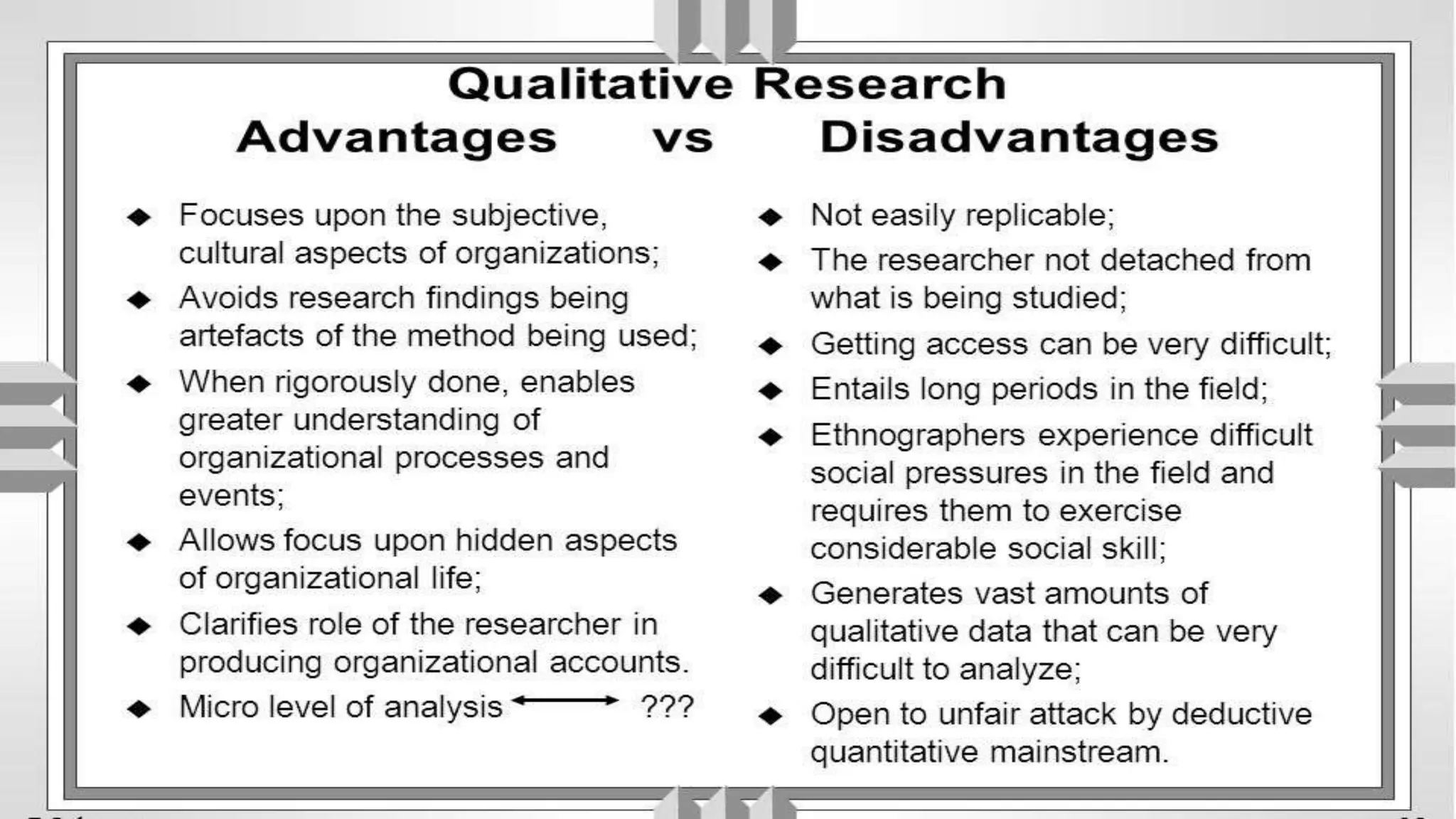
