This document discusses the significance and various aspects of non-verbal communication, emphasizing that it comprises more than just words, with body language impacting audience perception significantly. It covers different types of non-verbal communication such as kinesics, oculesics, haptics, proxemics, and chronemics, detailing their roles in expressing emotions and interpersonal relationships. The document concludes by encouraging awareness and the application of positive body language to enhance communication effectiveness.

































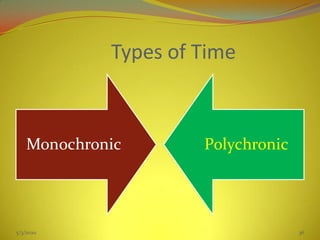
![Monochronic---- Polychronic
Time is money[scarce]
Do one thing at a time
Task oriented.
They scheduleall the
activities that start and
end at a certain time."[
Consider time
c0mmitments
(deadlines,schedules)
objectivesseriously
Time is flexible
Do many things
simultaneously.
Relation ship oriented.
Change plans often and
easily
Polychronic culture is
more focused on
relationships, rather
than watching the clock.
5/3/2020 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/manjula-non-verbalcommunication2-200503171953/85/R-Manjula-NON-VERBAL-COMMUNICATION-37-320.jpg)








![Self Assessment
Mark true or false to the followingquestions.
Youranswers will reflect your notions on body
language.
1. According to Albert Meherabian the impact of body language on
audience is 93% [ ]
2.Women have natural sensitivity towards body language than men.[ ]
3. Dishonest person maintain eye contact [ ]
4. Smoking a cigarette especiallybefore a interview indicates
nervousness [ ]
5. Showing your thumbs up indicates a success [ ]
5/3/2020 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/manjula-non-verbalcommunication2-200503171953/85/R-Manjula-NON-VERBAL-COMMUNICATION-46-320.jpg)
![ 6. Non verbal communication is anything except body language.[ ]
7.we have to maintain publicspace onlyonefoot distance. [ ]
8. Closed posturegivespositive impact on theaudience [ ]
9. Slouching is a close posture.[ ]
10.Proxemicsreferstothe studyof space [ ]
11.Theface is the most importantchannel of non –verbal
communication.[ ]
12.Monochromicpeoplemain punctuality[ ]
13. Metacommunication plays importantrole in presentation. [ ]
14. Peoplemaintain less distancewith theircloserone.[ ]
15. Polychronic cultured people like to do multiplethingsat the same
time.[ ]
5/3/2020 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/manjula-non-verbalcommunication2-200503171953/85/R-Manjula-NON-VERBAL-COMMUNICATION-47-320.jpg)
![ 16. Negative non verbal symbols like sadness, anger are more noticeable
than positive ones.[ ]
17. Thestudy of body movements , gestures and postures falls under the
category of Kinesics.
18. The term proxemics was coined by an anthropologist Edward Hall in
1960. [ ]
19. People like monotonous and weak voice [ ]
20. Looking at the ground during interviews is a good sign.[ ]
21. Sitting up straight is negative non-verbal symbol.[ ]
5/3/2020 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/manjula-non-verbalcommunication2-200503171953/85/R-Manjula-NON-VERBAL-COMMUNICATION-48-320.jpg)

