Embed presentation
Download to read offline

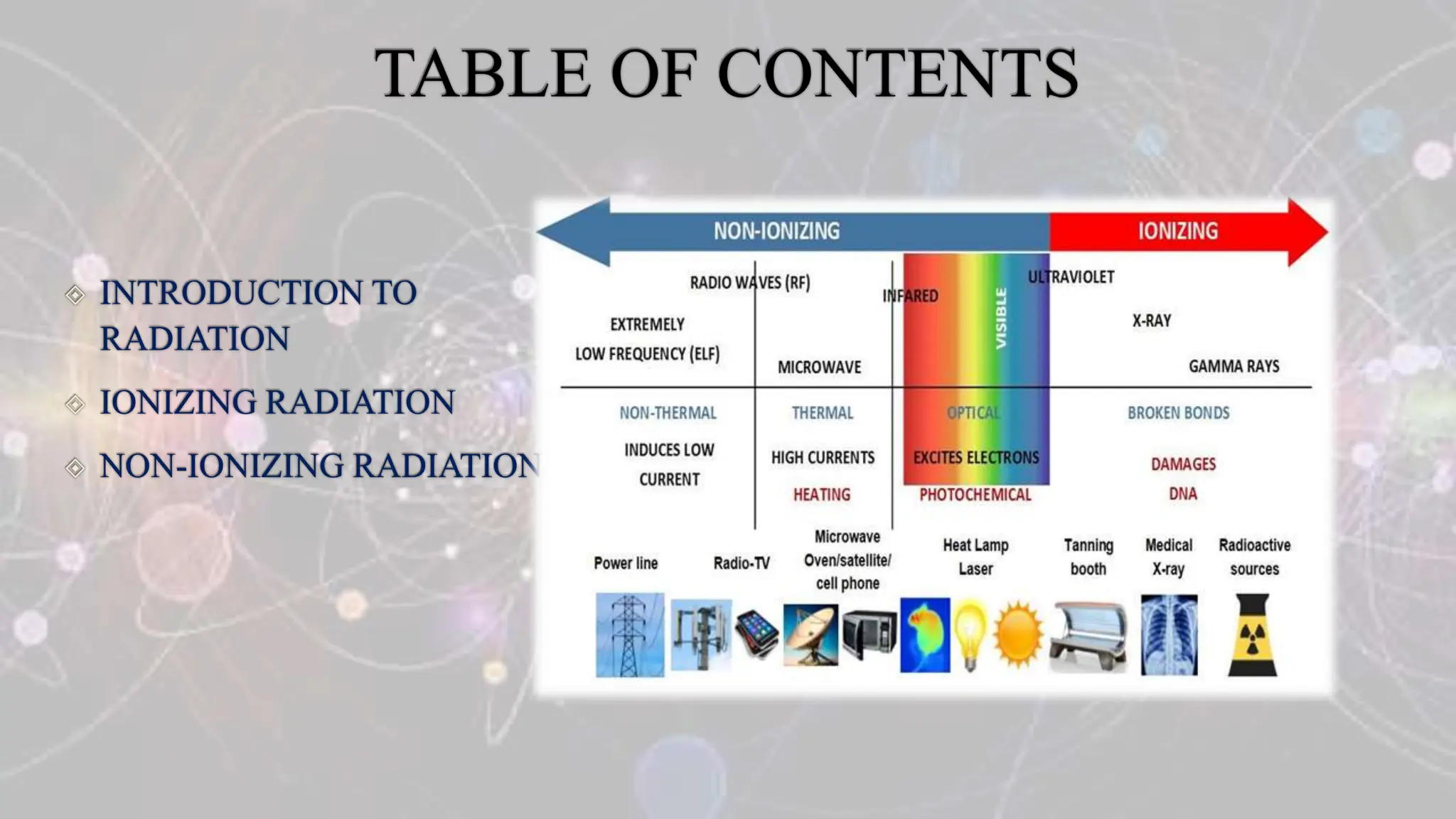

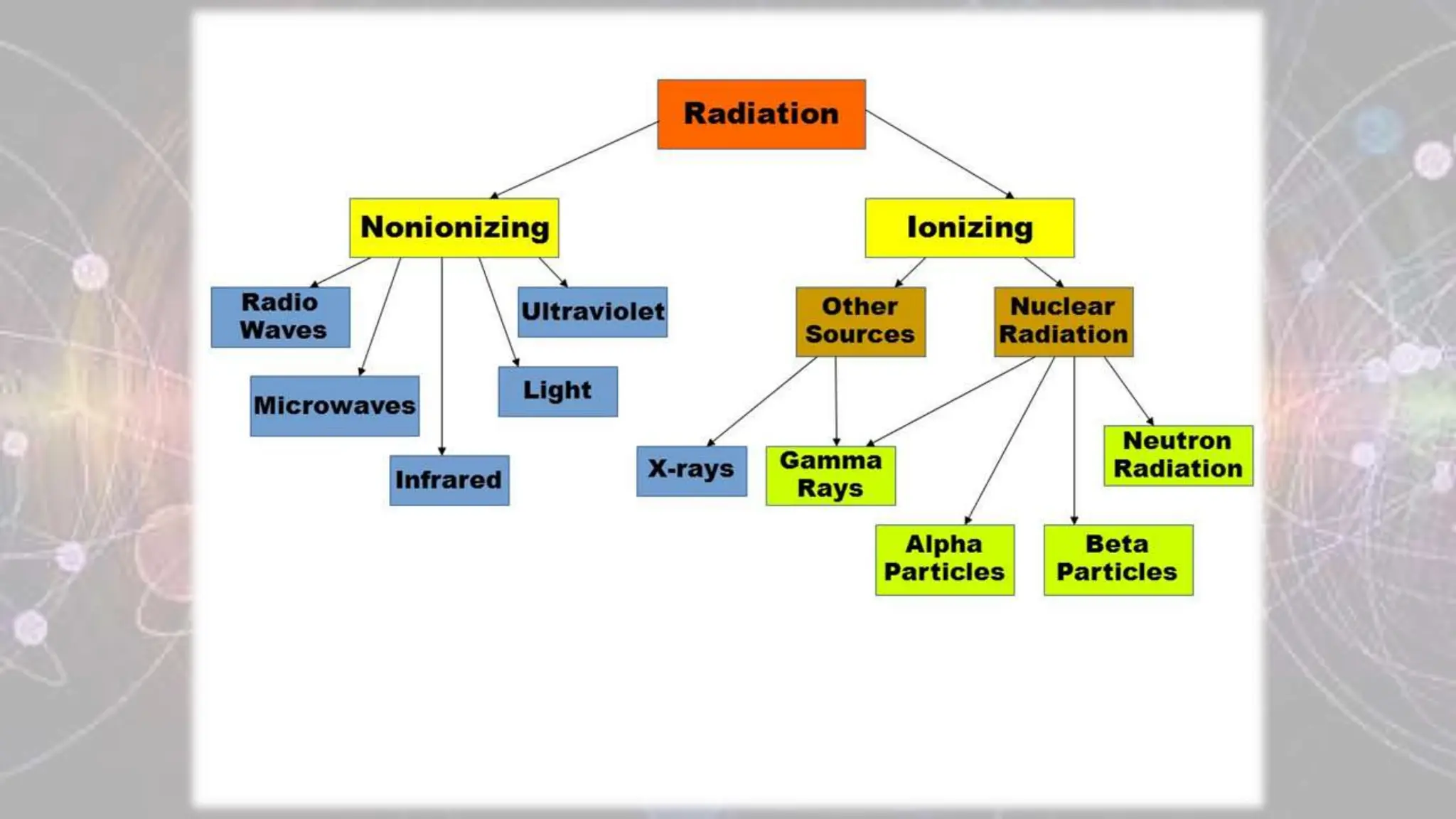




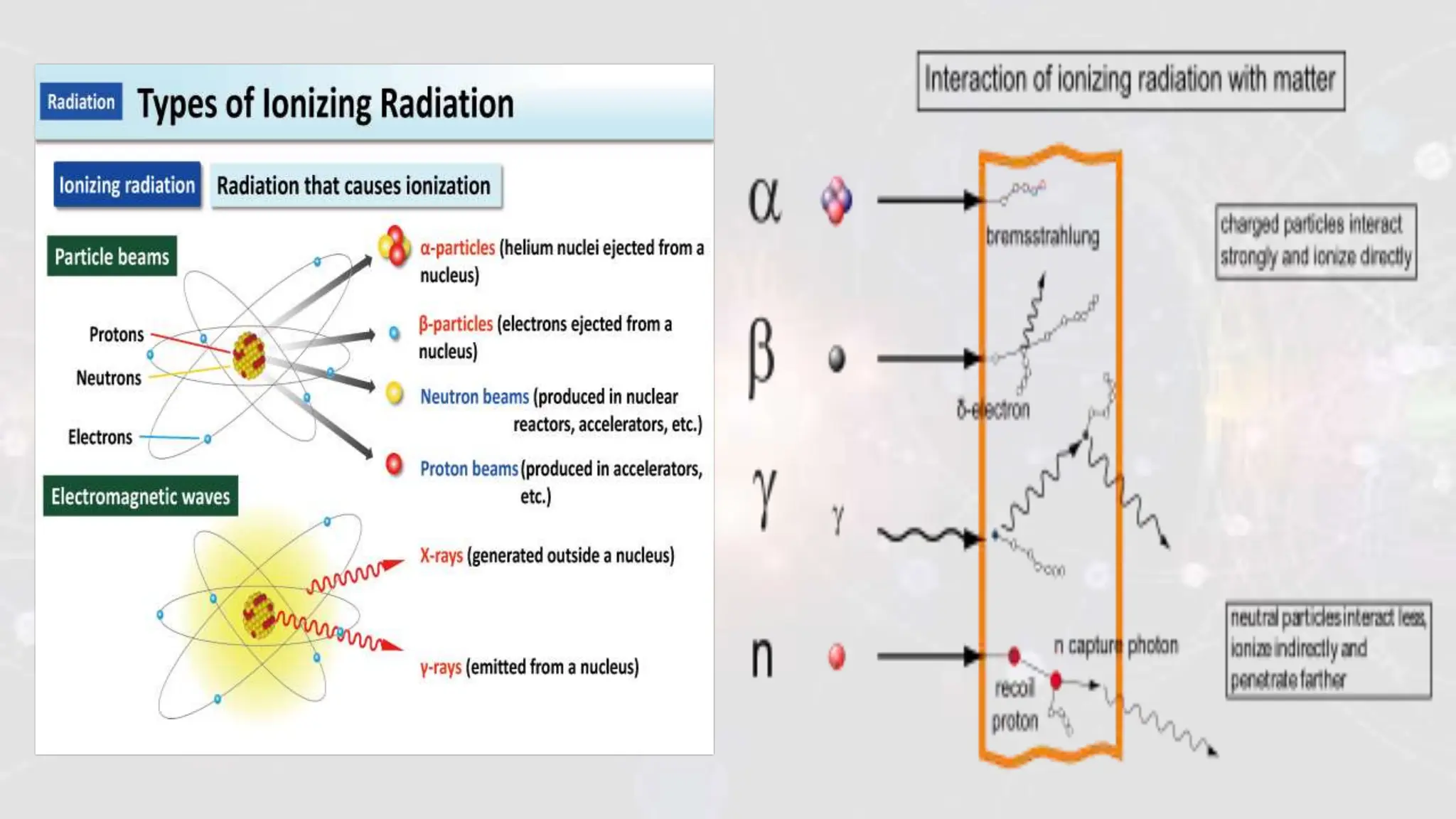




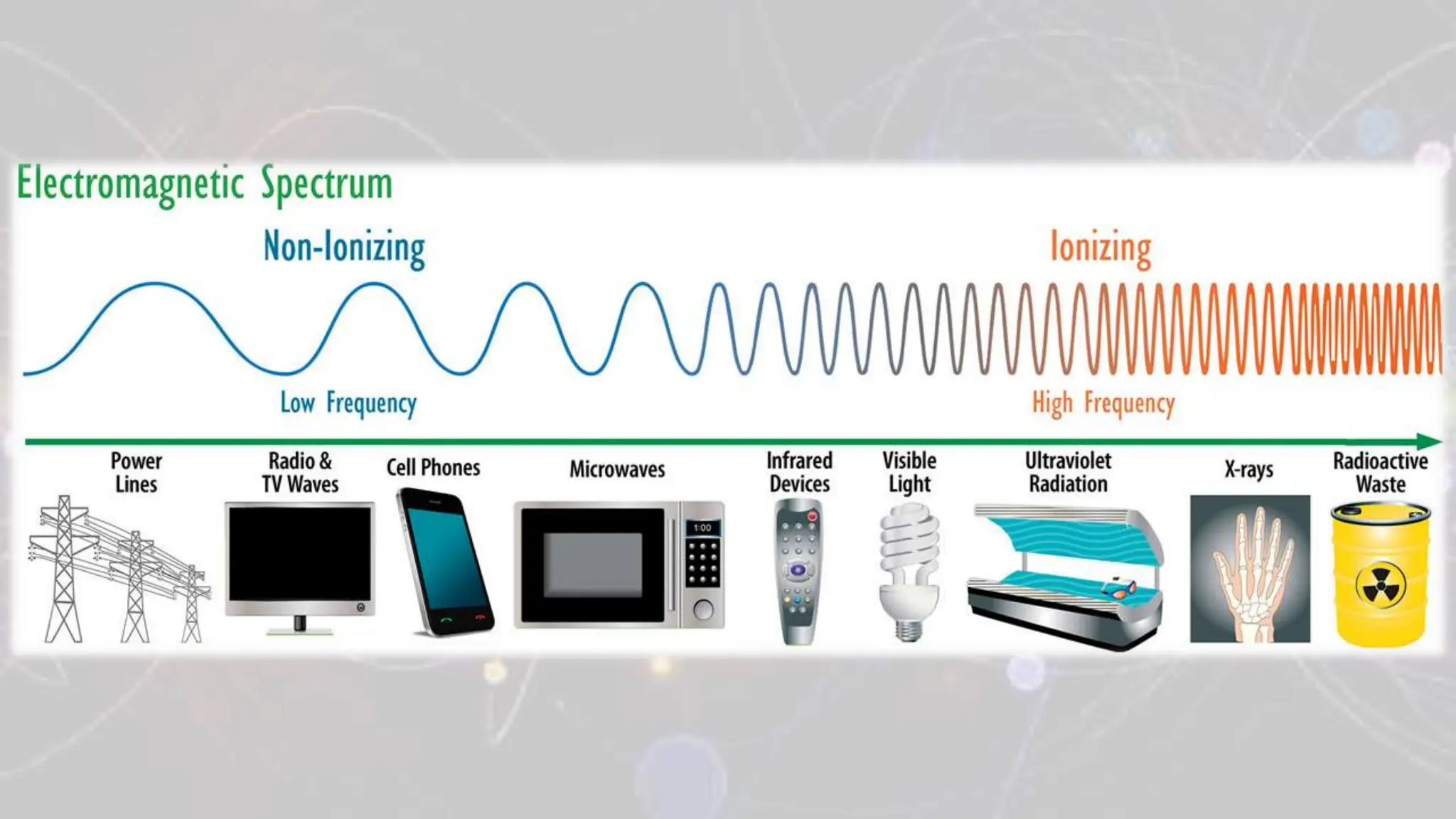


Ionizing radiation refers to radiation that has enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, resulting in the formation of charged particles (ions). This type of radiation carries enough energy to break chemical bonds and can cause damage to biological tissues. Examples of ionizing radiation include gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ionizing radiation can be classified into two types: electromagnetic radiation (such as gamma rays and X-rays) and particle radiation (such as alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons). Electromagnetic radiation travels in the form of waves and can penetrate through different materials to varying degrees based on their energy levels. Particle radiation consists of fast-moving particles that can be emitted from radioactive materials and can cause damage by colliding with atoms in tissues. Non-ionizing radiation, on the other hand, refers to radiation that does not have enough energy to remove electrons from atoms and does not produce ions. This type of radiation includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, and visible light. Non-ionizing radiation is generally considered less harmful to biological tissues compared to ionizing radiation, as it lacks the energy to cause direct damage to DNA and cells. While non-ionizing radiation is generally considered safe at typical levels of exposure, prolonged or intense exposure to certain sources of non-ionizing radiation, such as UV radiation from the sun or high-intensity electromagnetic fields, can have potential health effects. These effects range from skin burns and eye damage to an increased risk of certain types of cancer. It is important to understand the distinctions between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation and to take appropriate precautions to minimize exposure to potentially harmful forms of radiation. Protective measures may include using shielding materials, maintaining safe distances from radiation sources, and following safety guidelines and regulations in different settings where radiation is present.















