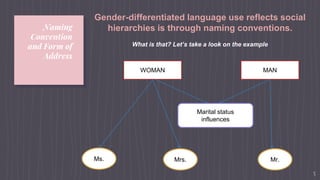
This document discusses language and gender. It defines gender as the socially constructed differences between women and men. Gender ideology refers to beliefs about appropriate gender roles and how ideology legitimizes inequality. Language shapes understanding of the social world and identities. Gender-differentiated language reflects social hierarchies, such as through naming conventions where marital status influences titles for women and men. A study found that female and younger male professors were referred to by first names while older male faculty were referred to by title and last name. The generic masculine pronoun "he" can refer to humans in general but really only refers to men. There are strategies to avoid the generic masculine like rewriting in plural or using "one." The document concludes it is important to understand gender