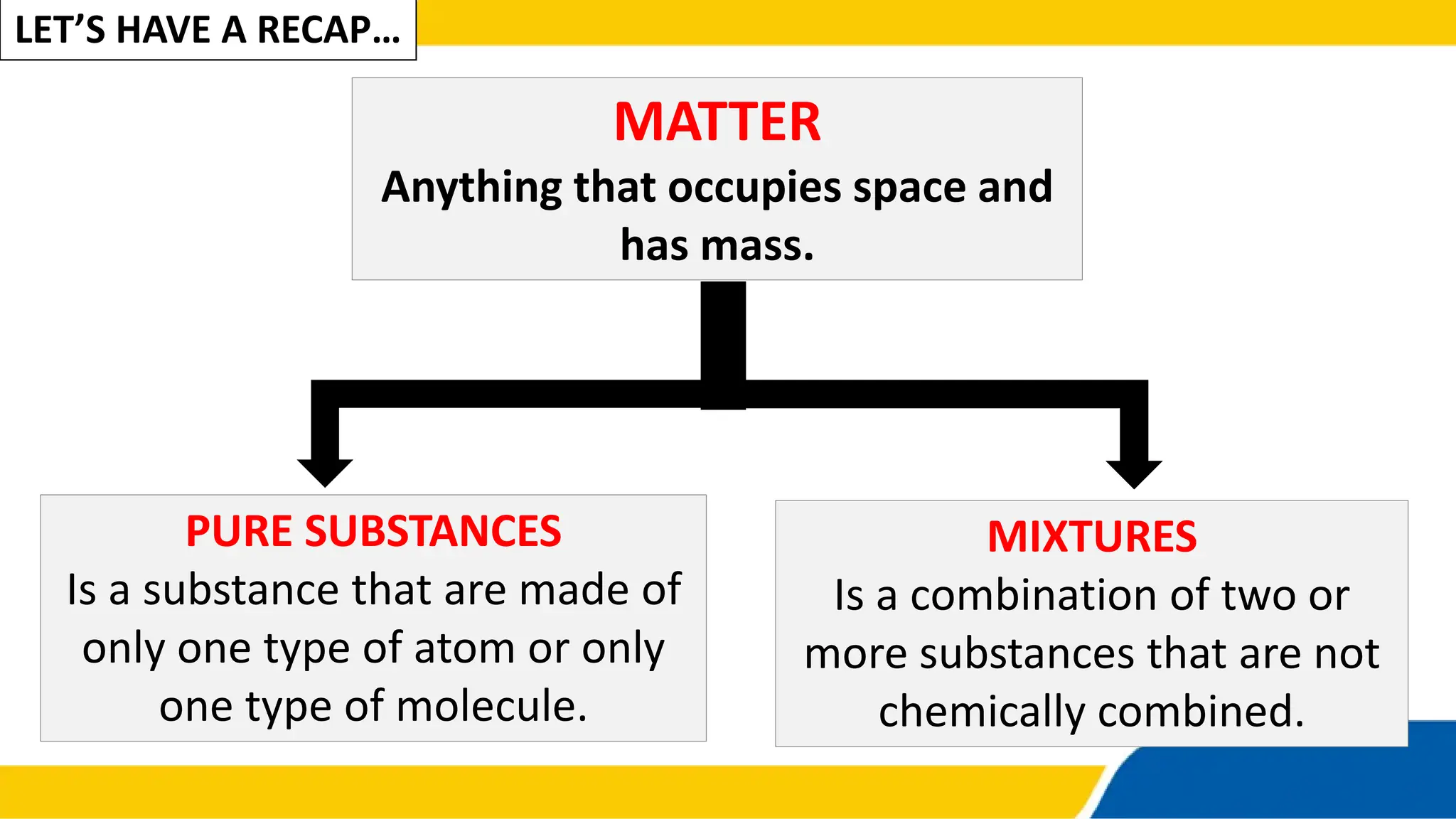
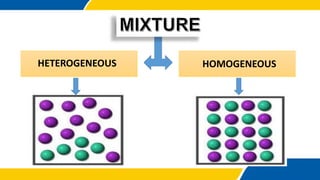
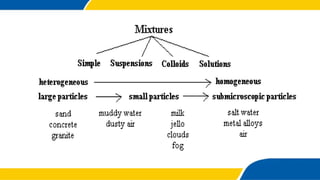
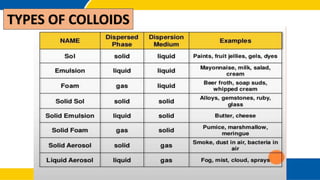
The document defines matter, pure substances, and mixtures. It explains that mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically combined and can be separated into their original substances. The document also discusses homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, and classifies mixtures as solutions, suspensions, or colloids based on particle size. Examples of each type of mixture are provided. Students are expected to learn to identify different types of mixtures and appreciate their importance.