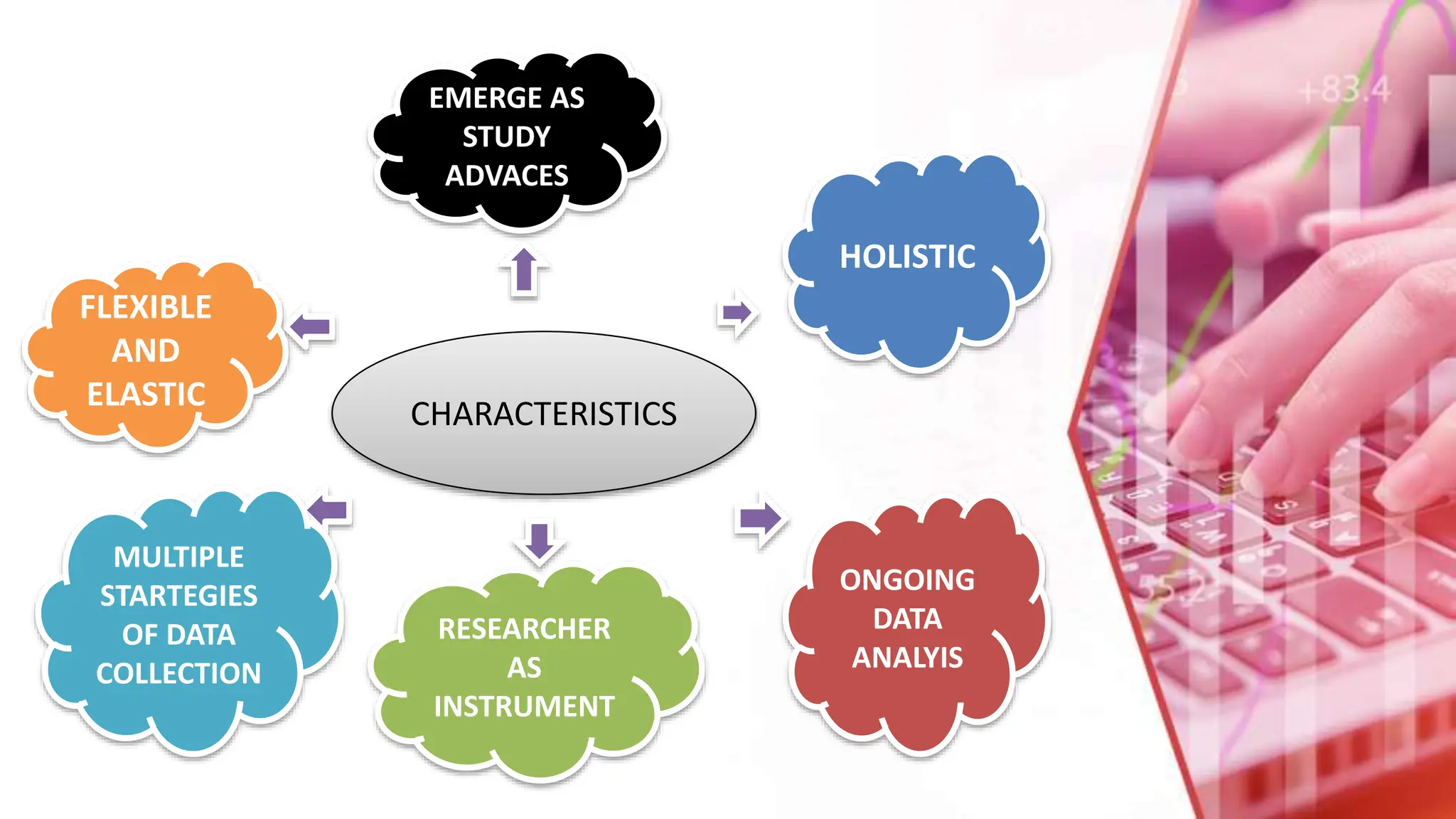
