Øk¶V o fx;j ij vf/kd fd;k tkrk gSA Lok/khurk ds
ckn rhljh iapo'khZ; ;kstuk dky ds ckn dh okf"kZd ;kstuk 1968&69 rd jkT; esa
ekRL;dh LFkyu ij gh vf/kd tksj fn;k x;kA
jkT; esa pkSFkh iapo"khZ; ;kstuk dky ls ekRL;dh LFkyu dh 'kSyh dks
ekRL;dh ikyu (culture fisheries) dh vksj cnyus dk iz;kl 'kq: fd;k x;k vkSj
ikapoh iapo"khZ; ;kstukdky dh lekfIr rd jkT; ds leLr ty{ks=ksa es ekRL;dh
ikyu 'kSyh dks ykxw dj fn;k x;kA ty{ks=ksa esa okafNr fdLe dk cht lafpr dj
vkSj bldh ns[kjs[k o iks"k.k dh O;oLFkk dj eRL;k[ksV djds eRL; lEink ds
O;kolkf;d nksgu fd, tkus dks ekRL;dh ikyu dgk tkrk gSA tyk'k;ksa esa dkiZl
eNfy;ksa dk ikyu vkSj NksVs rkykcksa es dkiZl ds vykok >haxk o vU; eNfy;ksa ds
ikyu dks blh es j[kk tkrk gSA eNfy;ksa ds vykok eksrh] dey] flaxkM+s bR;kfn Hkh
ty{ks=ksa esa ikyu izkfof/k ls izkIr fd;s tkus yxs gSA ekRL;dh ikyu iw¡th ij
vk/kkfjr O;olk; gSA blesa dkQh vf/kd iw¡th fuos'k djrs gq, mRiknu fy;k tkrk
gSA mRiknd fØ;kvksa ds lkFk&lkFk eRL;k[ksV ds lk/kuksa ij Hkh fuos'k fd;k tkrk
gSA
KkrO; jgs fd ekRL;dh LFkyu mRiknu dh LFkkbZ fØ;k gSA ftldh fujUrjrk
ty{ks= dh izk—frd n'kk o blesa ekStwn eRL; lEink ij fuHkZj djrh gSA ekRL;dh
ikyu mRiknu dh vLFkkbZ fØ;k gS] tks iw¡th fuos'k dh fujUrjrk ij fuHkZj djrh gSA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-46-320.jpg)
![33
blesa fQ'k QkeksZ dk fuekZ.k] eRL; cht mRiknu o ifjogu] iks"k.k o ns[kjs[k
O;oLFkk vkSj iwjh izfØ;k ds lapkyu gsrq n{k o izf'kf{kr dk;ZdrkZvksa dh vko’;drk
gksrh gSA tcfd ekRL;dh LFkyu is'ksoj o [kkunkuh vuqHko ds eNqvkjksa o
O;kolkf;;ksa ij vf/kd fuHkZj djrk gSA ekRL;dh ikyu dh vlQyrk ;k bldk
v/kwjkiu vUrr% ekRL;dh LFkyu esa gh ifjofrZr gksrk gSA
jktLFkku esa 'kq#vkrh nkSj esa O;kolkf;d eRL; >ksy es DokfyVh fQ'k dh
vf/kdrk jgh vFkkZr ,slh eNfy;k¡ vf/kd ek=k es idM+h xbZ] ftudk cktkj ewY;
vf/kd jgrk FkkA tSls&tSls ekRL;dh LFkyu ‘'kSyh ls vfrnksgu djds eRL; mRiknu
c<+rk x;k] eRL; >ksy esa DokfyVh fQ'k vkSj eRL; mRiknu dh ek=k Hkh ?kVrh
eglwl gksus yxhA lkFk gh vf/kd eNyh mRiknu o jktLo izkfIr ds lkFk&lkFk
LFkkuh; Lrj ij jkstxkj nsus dk ncko Hkh c<rk x;kA QyLo#i ekRL;dh ikyu dh
'kSyh dh vksj ifjorZu vko’;d gksrk pyk x;kA
Hkkjr ljdkj }kjk tkjh *gS.M+ cqd vkWu fQ'kjht LVsfVfLVd 2018* esa
jktLFkku es o"kZ 2017 esa jktLFkku ds eRL; >ksy essa fofHkUu Js.kh dh eNfy;ksa dk
fuEu izdkj ls fooj.k fn;k x;k gS &
o"kZ ,oa
bdkbZ
mRikfnr eNfy;ksa dk fooj.k
estj
dkiZl
fons'kh
dkiZl
ekbZuj
dkiZl
ejZYl dSV
fQ'k
vU;
eNfy;k¡
;ksx
2017 eS-Vu 39015 4090 9130 0 1800 0 54035
% 72-2 7-6 16-9 0 3-3 0 100-0
jktLFkku es o"kZ 1992 esa Hkkjr ljdkj dh dsfUnz; izofrZr lgk;rk ls
*vUr%nsZ'kh; eRL; lka[;dh fodkl ;kstuk* vUrxZr eRL; L=ksrksa o eRL; mRiknu
dk vkadyu dk dk;ZØe 'kq: fd;k x;kA ;g ;kstuk o"kZ 2014&15 rd la’kksf/kr
mÌs'k; o u, uke *LVªsUFkfuaaaaaax vkWQ MkVk csl ,.M ft;ksxzkfQdy flLVe vkWQ nh
fQ'kjht lsDVj* ls tkjh gSA lEHkor% bl ;kstuk ls dqN rdfudh vkadM+s] fo’ys'k.k
o fu"d"kksZ ls vf/kd Li"V tkudkjh fey ldsA oSls bl ;kstuk dh dksbZ fjiksZV ;k
vkys[k ugh fey ldk gSA
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-47-320.jpg)
![34
18 -jktLFkku esa ekRL;dh {ks= esa ekuoh; lalk/ku fodkl vkSj lkekftd
lqj{kk dk;ZØe
Hkkjr ljdkj }kjk tkjh *gS.M+ cqd vkWu fQ'kjht LVsfVfLVd 1988* esa
jktLFkku esa o"kZ 1987 esa dk;Zjr eNqvkjksa dh la[;k 510 nh xbZ gSA blh iqLrd ds
o"kZ 2004 laLdj.k esa o"kZ 2003 esa ;g la[;k 2985 nh xbZA tcfd bl iqLrd ds
laLdj.k 2014 esa o"kZ 2013 esa ;g la[;k c<+dj 7316 gks xbZ gSA bles 2638 iq#"k]
1693 fL=;ka vkSj 2985 cPpsa jgs gSA bu essa 2833 dks ekRL;dh ds jkstxkj esa lfØ;
ekuk x;k gSSA lfØ; eNqvkjksa ds bu vkadM+ksa esa 675 Jfedksa dks iw.kZdkyhu] 974 dks
va'kdkyhu o 1184 dks ;nkdnk jkstxkj esa ekuk x;k gSA eRL; foHkkx dh okf"kZd
izxfr izfrosnu esa o"kZ 2015&16 esa jkT; es lfØ; eNqvkjksa dh la[;k c<+dj 17500
gks xbZ gSA buesa iw.kZdkyhu jkstxkj esa 7560 vkSj 7292 eNqvkjksa dks va'kdkyhu
jkstxkj esa ekuk x;k gSA 'ks"k cps 2648 eNqvkjksa dks ekRL;dh {ks= esa ;nkdnk
jkstxkj esa dk;Zjr ekuk x;k gSA
Hkkjr ljdkj }kjk tkjh *gS.M+ cqd vkWu fQ'kjht LVsfVfLVd 2018* esa
jktLFkku esa o"kZ 2017 esa dk;Zjr eNqvkjksa dh la[;k 16500 nh xbZ gSA bles 16500
iq#"k dks gh bl O;olk; esa lfØl ekuk x;k gS vkSj fL=;ka vkSj cPpksa dh la[;k
'kwU; n'kkZbZ x;h gSA bu vkadM+ksa esa 7290 eNqvkjksaa dks iw.kZdkyhu] 6082 dks
va'kdkyhu o 3128 dks ;nkdnk jkstxkj esa ekuk x;k gSA mYys[kuh; gS fd ekRL;dh
fodkl dh 'kq:vkr ds 60 o"kZ iwoZ LFkkuh; Lrj ij bl {ks= esa jkT; dk dksbZ O;fDr
jkstxkj esa ugh FkkA
vkerkSj ij cM+s eNyh Bsdsnkj jkT; ds ckgj ds O;kolkf;d n{k o dq'ky
eNqvkjksa dks vfxze jk'kh nsdj iwjs eRL; o"kZ ds fy, vkjf{kr dj ysrs gSA QyLo:i
y?kq Bsdsnkjksa vkSj eRL; —"kdksa dks dq'ky eRL; Jfedksa dh O;oLFkk esa dkQh
ijs'kkfu;ksa dk lkeuk djuk iM+rk gSA eRL; Jfedksa dks eRL;k[ksV dk Hkqxrku eNyh
dh fdLe o bdkbZ Hkkj vuqlkj izfr fdyksxzke dh nj ls fd;k tkrk gSA lkekU;r%
tkyksa o ukoksa dh O;oLFkk Øe'k% eRL; Jfedksa o eRL; mRikndksa }kjk dh tkrh gSA
jkT; dh ekRL;dh {ks= esa jkstxkj es yxs bu eNqvkjkasa dh leL;k dks le>k
x;kA jktLFkku dk nf{k.kh Hkkx vkfnoklh ckgqY; {ks= gSA ;g leqnk; vkfndky ls
eNfy;ksa o bl ds f'kdkj ds izfr vkdf"kZr jgk gSA ;|fi bl dk mÌs’; Lo;a ds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-48-320.jpg)
![35
Hkkstu dh iwfrZ djuk gh jgk gSA bu yksxksa dks ekRL;dh esa jkstxkj nsus ds fy,
izksRlkgu o lqfo/kk,a miyC/k djk dj vkfFkZd o lkekftd fodkl dh lEHkkouk,a
utj vkbZA bl mÌs’; dks ysdj nf{k.k jktLFkku ds tutkfr; ckgqY; {ks= esa eRL;
lgdkfjrk ds ek/;e ls tutkfr leqnk; dks ekRL;dh {ks= esa jkstxkj ls tksM+k
x;kA ikapoh iapo'khZ; o"kZ 1976&77 es *VªkbZcy lc&Iyku* ds vUrxZr eNyh ikyu
;kstukvksa dsk jktLFkku tutkfr {ks=h; fodkl lgdkjh la/k fy- ¼jktlla?k½ ds
