Embed presentation
Downloaded 72 times


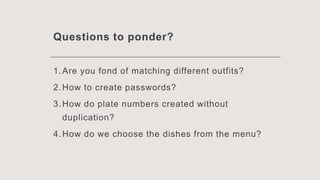

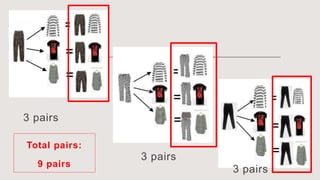


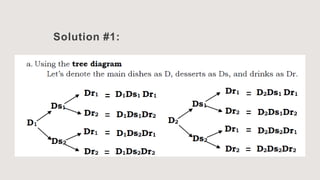


This document discusses permutation of distinguishable objects and provides examples. It introduces the topic with objectives around counting techniques and finding permutations. It then provides examples of counting outfit combinations and menu orderings. The fundamental counting principle is explained as the rule that if one event has m outcomes and a second has n outcomes, the total outcomes of both is m x n.










