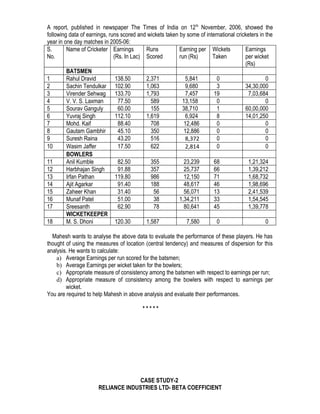
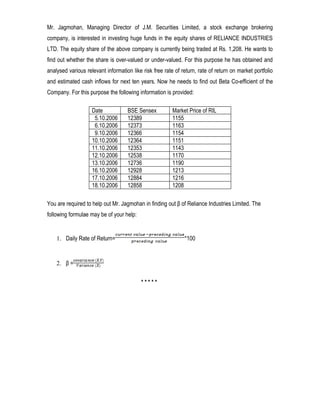
The document outlines the course plan for the Quantitative Techniques course at Punjab College of Technical Education. The course aims to teach students mathematical and statistical tools for business decision making. The syllabus covers topics like mathematics, statistics, probability, and hypothesis testing across 4 units. Case studies and assignments are included to apply the concepts to practical business situations. A lecture schedule with topics and assignment due dates is also provided.