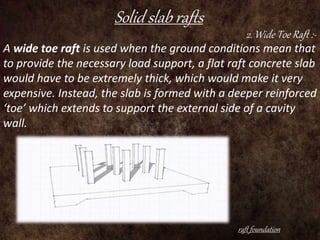
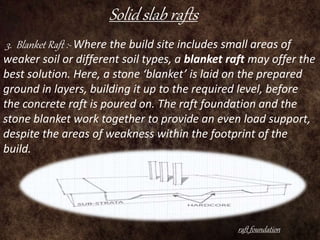
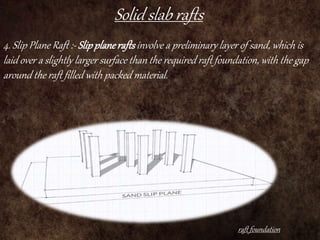
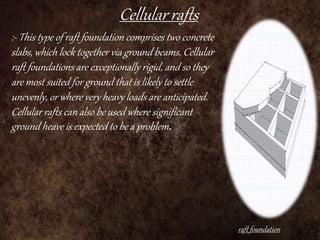
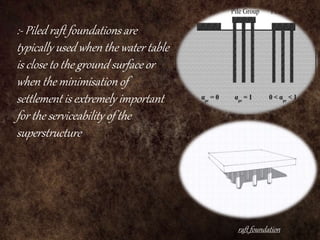
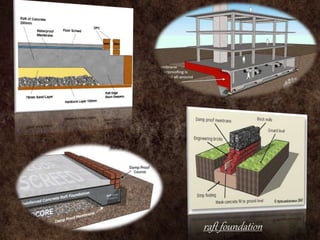
Raft foundations are concrete slabs that spread the load of a building evenly over a large area. They are often used when soil conditions are unstable or over 50% of the ground would need strip footings. There are different types including solid slab rafts, slab beam rafts, cellular rafts, piled rafts, and balancing rafts. Raft foundations are cheaper and easier to install than traditional footings and help reduce differential settlement. The main disadvantage is risk of edge erosion if not properly constructed.