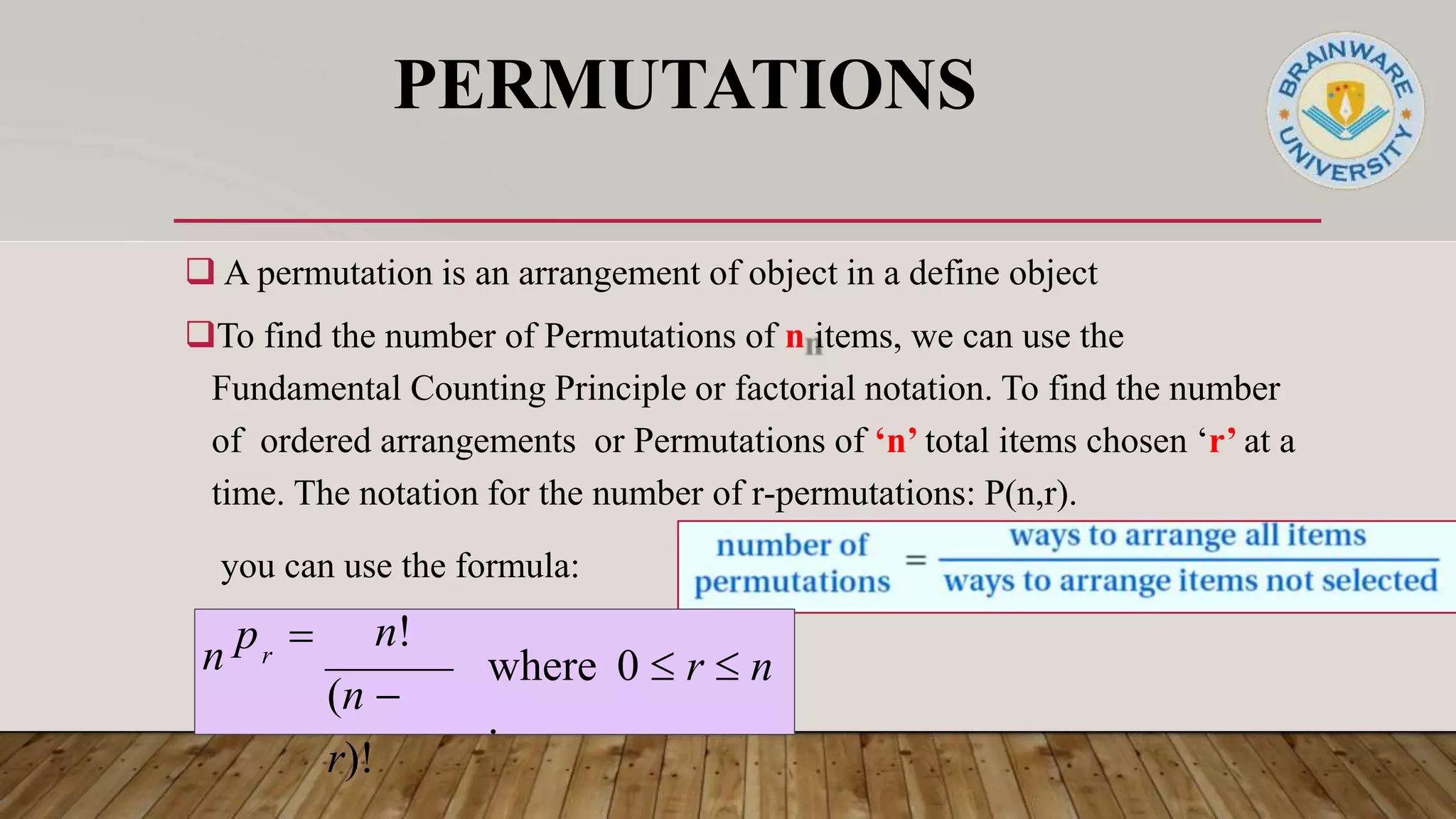
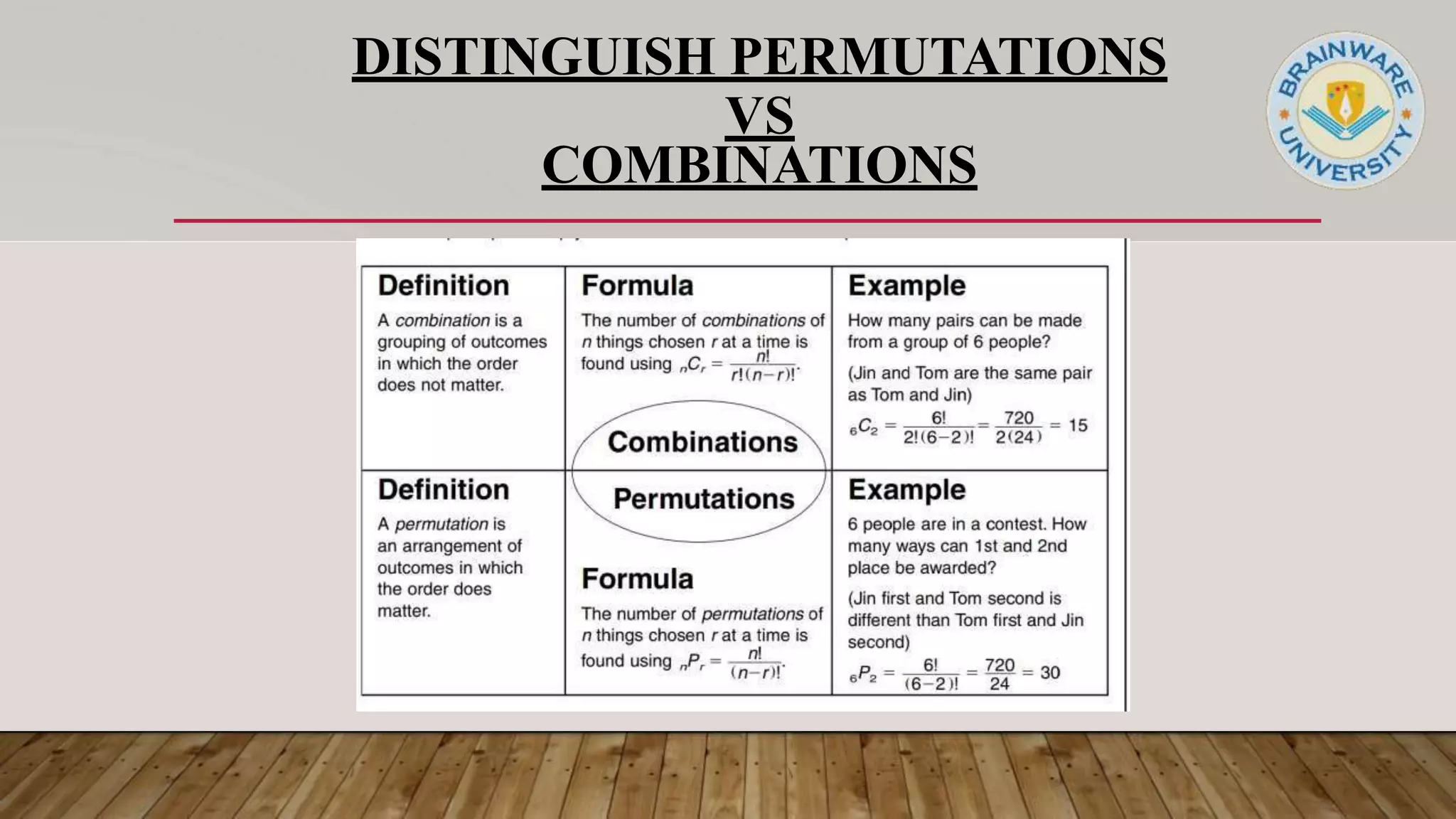
This document discusses permutations and combinations in discrete mathematics. It defines permutations as arrangements of objects that consider order, and combinations as selections of objects where order does not matter. The fundamental counting principle states that if one event has m outcomes and another n outcomes, the total outcomes of both is m x n. Permutations use factorials and combinations use factorials and binomial coefficients to calculate the number of arrangements and selections. The document provides examples of permutations, combinations, and distinguishes between them.