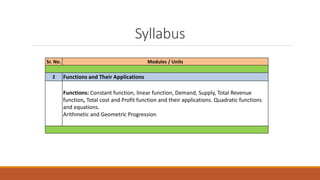
The document discusses functions and their applications in economics. It defines a function as a formula or rule relating a dependent variable to an independent variable. Some key function types discussed include:
1) Constant functions where the dependent variable is equal to a fixed constant value, regardless of the independent variable.
2) Linear functions where the dependent variable is equal to a constant plus the independent variable multiplied by another constant, forming a straight line graph.
3) Examples of demand, supply, total revenue, total cost, and profit functions are given, which are important in economics for showing how quantities vary with each other.