ek/;e ls 'kq: fd;k x;kA vjkoyh ioZr Js.kh esa fLFkr M+waxjiqj] ckalokM+k] mn;iqj
vkSj fljksgh ftyksa ds lkFk&lkFk fprkSM+x< o dksVk ftyksa dh Øe'k% izrkix<+ o
“kkgckn rglhyksa dks *VªkbZcy lc&Iyku* ds vUrxZr yk;k x;kA ijUrq eNyh ikyu
ls ykHkkUou dk dk;Z eq[;r% mn;iqj] ckalokM+k o M+waxjiqj ftyksa esa gh tksj&'kksj ls
fd;k x;kA
jkT; ljdkj }kjk fu/kkZfjr okf"kZd yht jk'kh ij egŸoiw.kZ tyk'k;ksa dks
nh/kZ&vof/k ij vkaoVu Þjktlla?kÞ dks fd;k x;kA vkfnokfl;ksa dh lgdkjh
lfefr;ksa ds ek/;e ls eRL;k[ksV ,oa foi.ku djk;k x;kA bu lfefr;ksa dks vko’;d
lqj{kk dop] buiqV~l] eRL;k[ksV ds lk/ku vkSj izksRlkgu Þjktlla?kÞ }kjk iznku
djk, x,A blds }kjk vkfnoklh dY;k.k ds vusd dk;ZØe Hkh lapkfyr fd;s x,A
vkaofVr ty{ks=ksa esa eRL; fodkl o lao/kZu dh izfØ;k o uhfr dk fu/kkZj.k vkSj
vko’;d fofŸk; O;oLFkk Hkh Þjktlla?kÞ }kjk dh xbZA ;|fi ty{ks= dk vkaoVu]
yht olwyh] rdfudh vf/kdkfj;ksa dh O;oLFkk vkSj eRL; —"kdksa dks izf'k{k.k esa
lg;ksx eRL; foHkkx }kjk fn;k x;kA
o"kZ 2013&14 ls eRL; foHkkx us bl tutkfr; {ks= esa vkftfodk fef'ku
;kstuk izkjEHk dh gSA bl ;kstuk dk izeq[k mÌs’; eRL;k[ksV ds Bsds ls eRL; jktLo
vtZu dh ctk; vkfnoklh leqnk; dks izR;{k jkstxkj miyC/k djk;k tkuk gSA ;g
;kstuk jkT; ds rhu egŸoiw.kZ tyk'k;ksa & ca/k t;leUn ¼mn;iqj½] ca/k ekgh ctkt
lkxj ¼ckalokM+k½ vkSj dM+kuk cSd okVj ¼Mwaxjiqj½ & esa 'kq: dh xbZA bu tyk'k;ksa
dks 'kwU; jktLo ekWMy ij fodflr fd;k tk jgk gSA bl esa eRL;k[ksV dh xbZ
eNfy;ksa ds foØ; ds fy, mPpre fufonknkrk dks *fy¶V dkUVªsDV* fn;k tkrk gSA
ftlds fy, bl dkUVªsDV dh leLr jk'kh vkfnoklh eNqvkjksa dks LFkkukukUrfjr dh
tkrh gSA lgdkjh lfefr;ska ds ek/;e ls vkfnoklh eNqvkjksa dks eNyh idM+kbZ dh
etnwjh nh tkrh gSA eNyh idM+kbZ dh ;g nj ns'k es lcls vf/kd gSA eRL; foHkkx
}kjk eNqvkjksa ds fy, uko o tky vkSj tyk'k;ksa esa eRL; cht lap;u dh O;oLFkk
dh tkrh gSA eRL; foHkkx }kjk bu eNqvkjksa dks dsfUnz; izoZfrr ;kstuk vUrxZr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-49-320.jpg)
![36
eNqvkjk dY;k.k dk;ZØe ds vUrxZr vkn'kZ eNqvkjk xkao dk fodkl] eNqvkjksa dk
lkeqfgd nq?kZVuk chek vkSj lsfoax de fjfyQ ;kstuk ls Hkh ykHkkfUor djk;k tk jgk
gSA eRL; foHkkx dh vkftfodk fef'ku ;kstuk esa o"kZ 2017&18 esa bu rhuksa tyk'k;ksa
ij 49 eNqvkjk lgdkjh lfefr;ksa ds ek/;e ls 6362 vkfnoklh eNqvkjksa dks izR;{k
jkstxkj miyC/k djk;k tk x;k gSA
ty{ks=ksa es vf/kd tyHkjko] eRL;k[ksV ij ykxw fu"ks/k _rq vkSj vuqKki=
tkjh gksus esa yxus okys le; ds dkj.k eRL; Jfedksa dk o"kZ esa 6&7 ekg dk le;
gh eNyh fudkyus ds fy, fey ikrk gSA fofHkUu ty{ks=ksa es eRL; Jfedksa ds izolu
es yxs le; ds dkj.k ,d Jfed dks izfr o"kZ 120 ls 150 eRL;k[ksV fnol gh dke
fey ikrk gSA bu ds dk;Z dk le; fuf’pr ugh gksrk gSA bUgsa ekSle dh izfrdwyrk
>syrs gq, [kqys esa jg dj jkr o fnu dke djuk gksrk gSA vkerkSj ij eRL;
mRikndksa }kjk 22 fdyksxzke dh rkSy ij 20 fdyksxzke dh etnwjh dk Hkqxrku fd;k
tkrk gSA jkT; es O;ofLFkr eNyh e.M+h ugh gksus ls ifjogu ds nkSjku gksus okys
yhdst vkSj eaM+hnkjksa }kjk euekuh “krksZ ds dkj.k Hkh eRL; mRiknd o Jfed
uqdlku esa jgrs gSA jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl] 1958 esa 18 o"kZ ls de vk;q ds O;fDr
dks eRL;k[ksV esa dk;Z djkuk oftZr gSA blds vykok bl fu;e esa eRL; Jfedksa o
mRikndksa dks dksbZ oS/kkfud laj{k.k ugh fn;k x;k gSA ;|fi jkT; es eRL; Jfedksa
ds dY;k.k ds fuEufyf[kr dk;ZØe lapkfyr fd;s x, gSA ysfdu bu dk vf/kdka'k
ykHk nf{k.k jktLFkku ds mn;iqj] M+waxjiqj o ckalokM+k ftyksa ds lgdkfjrk ds ek/;e
ls laxfBr eNqvkjksa rd gh lhfer jgk gSA
o"kZ eRL; ikyd
izf'k{k.k
¼la[;k½
Lkewfgd nq/kZVuk chek
¼la[;k½
Lsafox de fjyhQ
¼la[;k½
1998&99 57 & &
1999&00 217 954 &
2000&01 75 954 &
2001&02 607 3471 &
2002&03 977 11 &
2003&04 978 1235 430
2004&05 1043 3404 430
2005&06 947 4277 760](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-50-320.jpg)
![37
2006&07 1442 4356 760
2007&08 1471 5714 1208
2008&09 908 6131 1830
2009&10 1309 8848 1603
2010&11 645 10036 2054
2011&12 144 11675 1245
2012&13 412 10476 509
2013&14 382 13800 993
2014&15 436 10833 1180
2015&16 442 11027 1451
2016&17 410 11220 &
2017&18 608 11220 828
19- jktLFkku es oS/kkfud O;oLFkk
LorU=rk ds le; jktLFkku esa ekRL;dh fodkl dk dksbZ vfLrRo gh ugh FkkA
ml le; jkT;ksa ds LFkku ij 'kklu O;oLFkk izsflMsUlh vkSj jtokMksa es c¡Vh gqbZ
FkhA jktLFkku esa jtokM+ksa dk 'kklu FkkA bl dkj.k bafM;u fQ'kjht ,DV] 1897 ds
vUrxZr jktLFkku esa eRL;ks|ksx lEcU/kh ,DV o fu;e LorU=rk ds ckn gh cu ik;sA
;kstukdkjksa dh nwjnf'kZrk us bl jkT; ds le`) eRL; {ks=ksa ds laj{k.k o egŸo dks
igpkuk vkSj rRdky gh jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV 1953 ykxw dj fn;kA bl ,DV esa
fn;s x;as vf/kdkj ds vk/kkj ij jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl 1958 cuk, x,A
jktLFkku dh eRL; vkSj ekRL;dh ds oS/kkfud laj{k.k ds le>us ds fy, jkT;
ljdkj }kjk tkjh fd;s x, jktLFkku Hkw&jktLo vf/kfu;e 1956] jktLFkku bjhxs'ku
o Msªust ,DV 1954] jktLFkku iapk;rh jkt vf/kfu;e 1994 o jktLFkku jsxqys'ku
vkWQ cksfVx ,DV 1956 vkSj lEcfU/kr ,DV ds vUrxZr cuk;s x;s #Yl dks Hkh le>
ysuk vko’;d gSA
20- jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV] 1953
;g ,DV jktLFkku esa ekRL;dh dh lqj{kk] laj{k.k ,oa fodkl ds fy, cuk;k
x;k gSA bl esa dqy 14 /kkjk,a nh x;h gSA ;|fi /kkjk la[;k 14 dks 1957 es](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-51-320.jpg)
![38
foyksfir dj fn;k x;kA /kkjk la[;k 1 esa bldk uke vkSj rRdky izHkko ls lEiw.kZ
jkT; es ykxw fd;s tkus dh lwpuk nh xbZ gSA jkti= esa çdk'ku dh frfFk 12 vxLr
1953 ls ;g ,DV lEiw.kZ jktLFkku esa ykxw fd;k x;kkA /kkjk la[;k 2 esa fQ'k]
fQ'kjh vkWfQlj] fQf'kax vijk/k] fu/kkZfjr #Yl vkSj izkbZosV okVj dks ifjHkkf"kr
fd;k x;k gSA fQ'k es 'kSy fQ'k dks Hkh 'kkfey fd;k x;k gSA /kkjk 2¼ii½ ds vUrxZr
