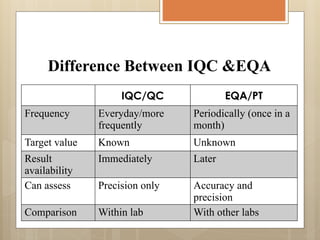
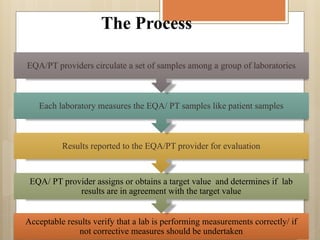
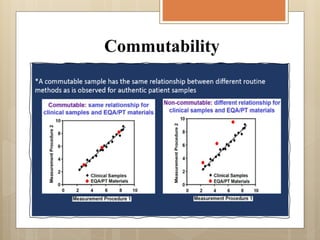
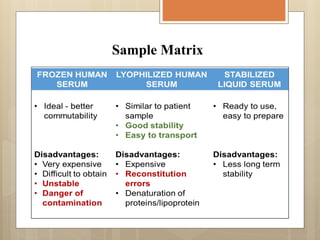
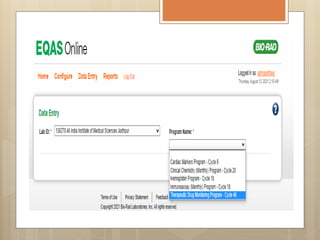
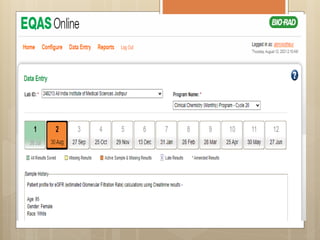
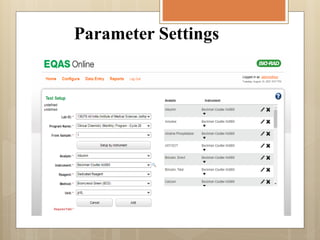
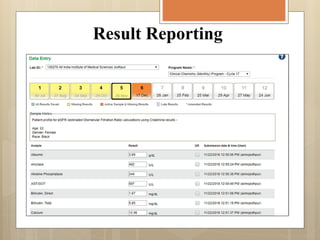
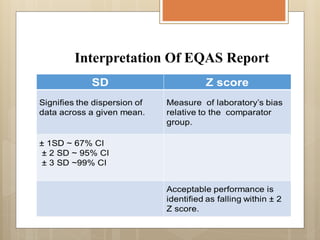
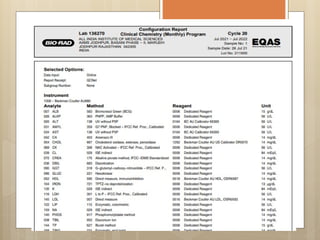
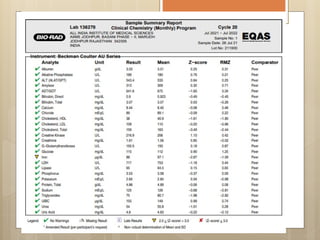
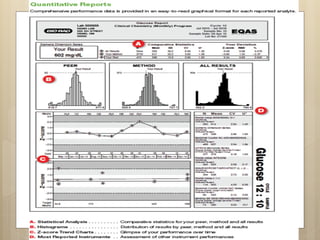
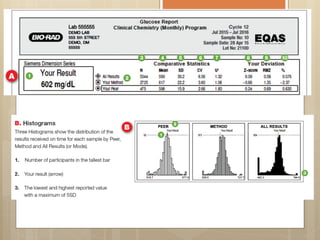
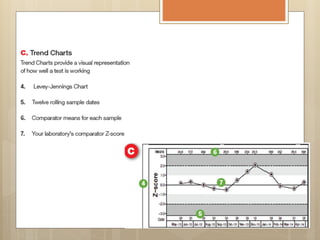
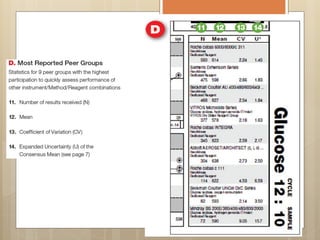
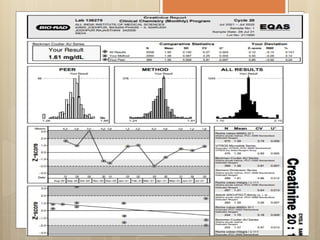
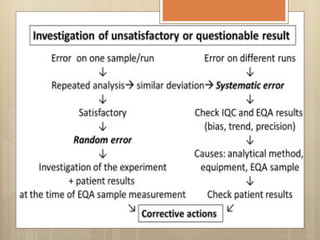
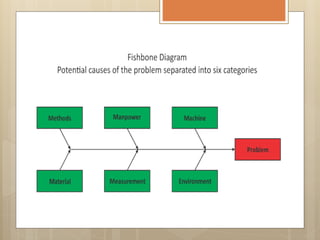
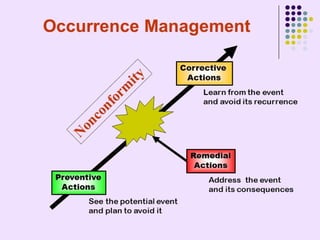
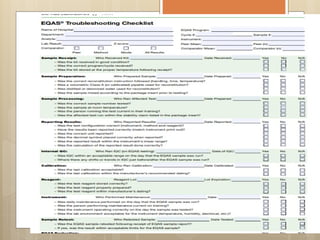
External Quality Assurance (EQA) programs assess laboratory analytical quality and reliability, enhance standardization efforts in clinical testing, and aid in corrective actions. EQA involves periodic assessments, comparison with target values, and participation in inter-laboratory comparisons, as mandated by ISO 15189. Choosing an EQA program requires careful consideration of factors such as sample commutability and participant numbers to ensure accurate lab performance.