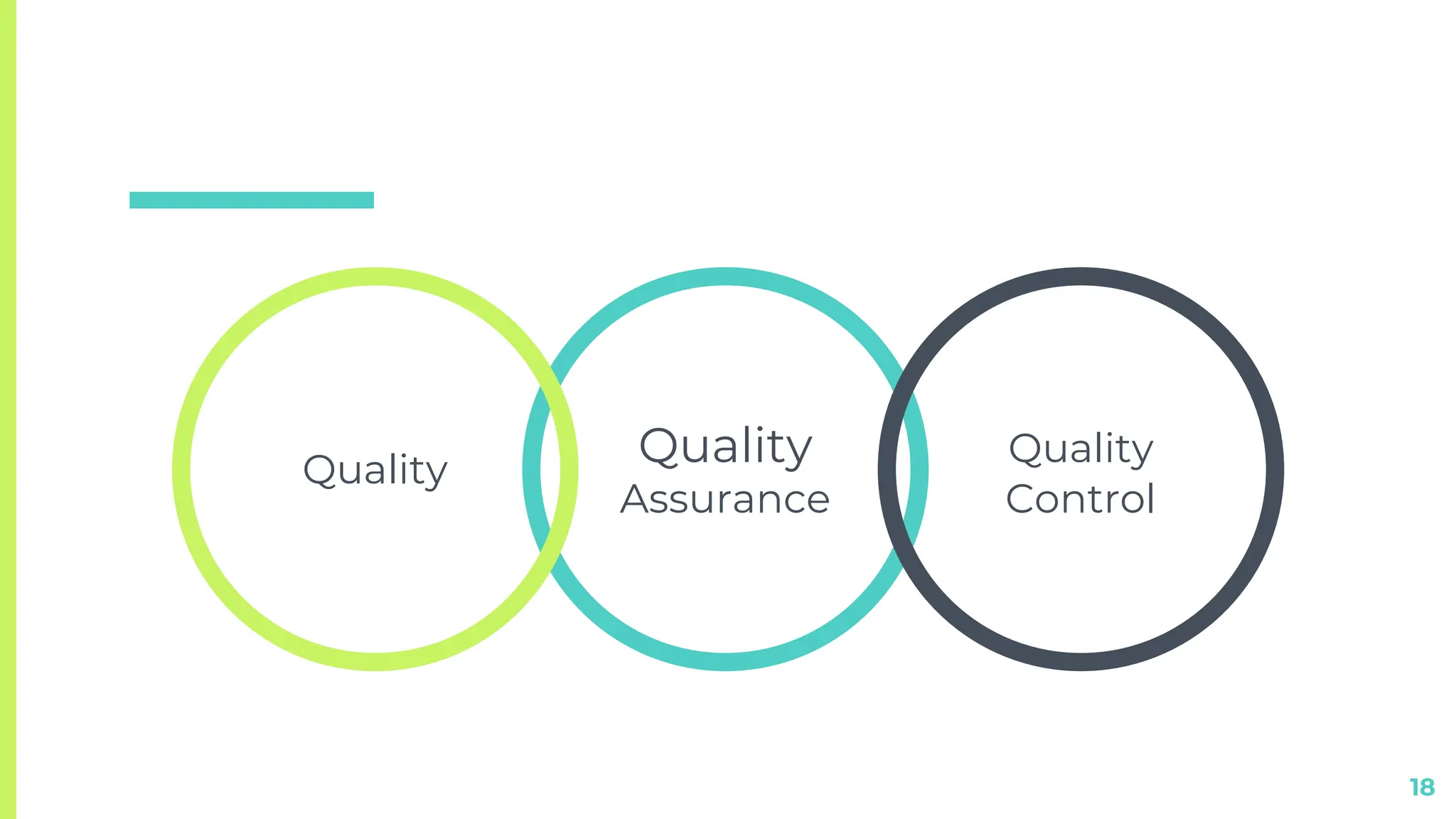
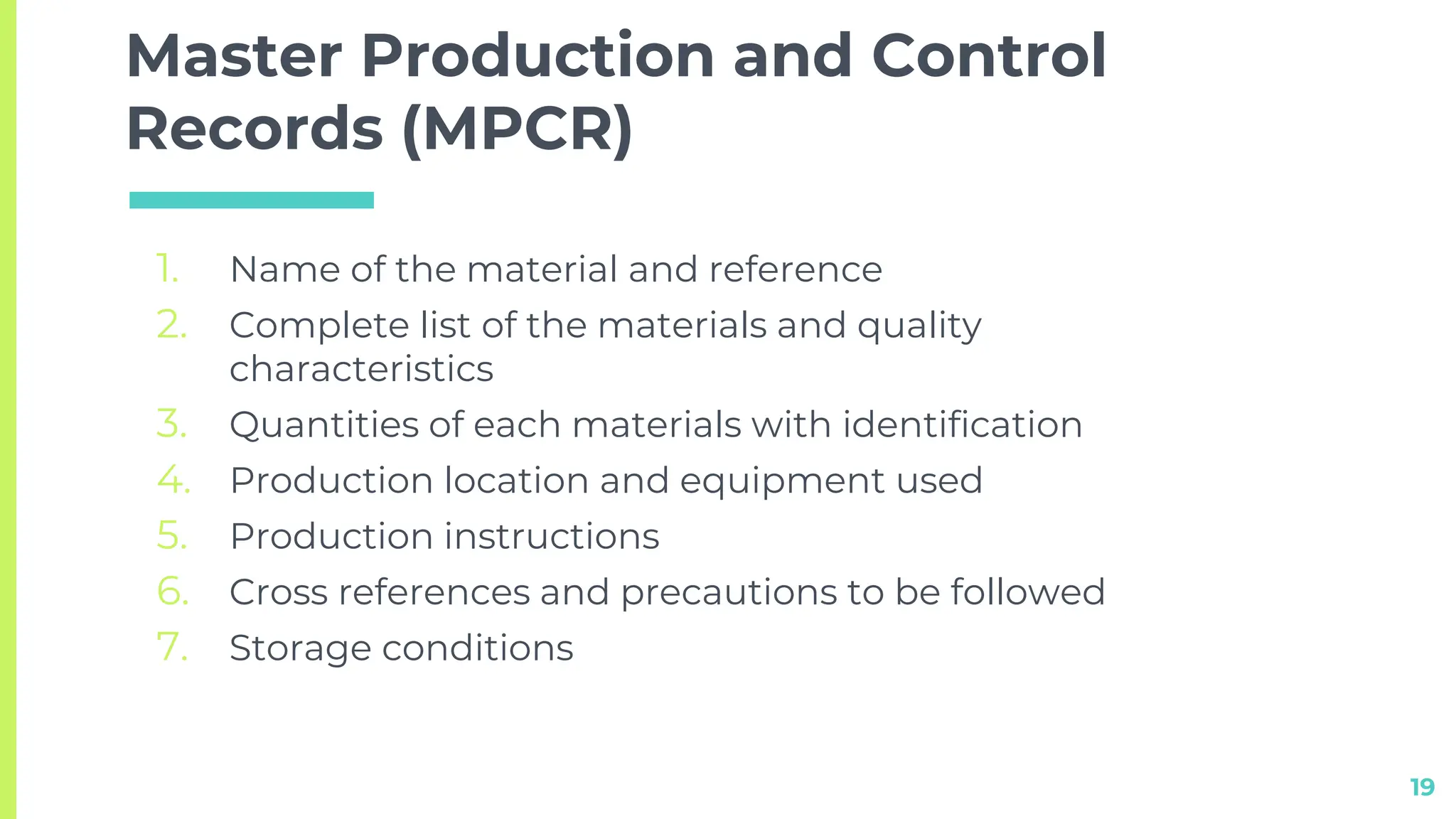
This document discusses quality assurance techniques in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It defines quality, quality assurance, and quality control, and describes the differences and responsibilities of quality assurance and quality control. Key points covered include in-process quality control, master production and control records, and batch production and control records. The document is presented by Shrikant Kavitake from Dattakala College of Pharmacy.