jkT; ljdkj us eRL; foHkkx ds fofHkUu Lrj ds vf/kdkfj;ksa dks fQ'kjht vkWfQlj
dh oS/kkfud 'kfDr;k¡ iznku dh gSA /kkjk la[;k 3 }kjk foLQksVd inkFkZ vkSj /kkjk
la[;k 4 esa fo"k] ykbZe ;k vU; fdlh fo"kSys inkFkZ ls eNyh ekjus dks izfrcfU/kr
fd;k x;k gSA ;|fi jkT; ljdkj dks /kkjk la[;k 4 dks fdlh {ks= esa fuyfEcr djus
dk vf/kdkj Hkh fn;k x;k gSA
/kkjk la[;k 5 esa jkT; ljdkj dks bl ,DV dh ikyukFkZ :Yl cukus dk
vf/kdkj fn;k x;k gSA ;g #Yl ;k bldk dksbZ Hkh Hkkx dks *izkbZosV okVj* ij ykxw
fd;s tkus ds fy, xtV uksfVfQds'ku tkjh djus dk vf/kdkj Hkh jkT; ljdkj dks
fn;k x;k gSA ekRL;dh fodkl esa fyftax ikfylh cukus ds fy, ;g /kkjk egŸoiw.kZ
LFkku j[krh gSA /kkjk la[;k 6 fQf'kax vFkkZr eRL;k[ksV dks izfrcfU/kr djrh gSA bl
/kkjk ds vuqlkj izkf/k—r vf/kdkjh ds ykbZlsUl tkjh fd;s ij gh fQf'kax dh vuqefr
dk izko/kku gSA /kkjk la[;k 7 esa jkT; ljdkj dks vf/klwpuk tkjh dj eNfy;ksa ds
cspku dks izfrcU/k djus vFkkZr fu"ks/k _rq ykxw djus dk vf/kdkj fn;k x;k gSA
/kkjk la[;k 8 es bl ,DV ;k #Yl ;k vkns'k ;k vf/klwpuk ds mYy?kau ij ltk dk
izko/kku fd;k x;kA buds igyh ckj mYy?kau ij vf/kdre 3 ekl ds dkjkokl ;k
500 #i;sa dk vFkZn.M+ vFkok nksuks dk dk izko/kku gSA tcfd ;gh vijk/k nqckjk
fd;s tkus ij vf/kdre ltk 6 ekl ds dkjkokl ;k 1000 #i;sa dk vFkZn.M+ vFkok
nksuks dk izko/kku fd;k x;k gSA
/kkjk la[;k 9 esa vijk/kh dks fcuk okjaV fxj¶rkj fd;s tkus dk vf/kdkj
iqfyl vkWfQlj ;k jkT; ljdkj }kjk ukfer vf/kdkjh dks fn;k x;k gSA /kkjk 10 esa
U;kf;d {ks= dks fn;k x;k gSA bl /kkjk vuqlkj izdj.k ij lquokbZ izFke Js.kh
eftLVªsV }kjk dh tkuh gS vkSj fQ'kjh vkWfQlj ;k mifujh{kd iqfyl ;k jkT;
ljdkj }kjk ukfer O;fDr dks dksVZ esa izdj.k is'k djus ds fy, vf/k—r fd;k x;k
gSA /kkjk la[;k 11 esa nh x;h vuqlwph ds vijk/kksa dks izkf/k—r vf/kdkjh }kjk
vf/kdre 100 #i;s dk tqekZuk yxkdj mYy?kau ds izdj.k dks dEikmUM vFkkZr
le>kSrk ;k {kek fd;s tkus dk izko/kku gSA bl voLFkk esa nks"kh o tCr lEifŸk dks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-52-320.jpg)
![39
Hkh eqDr dj fn;k tkrk gSA /kkjk la[;k esa 12 ,DV dh ikyuk djk;s tkus ds fy,
izkf/k—r O;fDr dks Hkkjrh; n.M+ lafgrk ds vUrxZr yksd lsod ekuk x;k gSA /kkjk
13 esa bl ,DV dh ikyuk djk;s tkus o lgk;rk djus okys O;fDr ds fo#} fdlh
izdkj ds dksVZ dsl fd;s tkus ls lqj{kk nh xbZ gSA
21- jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl] 1958
jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV 1953 dh /kkjk 5 esa nh xbZ 'kfDr ds vUrxZr jkT;
ljdkj }kjk jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl] 1958 tkjh fd;k x;kA izkjEHk esa bl #Yl esa
dqy 15 fu;e fn;s x;sA ysfdu fu;e la[;k 16 dks o"kZ 2003 esa vkSj fu;e la[;k
17 o 18 dks o"kZ 2010 esa 'kkfey fd;k x;k gSA fu;e la[;k 1 esa bl #Yl dk
VkbZVy fn;k x;k gS vkSj bls *izkbZosV okVj* dks NksM+dj lEiw.kZ jktLFkku easa rRdky
izHkko ls vFkkZr jkti= esa çdk'ku dh frfFk fnukad 11 flrEcj 1953 ls ykxw fd;k
x;kA fu;e al[;k 2 esa flQZ ,DV dks ifjHkkf"kr fd;k x;k gS vFkkZr ,DV dk
eryc jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV] 1953 gSA
fu;e la[;k 3 essa crk;k x;k gS fd fQ'kjht vkWfQlj }kjk bl #Yl esa fn;s
x;s QkeZ eas gh ykblsUl tkjh fd;s tk;xsA fu;e la[;k 4 esa ykblsUl Qhl dk
fu/kkZj.k bl izdkj ls fd;k x;k gS& ¼1½ izkjEHk es mifu;e 4-1 esa QkeZ uEcj 1 esa
lhtuy ykblsUl tkjh fd;s tkus dk izko/kku fd;k x;kA bl esa MªSx uSV o dkLV
uSV ds fy, lkykuk nj Øe'k% 50 #i;k o 35 #i;k fu/kkZfjr dh xbZA ijUrq 1991
esa bl mifu;e 4-1 dks foyksfir dj fn;k x;kA ¼2½ mifu;e 4-2 esa QkWeZ uEcj 2
es ,axfyaXl ds fy, jkWM vkSj ykbZu vkSj gSM+ykbZu ds mi;ksx gsrq Qhl dh njsa
fu/kkZfjr dh x;hA izkjEHk esa ;g Qhl ,d o"kZ] ,d ekl vkSj ,d fnol ds fy,
Øe'k% 12 #i;k] 4 #i;k vkSj 1 #i;k fu?kkZfjr dh x;hA bu njksa dks o"kZ 1981 esa
c<+kdj Øe'k% 60 #i;k] 20 #i;k vkSj 5 #i;k fd;k x;kA o"kZ 2003 esa fQj ls
bu njksa dks c<+kdj Øe'k% 300 #i;k] 50 #i;k vkSj 10 #i;k fd;k x;kA ¼3½
mifu;e 4-3 esa uhykeh@VsUMj esa izkIr mPpre cksyh@VsUMj dks Loh—r dj QkWeZ
uEcj 3 esa ykblsUl tkjh djus dk izko/kku fd;k x;kA
ty{ks= esa O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV ls jktLo] jkstxkj vkSj eNyh mRiknu
c<+kus dh izfØ;k dks fu;fU=r djus okyk fu;e la[;k 5 gh ,slk fu;e gS] tks lcls
vf/kd ckj la'kksf/kr fd;k x;k gSA ;g O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV ds fy, uhykeh@VsUMj
dh izfØ;k gS vkSj bls yhftax ikfylh Hkh dgk tkrk gSA izkjEHk esa bl fu;e esa nks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-53-320.jpg)
![40
mifu;e gh fn;s x;s FksA mifu;e 5¼,½ esa i'kqikyu funs'kd ;k mudsss }kjk ukfer
dks izR;sd o"kZ 1 vxLr dks uhykeh;ksX; ty{ks=ksa dh lwph cukus vkSj vko’;d
dk;Zokgh ds fy, vf/k—r fd;k x;kA funs'kd i'kqikyu dks mPpre cksyh Loh—r
djus vkSj QkWeZ uEcj 3 esa ykbZlsUl tkjh djus ds fy, vf/k—r fd;k x;kA
mifu;e 5¼ch½ esa cksyh dks vLoh—r djus dk vf/kdkj fn;k x;kA
fu;e la[;k 5 esa la'kks/ku dh 'kq#vkr o"kZ 1973 ls dh xbZA bl esa mifu;e
5¼,½ esa eRL; ikydks dh lgdkjh lfefr;ksa dks uhykeh esa 12-5% izkbZt fizQsjsUl nsus
dk izko/kku fd;k x;kA fQj bl #Yl es ,d ntZu ls Hkh vf/kd ckj la'kks/ku fd;s
x;sA ysfdu eq[; o [kkl ifjorZu o"kZ 1977] 1981] 1991] 1997] 2003] 2004 vkSj
2010 esa fd;s x;sA orZeku esa fu;e la[;k 5 dks 5 mifu;eksa esa ck¡Vk x;k gSA
mifu;e 5¼1½ esa eRL; foHkkx ds v/khu vkus okys ty{ks=ksa esa eRL;k[ksV ds Bsds dh
VsUMj@uhykeh dk;Zfof/k nh xbZ gSA blds vUrxZr ,d o"kZ ds fy, Bsds QkWeZ uEcj
3 esa vkSj 5 o"khZ; yht ij vkaoVu QkWeZ uEcj 3, esa ykblsUl tkjh fd;s tkrs gSA
mifu;e 5¼2½ esa eRL; foHkkx ds v/khu vkus okys tyk'k;ksa dks eRL; ikyd fodkl
vfHkdj.k dks izf'kf{kr eRL; —"kdksa dks QkWeZ uEcj 3ch esa nh/kZ vof/k vkaoVu gsrq
dk;Zfof/k nh xbZ gSA mifu;e 5¼3½ esa jktLFkku tutkfr {ksf=; fodkl lgdkjh la/k]