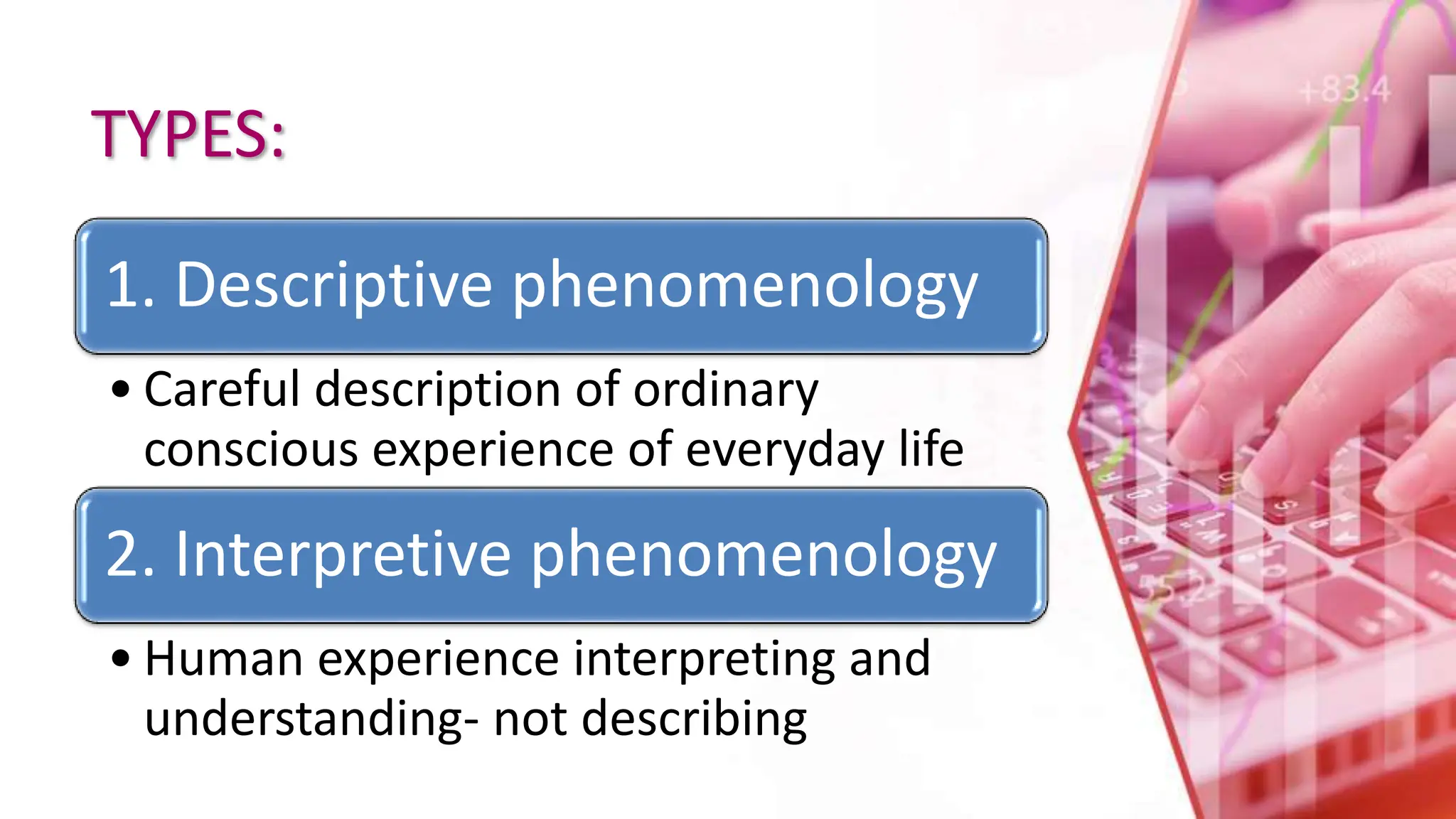
