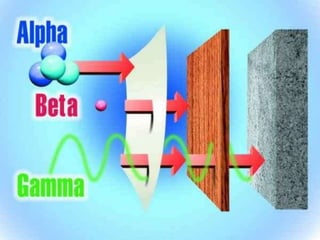
Radioactivity refers to the spontaneous emission of particles or electromagnetic radiation from unstable atomic nuclei during nuclear disintegration. It was discovered in 1898 by Henri Becquerel when uranium created an image on light-exposed film. Pierre and Marie Curie later coined the term radioactivity and studied it further. Radioactivity is important in medicine for imaging tumors and cancer treatment, and in science for determining the age of Earth and the universe, though it can be harmful or deadly in large amounts due to cell and tissue damage.