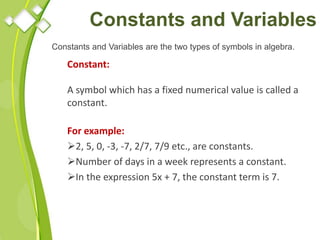
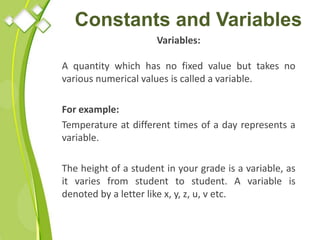
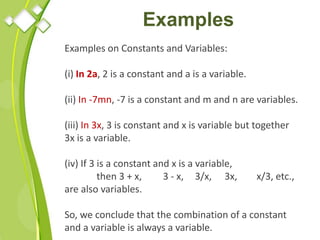
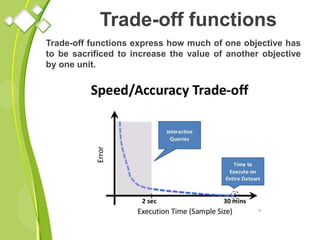
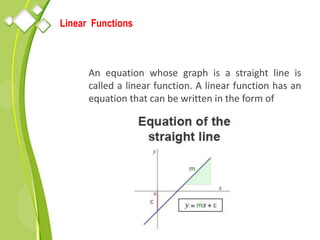
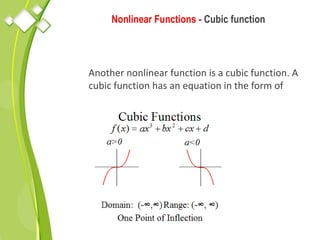
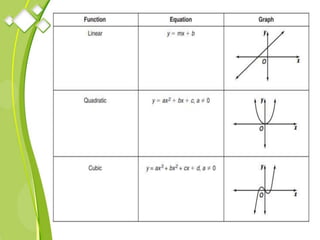
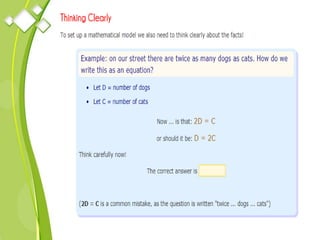
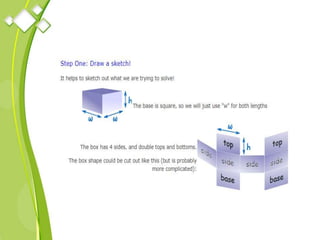
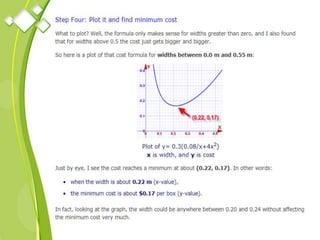
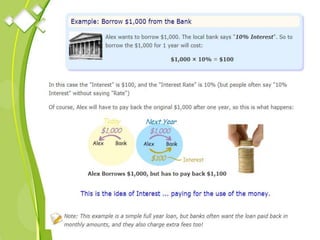
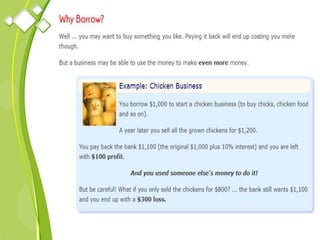
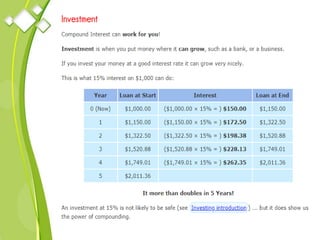
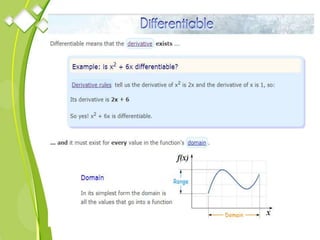
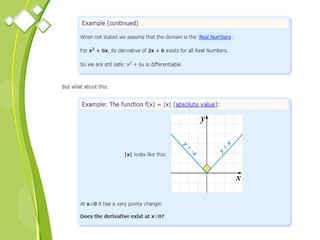
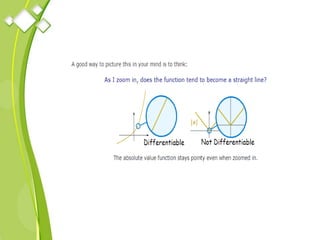
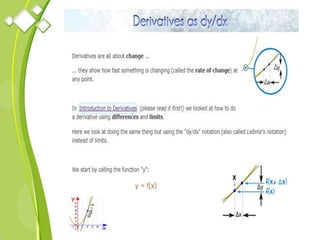
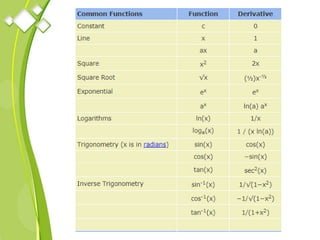
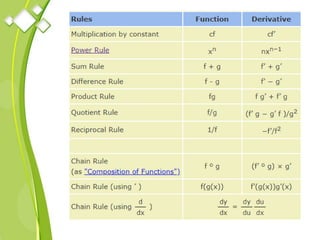
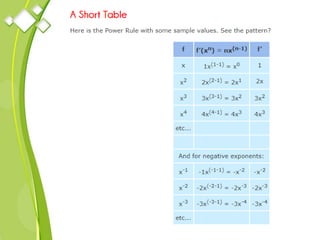
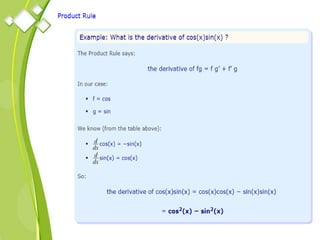
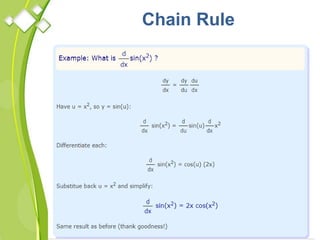
