1) The document discusses quality maintenance and provides definitions and implementation strategies for maintenance quality policies and objectives. It discusses preventing defects through quality control and quality assurance.
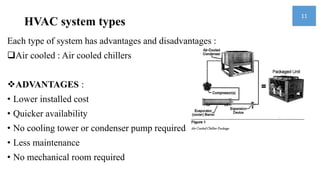
2) HVAC systems are described as important to provide healthy, comfortable conditions for occupants while reducing environmental impact. Different HVAC system types like air cooled and water cooled are outlined.
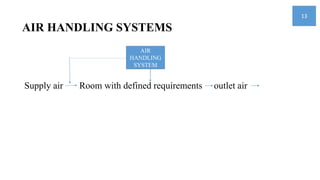
3) Components of air handling systems like fans, ducts, and pumps are explained in detail to understand their functions and potential problems. Maintaining quality is key to running operations with minimal breakdowns.