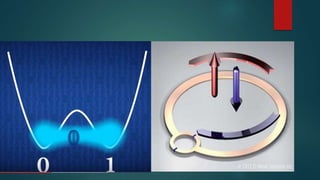
Quantum computing offers powerful solutions to problems that are intractable for classical computers. It uses quantum bits that can represent 0 and 1 simultaneously, exponentially increasing the number of possibilities. For example, a 500-qubit quantum computer could process more data than there are atoms in the observable universe. However, building useful quantum computers remains challenging due to issues like short qubit coherence times, high costs, and the difficulty of preventing quantum decoherence. Potential applications include optimization problems, machine learning, artificial intelligence, cryptography, and other areas that could benefit from quantum computing's speed.