mn;iqj dks izFke 5 o"kZ ds fy, vf/kdre vkaoVu vof/k 25 o"kZ ds fy, tyk'k;
vkaoVu dh O;oLFkk dh xbZ gSA mifu;e 5¼4½ esa lh o Mh Js.kh ds tyk'k;ksa dks
eRL; cht dks fQaXjfyaXl voLFkk rd ikyu ds fy, vkaoVu dk izko/kku fd;k x;kA
jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl 1958 ds mifu;e 5¼5½ esa eRL; foHkkx ls iapk;rh
jkt laLFkkvksa dks gLrkukUrfjr tyk'k;ksa dks yhftax ij fn;s tkus dh dk;Zfof/k nh
x;h gSA bl mifu;e dks Hkh 3 miHkkxks esa ck¡Vk x;k gSA igys miHkkx esa ftyk
ifj'kn] iapk;r lfefr vkSj xzke iapk;r dks Øe'k% ch] lh o Mh Js.kh ds bu
gLrkukUrfjr tyk'k;ksa esa Bsds nsus dh dk;Zfof/k nh x;h gSA bu laLFkkvksa dks 5 o"khZ;
vof/k ds fy, tyk'k;ksa ds vkaoVu dk vf/kdkj fn;k x;kA lEcfU/kr iapk;rh jkt
laLFkk gLrkukUrfjr tyk'k;ksa esa QkWeZ uEcj 3, esa ykbZlsUl tkjh djrh gSA egŸoiw.kZ
rF; gS fd iapk;rh jkt vf/kfu;e o fu;e esa 50 ,dM+ flpkbZ {kerk ls de ds
xzkeh.k iks[kjks esa eNyh ikyu ds Bsds ij ;g mifu;e 5¼5½ ykxw ugh gksrk gSA
fu;e la[;k 6 esa VsUMj@uhykeh esa Qhl o vekur jk'kh tek djk;s tkus dh
dk;Zfof/k nh x;h gSA izkjEHk esa bl fu;e dks 2 mifu;eksa esa ck¡Vk x;kA ysfdu vc
;g fu;e 4 mifu;eksa esa foHkkftr fd;s x, gSA fu;e la[;k 7 esa ykbZlsUl dh](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-54-320.jpg)
![41
vof/k nh x;h gSA izkjEHk esa ykbZlsUl tkjh fd;s tkus dh frfFk ls vkxkeh 30 twu
rd dh vof/k fu/kkZfjr dh x;hA ysfdu o"kZ 1981 es ;g vof/k cny dj 15 twu
vkSj fQj o"kZ 1991 esa 31 ekpZ dj nh xbZA fu;e la[;k 8 esa Qhl ds fjQ.M fd;s
tkus ls lEcfU/kr gSA fu;e la[;k 9 esa ykbZlsUl ds [kks tkus ;k u’V gks tkus dh
n'kk es ek= ,d #i;k dh Qhl tek djk;s tkuas ij MqfIydsV ykbZlsUl tkjh fd;s
tkus dk izko/kku gSA fu;e la[;k 10 esa ykbZlsUl dh ‘'krsZ nh xbZ gSA orZeku es bl
fu;e esa 'krksZ dh la[;k dqy 4 gh gSA ysfdu ;g pkjksa 'krsZ Hkh vusd mi'krksZ esa
foHkkftr dh x;h gS A ftudk laf{kIr fooj.k uhps fn;k x;k gS &
'krZ la[;k 10¼1½ esa ykbZlsUlh }kjk Lo;a ;k mlds ,tsUV ;k ukWfeuh }kjk
eRL;k[ksV fd;k tkosxk vkSj blds fy, fQ'kjh vkWfQlj }kjk tkjh ijfeV ¼QkWeZ
uEcj 4½ ij fyf[kr vuqefr yh tkosxhA 'krZ la[;k 10¼2½ esa fQ'kjh vkWfQlj }kjk
vko’;drk vuqlkj muds Lo;a ;k izkf/k—r vf/kdkjh ds gLrk{kj;qDr ijfeV ¼QkWeZ
uEcj 4½ tkjh fd;s tkosxsA vke cksypky esa QkWeZ uEcj 4 dks yscj ijfeV dgk
tkrk gSA jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl 1958 esa 'krZ la[;k 10¼3½ vkSj 10¼4½ gh ,slh 'krsZ
gS] tks eRL;k[ksV ds nkSjku ty{ks= dh eRL; izkf.krk dks lh/ks gh izHkkfor djrh gSA
'krZ la[;k 10¼3½ esa VsUMj@uhykeh ¼QkWeZ uEcj 3½ ls fy;s x, ty{ks=ksa esa eRL;k[ksV
ds nkSjku dke es fy;s tkus okys fx;j vFkkZr og midj.k ftuls eNyh dks idM+k
tkrk gS] dk fooj.k fn;k x;k gSA blds vuqlkj ykbZlsUlh eRL;k[ksV esa vxzfyf[kr
izdkj ds fx;j dk mi;ksx gh djsxk& ¼,½ lHkh izdkj ds tky ftuds es'k ;k [kkus
dh lkbZt xk¡B ls xk¡B rd Ms<+ bUp ls de ugh gks vFkkZr dqy 6 bUp ls de dh
ugh gks o dkLV uSV dh es'k xk¡B ls xk¡B rd ,d bUp ls de ugh gks vFkkZr dqy
4 bUp ls de dh ugh gksA ¼ch½ ykWx ykbZu gqDl ds lkFkA bUgs vke cksypky esa
dk¡Vs&M+ksj dgk tkrk gSA ¼lh½ jkWM+ o ykbZu] ftls cU'kh Hkh dgk tkrk gSA vkSj ¼Mh½
Lih;j] bles Hkkys] rhj ;k vU; dksbZ uqfdyh oLrq ‘'kkfey dh tk ldrh gSA ysfdu
nks ckrsa Hkh /;ku es j[kuh gSA ,d rks ;g fd unh ;k ty/kkjk esa jkWM+ o ykbZu dks
NksM+dj fdlh Hkh fx;j dk mi;ksx iqy ds 200 xt ds Hkhrj ugh fd;k tkosxkA
nwljh ckr ;g fd izku ¼>haxk½ idM+us okys tky dk mi;ksx fQ'kjh vkWfQlj dh
vuqefr ds fcuk ugh fd;k tkosxkA Hkys gh foxr 60 o"kksZ esa jktLFkku fQ'kjht
#Yl 1958 dks yxHkx ,d ntZu ls vf/kd ckj jktdh; xtV tkjh dj la'kksf/kr
fd;k x;k gSA ysfdu bl 'krZ la[;k 10¼3½ esa vHkh Hkh fczfV'k i)fr ds ek=d dks
eSfVªd i)fr esa ugh cnyk x;k gSA tcfd jktLFkku lfgr lEiw.kZ Hkkjr esa uki
tks[k dh eSfVªd i)fr gh ykxw gSA izkjEHk es “krZ la[;k 10¼3½¼,½ es jaxwu uSV ¼Qlyk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-55-320.jpg)
![42
tky½ ls eNyh idM+us ij izfrcU/k yxk;k x;k FkkA ysfdu o"kZ 1981 esa bl
izfrcU/k dks lekIr dj fn;k x;kA
eRL; izkf.krk ds laj{k.k esa egŸoiw.kZ fu;e la[;k 10¼4½ dks X;kjg miHkkxksa es
foHkkftr fd;k x;k gSA bu miHkkxks dk laf{kIr fuEu izdkj ls gS &
fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼i½ esa ykblsUlh }kjk fcuk fQ'kjh vkWfQlj dh vuqefr ds LVsd
uSV dks NksM+ dj fQDlM+ baftu yxkus ij izfrcU/k yxk;k x;k gSA fu;e la[;k
10¼4½¼ii½ esa izkjEHk esa ukS bUp yEckbZ ;k vk/kk lsj otu dh jksgw] dkyclw] ujsu]
dryk] egklhj o lWoy uked eNfy;ska ds idMus dks izfrcfU/kr fd;k x;kA vxj
;g fdLesa idM+ ess vk Hkh tkrh gS rks bUgs thfor gh okil ikuh esa NksM+k tk;xkA
26 vxLr 1981 dks la'kksf/kr dj jksgw] ujsu] dryk o egklhj fdLeksa ds ,d fd-xzk-
ls de dh idM+us ij izfrcU/k yxk;k x;kA ysfdu blh o"kZ 11 fnlEcj 1981 dks
fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼ii½ dks la'kksf/kr dj jksgw o ujsu fdLes 500 xzke ls de vkSj
dryk o egklhj ,d fd-xzk- ls de dh idM+us ij izfrcU/k yxk;k x;kA o"kZ 1991
esa bl fu;e dks la'kksf/kr fd;k x;k vkSj jksgw] ujsu] dryk] egklhj] flYoj dkiZ o
xzkl dkiZ ds 500 ls de ds idM+us ij izfrcU/k yxk;k x;kA o"kZ 2003 es fu;e
la[;k 10¼4½¼ii½ dks bl izdkj ls izfrLFkkfir fd;k x;k& vuqKki=/kkjh jksgw] ujsu]
dryk] egklhj] flYoj dkiZ vkSj xzkl dkiZ fdLe dh 500 xzke ls de otu dh
fdlh eNyh dks ugh idM+sxkA ;fn idM+h tk;s arks mls ikuh esa rqjUr gh NksM+ fn;k
tkuk pkfg,A rnkfi vkikr ifjfLFkfr;ksas tSls ikuh ds lw[k tkus ;k tyLrj ds de
gks tkus] ftlls eNyh thou ij ladV mRiUu gks ;k fdlh chekjh ds laØe.k esa]
fun'kd eRL; ch] lh o Mh izoxZ ds tyk'k;ksa ds ekeys esa] Åij of.kZr fdLe dh
500 xzke ls de otu dh eNyh idM+us dh vuqefr fo'ks"k vuqKk ns ldrk gSA —
"kdksa dks vkaofVr tyk'k;ksa dh n'kk esa ,slh vuqKk] bl iz;kstu ds fy, funs'kd
eRL; }kjk izkf/k—r foHkkx ds flapkbZ foHkkx ls ty Lrj lEcU/kh rF;kRed fjiksZV
