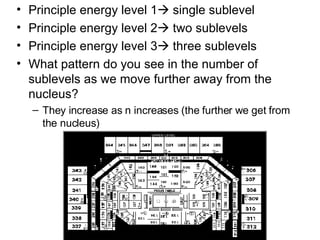
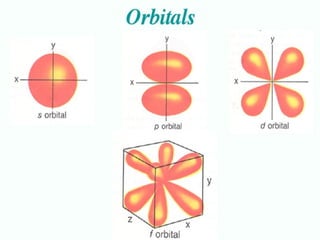
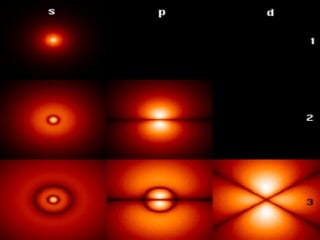
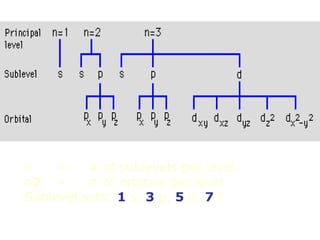
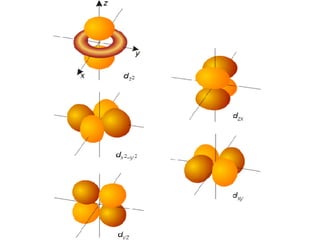
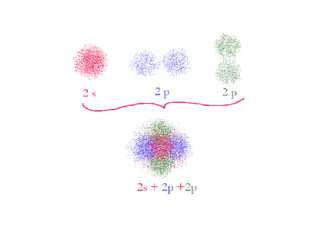
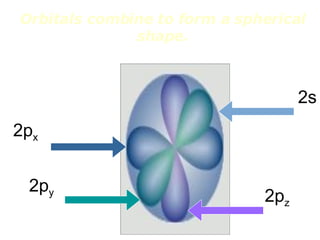
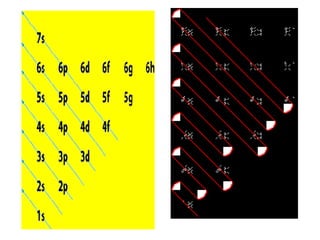
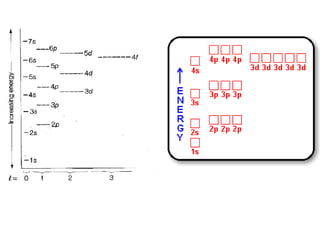
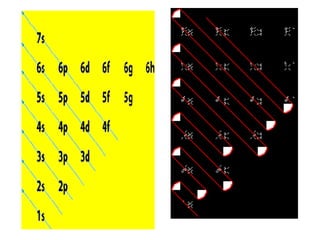
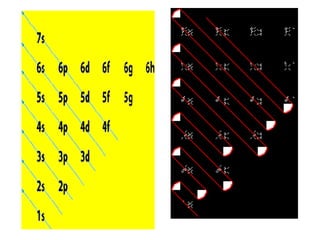
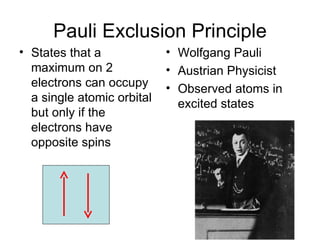
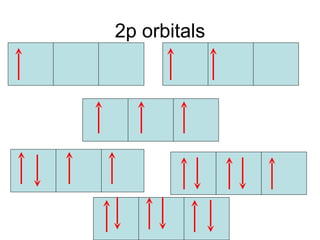
The four quantum numbers specify the location of electrons in an atom. The principal quantum number (n) determines the electron's energy level and orbital size. Higher n means a larger orbital farther from the nucleus, increasing the atom's energy. The angular momentum quantum number (l) corresponds to an orbital's subshell type (s, p, d, f). The third and fourth quantum numbers further specify an electron's orientation. Electrons fill atomic orbitals according to Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund's rule to achieve the lowest energy configuration.