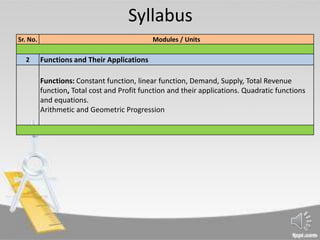
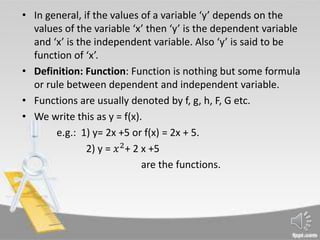
This document provides an introduction to functions and their applications in economics. It defines a function as a formula or rule relating a dependent variable to an independent variable. Some common types of functions are described, including constant functions where the dependent variable does not change (e.g. y=5), and linear functions which have the form of y=a+bx and graph as straight lines (e.g. y=6+3x). The document states that in economics, quantities like demand, supply, costs and revenues are modeled as variables that depend on other factors, and can thus be represented as functions.