izkIr gksus ds i'pkr nh tk;sxhA
fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼iii½ esa ,axfyaXl ds ykbZlsUlh dks NksM+dj dj vU;
ykbZlsUlh dks eNyh idM+us ds izR;sd dSp ;kfu >ksy dk fu;fer fjdkMZ j[kuk
gksxk vkSj izR;sd 15 fnu esa bl fjdkMZ dh izfr QkWeZ uEcj 5 esa jftLVMZ Mkd ls
fHktokuh gksxhA vke cksypky esa QkWeZ uEcj 5 dks dSp LVsVesUV dgk tkrk gSA
fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼iv½ esa fdlh Hkh izdkj ds oSKkfud ;k vkfFkZd egŸo dk
vlk/kkj.k y{k.k /;kku esa vkus ij fudVorhZ eRL; dk;kZy; dks lwfpr fd;k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-56-320.jpg)
![43
tkosxkA fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼v½ es ykbZlsUlh /kkfeZd LFkku ;k ugkus ds ?kkV ij
eNyh ugh idMs+xkA fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼vi½ es ykbZlsUlh eNyh dks ges'kk <+d dj
ifjogu djsxk rkfd tuHkkouk dks Bsl ugh igqpsaA fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼vii½ es
ykbZlsUlh ds fdlh Hkh ljdkjh lEifŸk ds mi;ksx ij jksd yxkbZ x;h gSA fu;e
la[;k 10¼4½¼viii½ es ykbZlsUlh ds >qXxh] >ksaiM+h ;k dksbZ vU; <+k¡pk] rVcU/k vkfn
dk fuekZ.k fcuk fQ'kjh vkWfQlj dh vuqefr ds ugh djsxkA fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼ix½
es ykblsUlh ;k mlds ,tsUV dks a izkf/k—r O;fDr] ftls /kkjk 9 es fcuk okjaV
fxj¶rkj djus ds fy, vf/k—r fd;k x;k gS] ds ekaxus ij ykblsUl o ijfeV
fn[kkuk gksxkA o'kZ 1991 esa fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼x½ dks 'kkfey dj eNfy;ksa ds lq[kku
ij izfrcU/k yxk;k x;k vkSj o'kZ 2004 esa fu;e la[;k 10¼4½¼xi½ dks “kkfey dj
ykbZlsUlh ;k mlds ,tsUV }kjk ty esa fons'kh ekaxqj vkSj fcx gSM eNfy;ksa ds
lap;u ij izfrcU/k yxk;k x;kA
fu;e la[;k 11 fu"ks/k _rq ls lEcfU/kr gSA izkjEHk esa fnukad 1 tqykbZ ls 15
flrEcj rd fu"ks/k _rq ykxw dh xbZA bl vof/k esa eRL;k[ksV ij izfrcU/k yxk;k
x;kA ysfdu jkWM vkSj ykbZu vkSj gSM+ykbZu ls eRL;k[ksV dks bl izfrcU/k ls eqDr
j[kk x;kA lkFk gh jkT; ljdkj dks vf/klwpuk tkjh dj bl vof/k dks jkT; ds
fdlh Hkh fgLlsa esa ?kVkus dk vf/kdkj Hkh fn;k x;k gSA ysfdu 1981 esa la'kks/ku dj
fu"ks/k _rq dh vof/k 16 twu ls 31 vxLr dh x;h vkSj jkWM vkSj ykbZu vkSj
gSM+ykbZu ls eRL;k[ksV dks gVk dj iw.kZr;k eRL;k[ksV ij Loh—fr ij izfrcU/k yxk
fn;k x;kaA fu;e la[;k 12 esa fQDlM+ baftu dks vkSj fu;e la[;k 13 esa bu
fu;eksa ds mYy?kau ij midj.kksa dks tCr djus dk vf/kdkj fn;k x;k gSA pw¡fd
eNyh tYnh lM+us okyk inkFkZ gSA bl dkj.k tCr eNyh dks izfØ;k viukdj
uhykeh djus vkSj izkIr jk'kh dks jktdh; dks"k esa tek djkus dk vf/kdkj fn;k x;k
gSA fu;e la[;k 14 esa ykbZlsUlh ;k mlds ,tsUV }kjk ykbZlsUl dh fdlh Hkh 'krZ ds
mYy?kau ij fQ'kjh vkWfQlj }kjk ykbZlsUl dks fujLr djus dk vf/kdkj fn;k x;k
gSA ykbZlsUl dSfUly fd;s tkus ij tkjh ijfeV Lor% fujLr le>s tkrs gS vkSj
tek leLr jk'kh tCr dj yh tkrh gSA
fu;e la[;k 15 esa oSKkfyd dk;ksZ ls eRL; foHkkx ds vf/kdkjh o LVkQ fdlh
Hkh ty{ks= es] fdlh Hkh rjhds ls] fdlh Hkh le;] fdlh Hkh lkbZt dh vkSj fdlh Hkh
izdkj dh eNyh dks idM+ ldsxkA fu;e la[;k 16 dks o"kZ 1991 esa tksM+dj 500
xzke ls de otu dh drYkk] egklhj] jksgw] fexzy] xzkl dkiZ o flYoj dkiZ ds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-57-320.jpg)
![46
39 vkSjkbZ 600 300 32-1 107-1 53&170
40 ,yfu;k 600 300 65-5 218-3 160&277
41 Mk;k 500 250 29-6 118-4 104&144
42 ekepkjh 400 200 46-9 234-6 155&325
43 Lo#i lkxj 381 190-5 95-1 499-2 152&1154
44 lhyhls<+ 276 138 60-4 437-6 87&848
45 xksBjk 244 122 55-7 456-7 98&820
46 cj/kk 137 68-5 46-0 671-5 481&876
47 lqjokfu;k 100 50 12-3 246-7 160&340
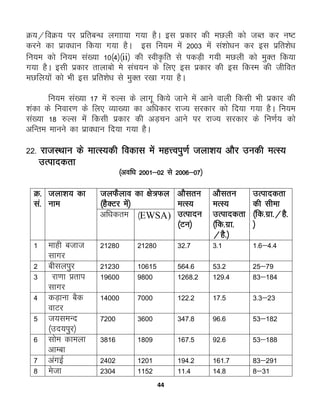
ftl ty{ks= esa O;kolkf;d vk/kkj ij eNyh mRiknu fd;k tkrk gS] mls
eRL; ty{ks= dgk tkrk gSA ml vuqdqyre ty {ks=Qy dks mRiknd ty
{ks=Qy vFkok izHkkoh ty{ks=Qy ¼EWSA = effective water spred area½ dgk
tkrk gS] tks mRiknd dks eNyh ikyu ls vko’;d vk; dh izkfIr djk dj o"kZ eas
iw.kZ le; dk;Zjr j[k ldsA bldh vko’;drk vkaoVu o yht fu/kkZj.k ds
lkFk&lkFk eRL; mRikfnrk] ty ifj"dj.k fØ;kvksa rFkk eRL; cht lap;u esa iM+rh
gSA
iw.kZ ty Hkjko ij 200 gSDVj ty QSyko ls vf/kd ds fLFkj ty{ks= dks
tyk'k; dgk tkrk gSA budk U;wure ty QSyko 40 gSDVj ls vf/kd gksrk gSA
;|fi vc vf/kdka'k tyk'k;ksa esa vusd dkj.kksa ls blls Hkh de ty QSyko dh
fLFkfr vkus yxh gSA eNyh mRiknu dh –f"V ls jktLFkku ds tyk'k;ks dks
fuEukafdr izdkj ls Js.kh—r fd;k tk ldrk gS &
o`gn ;k foLr`r tyk'k; %& jkT; esa bl Js.kh ds tyk'k;ksa ds uke gS & jk.kk
izrki lkxj] chlyiqj] ?kXxj fMizs'kUl o cksjksfiV~l] ekgh ctkt lkxj] dM+kuk cSd
okVj vkSj t;leUn ¼mn;iqj½A budk vf/kdre ty QSyko vkSj xgjkbZ Øe'k%
5000 gSDVj o 20 ehVj ls vf/kd gSA bu esa vksoj ¶yks dh fLFkfr cgqr de vk
ikrh gSA bu dk MSM LVksjst vf/kd gksrk gSA ykbo LVksjst {ks= esa isVk dk’r yxHkx
ugh gksrh gSA
e/;e tyk'k; %& jkT; easa bl izdkj ds tyk'k;ksa ds uke gS & ljnkjleUn]
tokbZ] ikoZrh lkxj ¼vaxkbZ½] estk] ljsjh] xEHkhjh] vkSjkbZ] jktleUn] xq<+k] xyok]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-60-320.jpg)
![47
ek'kh] eksjsy] dkyhfly] jkex<+] t;leUn ¼vyoj½ vkSj ckjSBkA buesa vf/kdre ty
QSyko o ty xgjkbZ Øe'k% 1 ls 5 gtkj gSDVj o 10 ehVj ls 20 ehVj rd gksrh
gSA vkerkSj ij buesa vksoj ¶yks dh fLFkfr 7 o"kZ esa ,d ckj gh vk ikrh gSA ;g
tyk'k; eq[;r% flapkbZ ds fy, gh cuk, x, gSA ugjksa ls ikuh fudy tkus ds ckn
ykbo LVksjst {ks= esa isVkdk’r Hkh gksrh gSA budk MSM LVksjst lkekU; gh gksrk gS] tks
eRL; lEink dks lqjf{kr j[ks esa i;kZIr gksrk gSA rnkfi flYV ds teko ls bl {ks=
esa deh gks tkuk vuqHko fd;k tk jgk gSA
lhekUr tyk'k; %& jkT; esa bl izdkj ds izeq[k tyk'k;ksa ds uke gS &
flyhls<+] eku ljksoj ¼vyoj½] lkse dkeyk vkEck] [kkjh] mEesn lkxj] tSriqjk]
cj/kk] nqxkjh] xksBjk] ikbZokykiqjk] cukfd;k] cksjnk] okWxu] jke lkxj] dkyk[kks]
