1) The document reviews a journal article that examines the effects of using short stories on non-English major university students' speaking and writing skills.
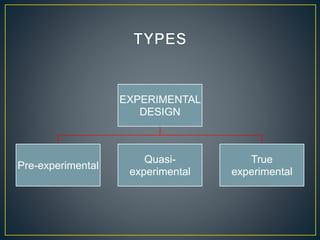
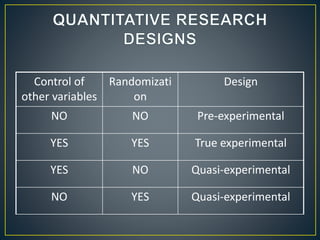
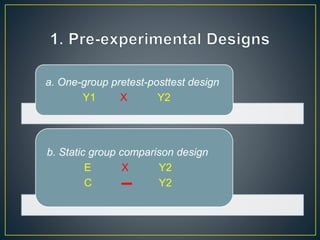
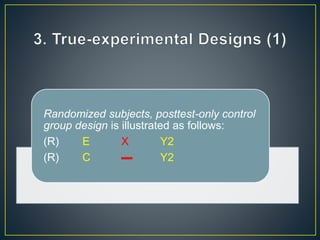
2) The study used a quasi-experimental design with 40 undergraduate students assigned to either an experiment group that learned with short stories or a control group.
3) Results found that using short stories for one semester improved students' speaking and writing abilities compared to the control group who did not use short stories.