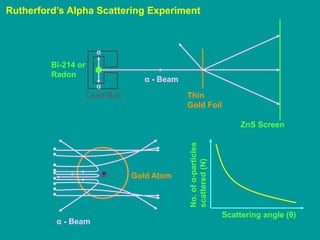
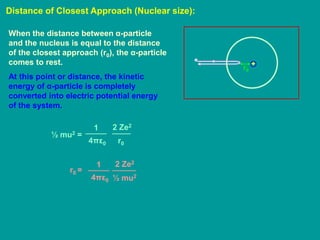
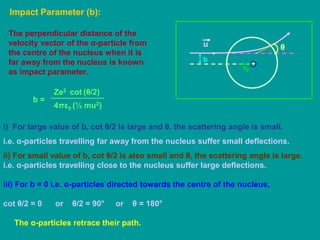
1. Rutherford's alpha scattering experiment showed that the positive charge and mass of an atom are concentrated in a tiny nucleus at the center. Some alpha particles were deflected through large angles, including backwards, indicating the presence of a dense, positively charged nucleus.
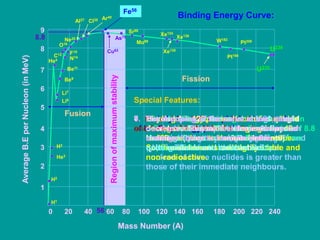
2. The binding energy curve shows that binding energy per nucleon initially rises rapidly then levels off at a maximum around iron before dropping again. Nuclides with binding energies close to the maximum are most stable.
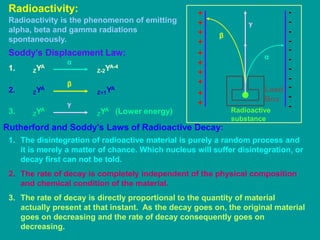
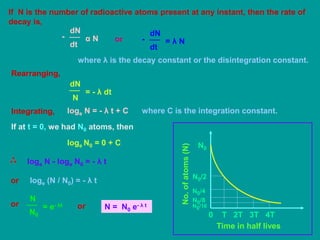
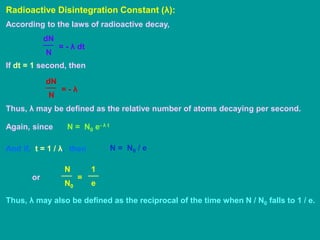
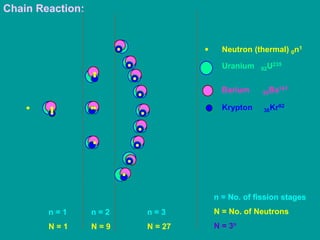
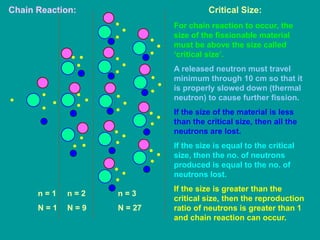
3. Radioactive decay follows predictable laws: the rate of decay is proportional to the amount of radioactive material and independent of conditions; decay occurs randomly between nuclei. Half-life is the time for half the nuclei to decay.






![Mass – Energy Relation:
According to Newton’s second law of motion, force acting on a body is
defined as the rate of change of momentum.
d
dt
F = (mv)
dv
dt
= m
dm
dt
+ v
If this force F displaces the body by a distance dx, its energy increases by
dv
dt
= m
dK = F.dx dx
dm
dt
+ v dx
dx
dt
= m
dK dv
dx
dt
+ v dm
= m v dv + v2 dm ………… (1)
dK
According to Einstein’s relation of relativistic mass,
m =
m0
[1 – (v2 / c2)]½](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicnucleus-220724151316-12039d2a/85/atomic_nucleus-ppt-10-320.jpg)

![Mass Defect:
It is the difference between the rest mass of the nucleus and the sum of the
masses of the nucleons composing a nucleus is known as mass defect.
Δm = [ Zmp + (A – Z) mn ] - M
Mass defect per nucleon is called packing fraction.
Binding Energy:
It is the energy required to break up a nucleus into its constituent parts and
place them at an infinite distance from one another.
B.E = Δm c2
Nuclear Forces:
They are the forces between p – p, p – n or n – n in the nucleus. They can be
explained by Meson Theory.
There are three kinds of mesons – positive (π+), negative (π-) and neutral (π0).
π+ and π- are 273 times heavier than an electron.
π0 is 264 times heavier than an electron.
Nucleons (protons and neutrons) are surrounded by mesons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicnucleus-220724151316-12039d2a/85/atomic_nucleus-ppt-12-320.jpg)