lSaFky] Hk.M+kjh] Nhrksyh] NkijokM+k] cqpkjk] tokgj lkxj] dksVk cSjkt] Hkhe lkxj]
jk;iqj] eku ljksoj ¼lokbZ ek/kksiqj½] uhnM+] Hkxorx<+] txj] ikWpuk] eksguiqjk]
ekepkjh] pk¡nlsu] fdjkoy] osLV cukl] uekuk] mn; lkxj] ljtuk] cM+xk¡o] Qrsg
lkxj] fiNksyk vkSj tk[keA buesa vf/kdre ty QSyko o xgjkbZ Øe'k% 2 lkS ls
,d gtkj gSDVj rd o 10 ehVj ls de jgrh gSA vkerkSj ij buesa 5 o"kZ esa ,d ;k
nks ckj vksoj ¶Ykks dh fLFkfr tkrh gSA budk fuekZ.k flapkbZ ds fy, gh fd;k x;k
gSA bl dkj.k ugjksa ls vf/kdre ty fudklh dj yh tkrh gSA fQj Hkh MSM LVksjst
ij lkekU;r% 40 gSDVj rd ikuh QSyk jgrk gSA vlkekU; ifjfLFkfr;ksa vkSj flYV
tek gks tkus ds dkj.k buesa ls vf/kdka'k tyk'k;ksa ds lw[kus dh fLFkfr vk tkrh gS
vFkok lw[k gh tkrs gSA ijUrq izk—frd iztuu {ks=] isVkdk’r o ty xzg.k {ks= ls
mRiUu moZjrk vkSj dbZ vU; dkj.kksa ls buesa LFkkuh; eRL; izkf.krk cuh jgrh gSA
23- eRL;k[ksV ds lk/ku
'kkSfd;k vkSj O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV esa vUrj gksrk gSA eNyh idM+uk ekuo
dk 'kkSd Hkh jgk gS vkSj thou;kiu dk lk/ku HkhA ekuo lH;rk ds çkjfEHkd dky esa
eNyh dk f'kdkj ydM+h] iRFkj] rhj] Hkkys bR;kfn çkxSgkfrd gfFk;kjksa ls fd;k
tkrk FkkA vkt Hkh eNyh ds mFkys ty esa vk tkus vkSj dbZ vkfnoklh {ks=ksa easa
eNyh dk vk[ksV bUgha ls fd;k tkrk gSA T;kss&T;ksa ekuo dh Hkkstu dh lEcU/kh
vko’;drk,¡ c<+rh xbZ] bl dh iwfrZ ds fy, eNyh idM+us ds lk/kuksa esa Hkh mÙkjksÙkj
çxfr gksrh xbZA Ñf=e /kkxksa dh [kkst o bl ds O;kid mi;ksx ls eNyh ds tkyksa
ds fMtk;u o dk;Z{kerk esa ØkfUrdkjh lq/kkj gqvk gSA ijUrq vUr%LFkyh; eRL;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-61-320.jpg)
![48
ty{ks=ksa esa ç;qDr tkyksa ds fMtk;u esa lkeqfæd ekRL;dh dh vis{kk fodkl o lq/kkj
dh xfr dkQh de jgh gSA
O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV esa eNyh idM+us ds lk/kuksa dks vxzfyf[kr çdkj ls
oxhZÑr fd;k tk ldrk gS & ¼1½ eRL; Jfed vkSj ¼2½ eRL;kk[ksV ds midj.kA
eNyh idM+us ds midj.kksa dks vxzfyf[kr oxksZ esa j[kk tkrk gS& ¼1½ Øk¶V
(Crafts) vkSj ¼2½ fx;j (Gears)A eNyh ekjus esa ç;qDr midj.k ¼ fofHkUu çdkj ds
tky] dk¡Vs vkSj çkxSgkfrd gfFk;kj vkfn ½ dks fx;j vkSj bu midj.kksa dks dke esa
ysus okys ek/;e ¼fofHkUu çdkj dh ukosa] Mksafx;k¡] tgkt] joM+ dh V;wc] ydM+h ds
yës bR;kfn½ dks Øk¶V dgk tkrk gSA ;g nksuksa midj.k dk;Z ç.kkyh] mi;ksx o
fMtk;u esa fHkUu gSA ijUrq eNyh ekjus esa bu dk ,d lkFk mi;ksx fd;k tkuk
vko’;d gksrk gSA
jktLFkku esa gj çdkj ds ty{ks=ksa esa eRL; vf/kfu;e ds vUrxZr fcuk
vuqKki= ds eNyh idM+uk o ekjuk fu"ks/k gSA ijEijk ds #i eas Hkh fdlh dks eNyh
vk[ksV dk vf/kdkj ugh gSA futh ty{ks=ksa dks NksM+dj vU; ty{ks=ksa esa eRL; fu;e
ds vUrxZr mRikndksa dks eRL;k[ksV esa Hkkx ysus okys eRL; Jfedkasa dk ijfeV ysuk
iM+rk gSA bu ty{ks=ksa esas ç;qä fd, tkus okys tkyksa dh U;wure eS'k ckj fu/kkZfjr
gksus ls eRL; vf/kdkfj;ksa dk i;kZIr fu;a=.k jgrk gSA leLr çdkj dh ukoksa dks
ykblsUl tkjh djus dk vf/kdkj ifjogu foHkkx ds ikl gSA ijUrq o"kZ 1995&96 esa
jktLFkku ukS pkyu fofue; vf/kfu;e] 1956 dh /kkjk 3 o 7 ds micU/kksa esas NwV nsrs
gq, eNyh idM+us ds dke vkus okyh ukoksa ¼tks eksVj ukSdk u gks½ ds iathdj.k o
çek.k i= tkjh djus dk vf/kdkj eRL; foHkkx dks fn, x, gSA
24- Øk¶V
bu dk mi;ksx eRL; vk[ksV ds vfrfjDr ty ifjogu esa Hkh fd;k tkrk gSA
bUgsa pykus ds rjhds ds vk/kkj ij fuEukafdr nks Hkkxksa esa j[kk tkrk gS&
¼1½ ekuo 'kfä ls pfyr (Un-mechanised) % ;g midj.k pIiw ;k gok ls
Hkjh iky ls pyk, tkrs gSA fofHkUu çdkj dh ukosa] ukSdk] ydM+h ds yës] ck¡l ls cus
ctjs] gok ls Hkjh V;wc bR;kfn blh oxZ esa 'kkfey fd;s tkrs gSA vkerkSj ij](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-62-320.jpg)
![49
vUr%LFkyh; eRL; ty{ks=ksa esa bUgha midj.kksa dk lokZf/kd o O;kid mi;ksx fd;k
tkrk gSA
¼2½ bZ/ku ls pfyr (Mechanised) % ;g midj.k fdlh batu esa bZ/ku ds
}kjk pyk;s tkrs gSA batu dks midj.k ds ckgj (Out board) vFkok Hkhrj (In
board) dh vksj yxk;k tkrk gSA ikuh ds cM+s tgkt] eksVj cksV bR;kfn blh oxZ esa
'kkfey fd;s tkrs gSA
Øk¶V dks isans dh vkÑfr ij fuEu çdkj ls oxhZÑr fd;k tkrk gS&
fooj.k lery isank
(Flatten bottom)
xksy isank
(Rounded bottom)
uqdhyk isank
(Keeled bottom)
isank lery xksy uqfdyk
Xkfr /kheh /kheh rst
mi;ksx 'kkUr ekSle esa]
de xgjs ikuh esa
v'kkUr ekSle esa]
vf/kd xgjs ikuh esa
'kkUr ekSle esa]
vf/kd xgjs ikuh esa
fuekZ.k lkexzh ds vk/kkj ij ukoksa dks uhps fn;s vuqlkj oxhZÑr fd;k tk
ldrk gS &
1- ydM+h ls fufeZr & ukoksa ds fuekZ.k esa ydM+h dk mi;ksx lfn;ksa ls gksrk jgk gSA
Hkkjr esa ydfM+;ksa dh yxHkx 5000 ls Hkh vf/kd fdLesa ik;h tkrh gSA ijUrq buds
fuekZ.k esa yxHkx 200 fdLe dh ydfM+;k gh mi;ksxh ik;h x;h gSA vkerkSj ij
lkxoku] 'kh'ke] ccwy] vke o uhe dh fofHkUu fdLesa gh çeq[krk ls dke vkrh gSA
ukoksa ds fuekZ.k esa ydM+h ds fdLe ds p;u esa miyC/krk] etcwrh]
>Vdk o ruko lgus dh {kerk vkSj Qaxl] cSDVhfj;k o ,Yxh ds vkØe.k ls
çfrjks/kd {kerk dks /;ku esas j[kk tkrk gSA ;g lw[kus ij ueh lks[kus ij ugh Qwys
vkSj vkfFkZd –f"V ls Hkh ykHknk;d gksA
bl ds fuekZ.k esa ydM+h ds mi;ksx ls vxzfyf[kr ykHk gS & ¼1½ bu esa
vpkud >Vdk lgus dh 'kfä vkSj mRiykou {kerk vf/kd gksrh gS] ¼2½ ;g çpqj
ek=k esa loZ= miyC/k gks tkrh gS] ¼3½ bl ls fuekZ.k dk;Z ljy gksrk gS, vkSj ¼4½
bl ij tax ugh yxrk gSA
ydM+h ds mi;ksx ds nks"kksa dks vkxs crk;k x;k gS & bl esa ueh dks
lw[kus dh vf/kd {kerk gksus ls cukoV esa ifjorZu vk tkrk gS] ¼2½ bl ij Qaxl]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-63-320.jpg)
![50
cSDVhfj;k o ,Yxh dk vkØe.k 'kh?kz gksrk gS] ¼3½ bu esa dkcZfud inkFkZ dh vf/kd
ek=k esa gksus ls tYnh lM+ tkrh gS] vkSj ¼4½ fo'ks"k ns[k&js[k dh t#jr gksrh gSA
2- yksgs ls fufeZr& yksgk o fVu ls fufeZr ukoksa dks blh oxZ esa j[kk tkrk gSA fVu
o ydM+h ls cuh gqbZ ukosa Hkh bl essa 'kkfey dh tkrh gSA fVu ds mi;ksx ds dkj.k