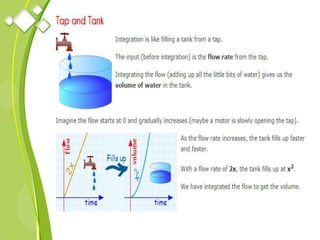
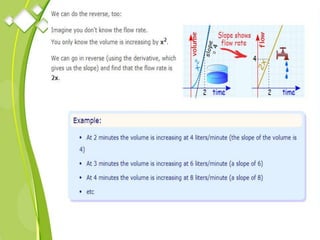
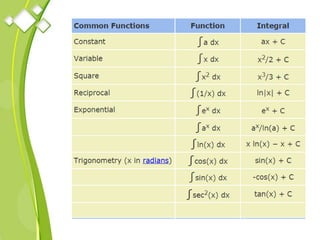
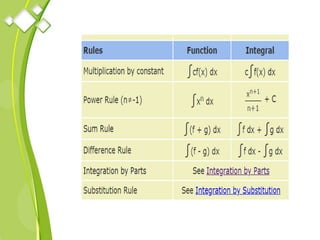
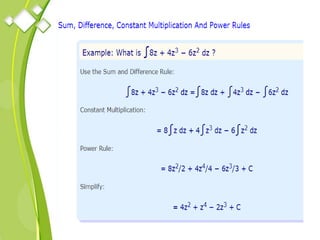
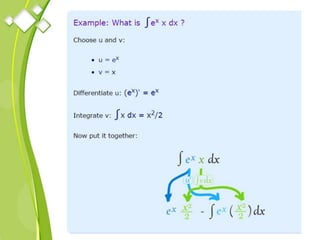
This document outlines the syllabus for a Quantitative Methods for Management course. The syllabus covers 5 units: (1) functions, mathematical models, differentiation, integration and optimization; (2) univariate and bivariate data analysis; (3) probability distributions and expected value; (4) index numbers and time series analysis; (5) hypothesis testing. 80% of exam questions will be problems and 20% will be theory-based. Key concepts covered include linear and nonlinear functions, mathematical modeling, differentiation, integration, probability distributions, hypothesis testing and index numbers. References for the course are also provided.