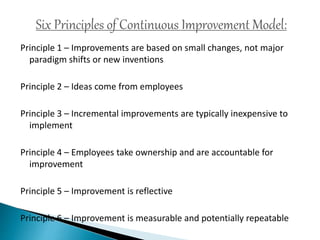
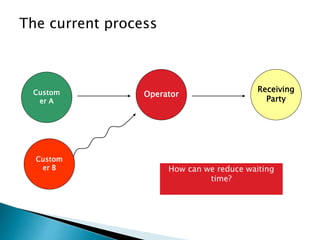
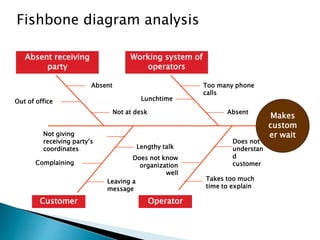
This document discusses quality management and continuous improvement. It defines quality as fitness for use and as a predictable degree of uniformity and dependability at low cost. Quality management aims to manage all organization aspects to meet customer needs. There are two aspects of quality - features that meet customer needs and freedom from trouble with fewer defects. Cost of quality includes prevention, appraisal, internal failure, external failure, and opportunity costs. The document outlines the history and key figures in quality management from 1900 to present. It discusses the elements of quality management including commitment, customer satisfaction, measurement, prevention, training, and continuous improvement.