vxzfyf[kr gksrs gS & ¼1½ bl esas fuekZ.k çfØ;k ljy vkSj de rduhdh dkS'ky dh
gksrh gS] ¼2½ ;s vis{kkÑr vf/kd etcwr o fVdkÅ gksrh gS] ¼3½ fuekZ.k çfØ;k ds
nkSjku lkexzh dk nq#i;ksx U;wure gksrk gS] vkSj ¼4½ bl ls cuh ukoksa esa vUnj o
ckgj nksuks vksj batu yxkus dh lqfo/kk jgrh gSA
bl lkexzh ds vxzfyf[kr nks"k Hkh gksrs gS & ¼1½ bl ij tax tYnh
yxrk gS] ¼2½ bl dh LisflfQd xzsfoVh 7-84 gksrh gS] tcfd ydM+h dh ek= 0-8 gh
gksrh gS] vkSj ¼3½ bl ls cuh ukoksa dh mfpr ns[k&Hkky dh t#jr gksrh gSA
3- QkbZcj Xykl ls fufeZr & lcls igys nf{k.k vÝhdk esa 1954 esa QkbZcj Xykl ls
ukoss cukbZ xbZA vkxs fn, dkj.kksa ls bl çdkj dh ukoksa dk çpyu c<+rk tk jgk gS
& ¼1½ ;s vf/kd fVdkÅ o gYdh gksrh gS] ¼2½ bu esa Ã/ku o j[k&j[kko dk O;; de
vkrk gS] ¼3½ bu esa batu vklkuh ls yxk;k tk ldrk gS] vkSj ¼4½ ;s tax] cSDVhfj;k
o ,Yxh ds çHkko ls eqä gksrh gSA
bu ds nks"k Hkh vkxs fn;s tk jgs gS & ¼1½ bu ij fuekZ.k O;; vf/kd
vkrk gS] rFkkfi vf/kd la[;k esa cukbZ tkus ij vis{kkÑr lLrh iM+rh gS] ¼2½ bu ds
fuekZ.k esa mPp rduhdh dkS'ky o lkexzh dh t#jr iM+rh gS] vkSj ¼3½ bu ds
fuekZ.k esa dke vkus okys feJ.k dks vius okLrfod #i esa vf/kd le; rd lqjf{kr
j[kus esa dfBukbZ vkrh gSA
jktLFkku esa O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV esa vf/kdrj ydM+h o fVu ls cuh
ukosa gh dke esa yh tkrh gSA bu dk Ýse ccwy ;k vke dh ydM+h vkSj eq[; <k¡pk
fVu dh píjksa ls cuk gksrk gSA bu dk isank lery gksrk gSA bUgsa pIiqvksa dh enn ls
pyk;k tkrk gS] tks ydM+h o ck¡l cus gksrs gSA bu dh Hkkj ogu {kerk vf/kd ugh
gksrh gSA thi] Vªd o VSªSDVj esa dke vkus okyh jcM+ V;wc esa gok Hkj dj Hkh eNyh
vk[ksV esa mi;ksx esa yh tkrh gSA jktLFkku ds cM+s tyk'k;ksa esa QkbZcj Xykl ls
fufeZr ukos batu dh enn ls pykbZ tk jgh gSA ;|fi bu dk eq[; mi;ksx eNyh
ds ifjogu esa gh fd;k tkrk gSA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-64-320.jpg)
![51
25- fx;j
bUgsa fuEufyf[kr nks oxksZ esa j[kk tkrk gS &
¼1½ fLFkj midj.k (Passive gears) % ;g ,d LFkku ij fLFkj jgrs gS vkSj eNyh
Lo;a vk dj bu esa Q¡l tkrh gSA fofHkUu fxy uSV~l] VªsIl o dk¡Vsa&Mksj blh oxZ ds
çeq[k mnkgj.k gSSA
¼2½ vfLFkj midj.k (Active gears) % ;g Lo;a vkxs c<+ dj eNyh dks ?ksj ysrs gSA
NUVs] pkSUnh o dkLV uSV~l bl oxZ ds çeq[k mnkgj.k gSA
Hkkjr ds vUr%LFkyh; ty{ks=ksa esa fofHkUu fdLe ds tkyksa ls eNyh
idM+h tkrh gSA ijUrq jktLFkku esa eNyh idM+us ds bu midj.kksa dh vR;Ur lhfer
fdLesa dke esa yh tkrh gSA
fLFkj] xgjs o tyh; ouLifr jfgr ty{ks=ksa esa fxy uSV~l (Gill
nets) dk mi;ksx O;kid rkSj ij fd;k tkrk gSA vkerkSj ij ty dh lrg ij rSjus
okys fxy uSV~l gh dke esa fy;s tkrs gSA bUgsa Qlyk tky Hkh dgk tkrk gSA ty
dh e/; lrg rd Mwc tkus okys fxy uSV~l Hkh dke esa fy;s tkrs gSA bUgasa MqxMqxh
tky dgk tkrk gSA
fdlh Hkh tky ds QUns dh xk¡B ls xk¡B rd dh yEckbZ dk eS'k ckj
(Mesh bar) vkSj nks xk¡Bksa dh dqy yEckbZ dks eS'k lkbZt (Mesh size) dgrs gSA
ftl bdkbZ Hkkj lewg dh eNfy;k¡ ty{ks= esa gksrh gS] mlh ds vuq:i eS'k lkbZt ds
fxy uSV~l dh O;oLFkk dh tkrh gSA
O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV esa flu uSV~l (Seine nets) ;k MªSx uSV~l
(Drag nets) dk Hkh mi;ksx cM+s iSekus ij fd;k tkrk gSA bu ds }kjk eNyh dks
?ksjdj ty ls ckgj ?klhV fy;k tkrk gSA bUgsa dke esa ysus ds fy, vf/kd eRL;
Jfedksa dh vko’;drk iM+rh gSA de tyh; ouLifr ;qDr mFkys ty{ks=ksa esa fdukjs
ij NUVk tky vkSj ty ds e/; ukoksa }kjk pkSUnh tky dk mi;ksx fd;k tkrk gSA
NUVk tky ds uhps ikdsV~l cuh gksrh gS] tc fd pkSUnh tky ds chp esa ,d yEch
lw¡M+ gksrh gSA igkM+h {ks=ksa esa lhi tky vkSj vojks/k jfgr ry ds tyk'k;ksa esa vklkeh
pkSUnh Hkh dke esa yh tkrh gSA ;s tky Mªsx uSV ds gh la'kksf/kr #i gSA ?klhVk tky](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-65-320.jpg)
![52
dks Hkh blh oxZ esa j[kk tkrk gS] ftl ds uhps dh vksj ikdsV~l ugh gksrh gSA bl
dk mi;ksx eRL; cht ,df=r djus easa fd;k tkrk gSA
Mªsx uSV ds lkFk&lkFk dHkh&dHkh fo'ks"k çdkj ds lgk;d tky Hkh
cka/k fn;s tkrs gS & ¼1½ yxHkx ,d ls Ms<+ ehVj pkSM+bZ ds rkju tky dks Mªsx usV
ds Åijh fljs ij cka/k fn;k tkrk gSA ;g Qlys tky gh gksrs gS] tks eq[; tky dks
vkxs ?klhVus ij ihNsa dh vksj QSy tkrs gSA bl tky ls eNfy;ksa dks mNyus ls
jksdus esa lgk;rk feyrh gSA ¼2½ NksVh lkbt o de bdkbZ Hkkj dh eNfy;ksa dks
idM+us ds fy, Mªsx usV ds Åijh fgLls ij NksVs [kkus dh tkyh dh ,d ls Ms<+
ehVj pkSMh ifê;k¡ fpidk nh tkrh gSA bUgsa volj vuqlkj rRdky vyx fd;k tk
ldrk gSA ;s tky icnk eNyh dks idM+us esa vR;f/kd lgk;d gksrs gSA
ufn;ksa o ÅFkys ty{ks=ksa esa eNyh vk[ksV esa dkLV usV (Cast nets) dk
mi;ksx Hkh fd;k tkrk gSA bu ls gj fdLe dh eNyh idM+h tk ldrh gSA ;|fi
pkjk eNyh vkSj o"kkZ&iwoZ feLVl fdLe dh eNfy;ksa dks idM+us esa vf/kd dke vkrk
gSA fcuk ikdsV~l o ikdsV~l ds dkLV usV Øe'k% tyh; ouLifr jfgr vkSj tyh;
ouLifr ;qä vlery ty{ks=ksa esa mi;ksxh jgrs gSA
dk¡Vk&Mksj ls eNyh idM+uk ,d vke ckr gSA bl dk mi;ksx
euksjatu rFkk O;kolkf;d eRL; vk[ksV esa O;kid rkSj ij fd;k tkrk gSA
O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV esa ,d eq[; Mksjh ¼ftls nke.k dgrs gS½ ij 1&1-5 ehVj dh
nwjh ij 0-2&0-4 ehVj yEch Mksfj;ka yVdkbZ tkrh gSA bu Mksfj;ksa ds fljksa ij 9 ;k
11 uEcj ds dk¡Vs yxs gksrs gSA bu dk¡Vksa ds fljksa ij pkjk eNyh ;k ek¡l dk VqdM+k
yxk;k tkrk gSA nke.k dh yEckbZ 500&600 ehVj rd gksrh gS vkSj bl ij ydM+h
dk VqdM+k] ,sjk uked tyh; ouLifr vFkok ¶yksV~l ck¡/k dj ty dh lrg ij
rSjk;k tkrk gSA dk¡Vs&Mksj dk mi;ksx eq[;r% tyh; ouLifr ;qä ty{ks=ksa esa fd;k
tkrk gSA bu ls Hk{kd fdLe dh yk¡ph] flaxkM+k] l¡oy bR;kfn eNfy;k¡ çeq[krk ls
idM+h tkrh gSA
tyh; ouLifr ls Hkjs iM+s ty{ks=ksa esa fMi usV (Dip net) ;k Ldwi
usV (Scoop net) dk dk Hkh mi;ksx fd;k tkrk gSA bls Vkik tky (Tapa jal) Hkh
dgk tkrk gSA jktLFkku esa O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV esa Vkik tky o fiatjksa (cages) dk
mi;ksx çfrcfU/kr gSA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-66-320.jpg)
![53
26-pêh tky
jktLFkku fQ'kjht #Yl] 1958 esa of.kZr fu;e la[;k 10 esa nh x;h 'krZ
la[;k 10¼3½ ds vuqlkj gh jktLFkku ds O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV esa dke es fy;s tkus
okys fx;j vFkkZr og midj.k ftuls eNyh dks idM+k tkrk gS] dk fooj.k fn;k
x;k gSA blds vuqlkj ykbZlsUlh eRL;k[ksV esa fuEufyf[kr izdkj ds fx;j dk
mi;ksx gh djsxk&
1. lHkh izdkj ds tky ftuds es'k ;k [kkus dh lkbZt xk¡B ls xk¡B rd Ms<+ bUp
ls de ugh gks vFkkZr dqy 6 bUp ls de dh ugh gks o dkLV uSV dh es'k
xk¡B ls xk¡B rd ,d bUp ls de ugh gks vFkkZr dqy 4 bUp ls de dh ugh
gksA
2. ykWx ykbZu gqDl ds lkFkA bUgs vke cksypky esa dk¡Vs&M+ksj dgk tkrk gSA
3. jkWM+ o ykbZu] ftls cU'kh Hkh dgk tkrk gSA
4. Lih;j] bles Hkkys] rhj ;k vU; dksbZ uqfdyh oLrq 'kkfey dh tk ldrh gSA
bu midj.kksa ds mi;ksx esa fuEufyf[kr nks ckrsa Hkh /;ku es j[kuh gksrh gS&
¼,½ unh ;k ty/kkjk esa jkWM+ o ykbZu dks NksM+dj fdlh Hkh fx;j dk mi;ksx iqy ds
200 xt ds Hkhrj ugh fd;k tkosxk] vkSj ¼ch½ izku ¼>haxk½ idM+us okys tky dk
mi;ksx fQ'kjh vkWfQlj dh vuqefr ds fcuk ugh fd;k tkosxkA
bu fu;eksa esaa ykblsUlh }kjk fcuk fQ'kjh vkWfQlj dh vuqefr ds LVsd uSV
dks NksM+ dj fQDlM+ baftu yxkus ij Hkh izfrcU/k yxk;k x;k gSA
tc eRL; >ksy esa fu;ekuqlkj idM+h tkus okyh eNfy;ksa esa deh vkus yxrh
gS vFkok ty{ks=Qy esa deh vk tkus ls lgtrk ls eNyh idM+us dh voLFkk vk
tkrh gSA ,slh fLFkfr es eRL; Jfed dke es fy, tkus okys tkyksa ds QUnksa ds eS'k
ckj dks de djds lh-ih-;w-bZ- c<+kus dk iz;kl djrk gSA ty{ks= dh mRikfnrk rFkk
Je fufof’V ds lEcU/k dks eRL; Je mRikfnrk vFkok lh-ih-;w-bZ- (C.P.U.E. = catch
per unit effort) dgrs gSA ;g izfr Jfed eNyh iSnkokj gS] ftls mRikfnrk izfr
Jfed esa O;Dr fd;k tkrk gSA ;g ,d vLFkkbZ lwpukad Hkh gS tks eRl;k[ksV ls
{ks=d esa eNyh dh fdlh fof'k"V fdLe dh vf/kdrk vkSj U;wurk dks n'kkZrk gSA ,slk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-67-320.jpg)
![54
ekuk tkrk gS fd dke es fy, tk jgs 10&15 izfr'kr fxy uSV~l vFkok Mªsx uSV ds
la'kksf/kr #i tSls NUVk tky ds fupys fgLls ;k pkSUnh tky ds fupys fgLls o lwaM
dh 10&15 izfr'kr Hkkx ds QUnksa dh eS'k ckj rhu pkSFkkbZ ls ,d bUp dh dj nh
tkos rks eRL; >ksy esa rqPN eNfy;ksa ds lkFk vU; eNfy;ksa dh NksVh lkbZt dh
ek=k c<+ tkrh gSA
jktLFkku ds O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV vkSj eRL; cht mRiknu dk;ksZ esa pV~Vh
tky vFkkZr ePNjnkuh ds diM+s ls cus tky dk mi;ksx fd;k tkrk gSA bldh eS'k
lkbZt 1@60 bUp vFkkZr ,d oxZ bUp esa 60 Nsn gksrh gSA oSls rks jktLFkku eRL;
fu;e 1958 es O;kolkf;d eRL;k[ksV ds tkyksa dh U;wure eS'k lkbZt fu/kkZfjr gksus
ds dkj.k pÍh tky dk mi;ksx QkeZ la[;k 3] 3¼,½ o 3¼ch½ esa tkjh fd;s x;s
vuqKki=/kkjh }kjk ugh fd;k tk ldrk gSA ysfdu mifu;e 5¼4½ ds vUrxZr tkjh
QkeZ uEcj 3¼lh½ esa tkjh lh o Mh Js.kh ds tyk'k;ksa esa eRL; cht dks fQaXjfyaXl
voLFkk rd ikyu ds fy, tkjh vuqKki=/kkjh }kjk eRL; cht fu"dklu ds fy,
fd;k tk ldrk gSA
ty{ks= es vkikr ifjfLFkfr;ksa esa eRL; cht ds fu"dklu vkSj pksjh fNis
feukst] rqPN eNfy;ka vkSj vU; eNfy;ks dh NksVh lkbZt dks idM+us ds fy, pV~Vh
tky dk mi;ksx fd;k tkrk gSA bl tky ds mi;ksx ls de xgjkbZ ds ty{ks= esa
ekStwn lkjh eNfy;ksa dk vk[ksV gks tkrk gSA lkFk gh blesa ekStwn tyh; dhM+s]
es<+d vkSj vU; tytho dks dkQh uqdlku gksrk gSA ;|fi vf/kd xgjkbZ ds
ty{ks=ksa esa lnhZ ds ekSle esa bl tky dk pksjh fNis mi;ksx dj feukst vFkkZr
tscjk] pnyk] fpyok o pky eNfy;ka vkSj rqPN eNfy;ka vFkkZr iqB`Bh] lqbZ;k]
[kjnk] lhlk] lkSyh] ?kksM+k o lqvk eNfy;ksa dks idM+k tkus dk iz;kl fd;k tkrk gSA
rktk o xhyh voLFkk esa bu eNfy;ksa dk cktkj es vf/kd ewY; ugh fey ikrk gSA
bl dkj.k bUgsa vukfFkZd ;k vuko';d eNfy;k¡ ekuh tkrh gSA ysfdu eNfy;ksa dh
;g fdLes lq[kk fn;s tkus ij vU; O;kolkf;d eNfy;ksa dh Hkakfr vf/kd ewY; ij
fcd tkrh gSA jktLFkku esa eNfy;ksa ds lq[kku ij izfrcU/k gksus ds dkj.k bu
eNfy;ksa dks xhyk gh vU; eNfy;ksa ds lkFk fNik dj jkT; ls ckgj Hkstk tkrk gSA
;g dk;Z lnhZ ds ekSle es gh fd;k tkuk ykHknk;d jgrk gSA vU; ekSle esa /kwi esa
lq[kkus ij bl fdLe dh vUr%LFkyh; eNfy;ksa ds nwf"kr gksus dh lEHkkouk jgrh gSA
;g nksuks dk;Z & pÍh dk mi;ksx vkSj vukfFkZd eNfy;ksa dk lq[kku & nh?kZdkyhu
ekRL;dh fodkl esa gkfudkjd jgrs gSA vr% bUgsa jksdus ds fy, eRL; foHkkx ges'kk
lrZdrk cjrrk gSA oSls jktLFkku fQ'kjht ,DV 1953 dh /kkjk 11 esa nh x;h](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-68-320.jpg)
![55
vf/klwph esa #Yl es fu/kkZfjr eS'k ls NksVh lkbZt dh eS'k ds tkyksa ls eRL;k[ksV dks
le>kSrk yk;d ekuk x;k gSA ijUrq eNyh dks lq[kkuk le>kSrk ;ksX; vijk/k ugh
gSA
jktLFkku eRL; fu;e] 1958 esa 'krZ la[;k 10¼3½ esa] dkLV uSV dh es'k xk¡B
ls xk¡B rd ,d bUp ls de ugh gks vFkkZr dqy 4 bUp ls de dh ugh gks] ds
mi;ksx dh vuqefr nh x;h gSA ?k?kfj;k ds vkdkj dk gksu ds dkj.k bls ?k?kfj;k
tky Hkh dgk tkrk gSA ;g tky ,d O;fDr }kjk vius dU/ksa o gkFkksa ds lgkjs dke
esa fy;k tkrk gSA eS'k ckj ds vk/kkj ij bl tky dks vxzfyf[kr rhu oxksZ esa j[kk
tkrk gS & ¼1½ [kkus dh lkbZt xk¡B ls xk¡B rd ,d ls M+s<+ bUp rd gks] rks bls
<Sb;k tky dgk tkrk gS] ¼2½ [kkus dh lkbZt xk¡B ls xk¡B rd vk/kk ls ,d bUp
rd gks] rks bls ckfj;k tky dgk tkrk gS] vkSj ¼3½ [kkus dh lkbZt xk¡B ls xk¡B
rd ,d pkSFkkbZ ls vk/kk bUp rd gks] rks bls drfj;k tky dgk tkrk gSA fQ'k
QkeksZ ij dke fy, tkus okys ?klhVk tkyks dks Hkh eS'k ds vk/kkj ij bUgh ukeksa
tkuk tkrk gSA oSls fQ'k QkWeksZ ij drfj;k lkbZt dk ÝkbZ DysD'ku uSV vFkkZr
?klhVk tky gh dke esa ysuk mfpr jgrk gSA ulZjh] fj;fjax vkSj vfHktud rkykcksa
esa pV~Vh tky dk mi;ksx gkuhdkjd jgrk gSA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalbookprint-201213173620/85/RAJSTHAN-PSC-FISHERIES-OBJECTIVE-69-320.jpg)