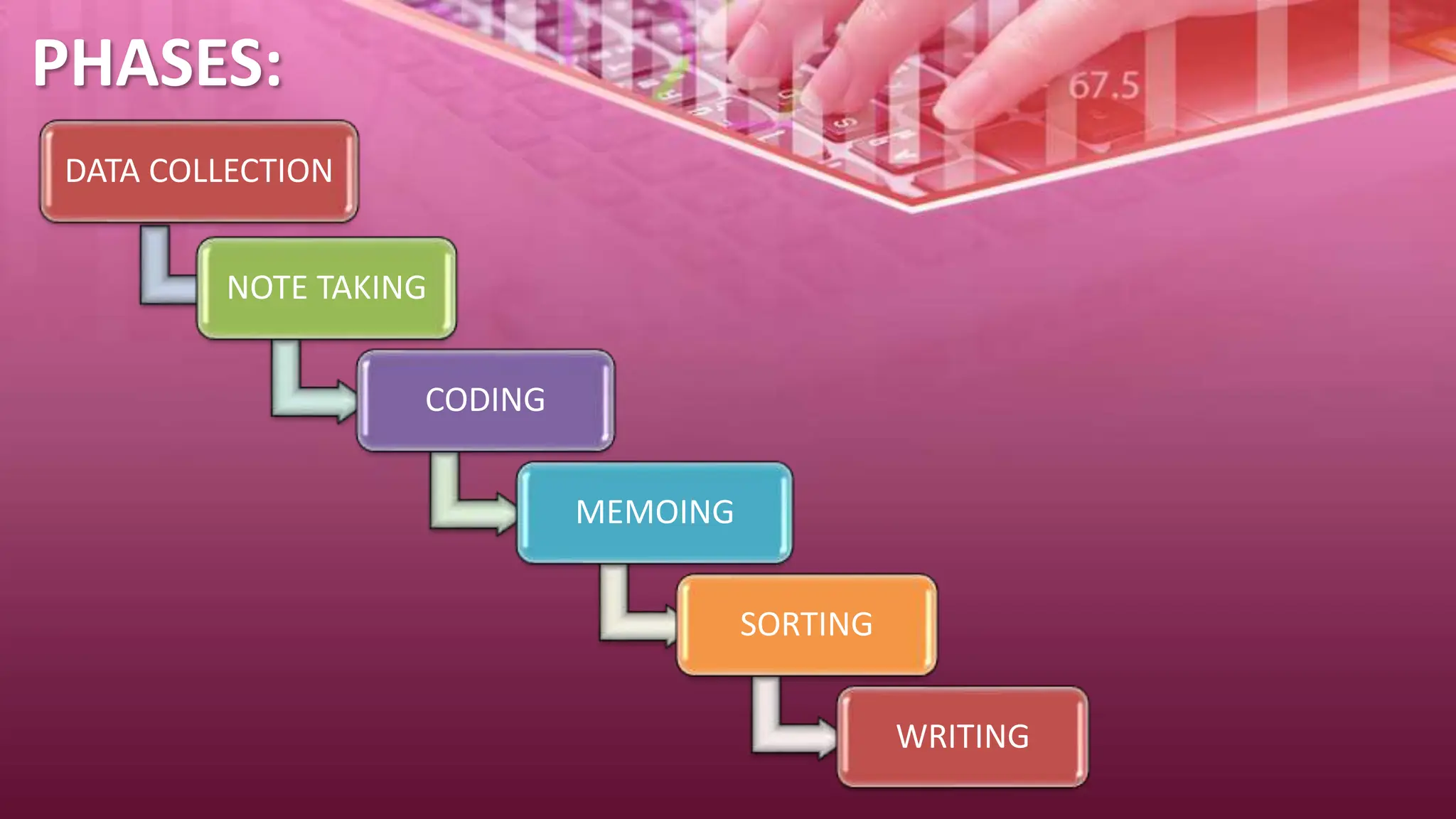
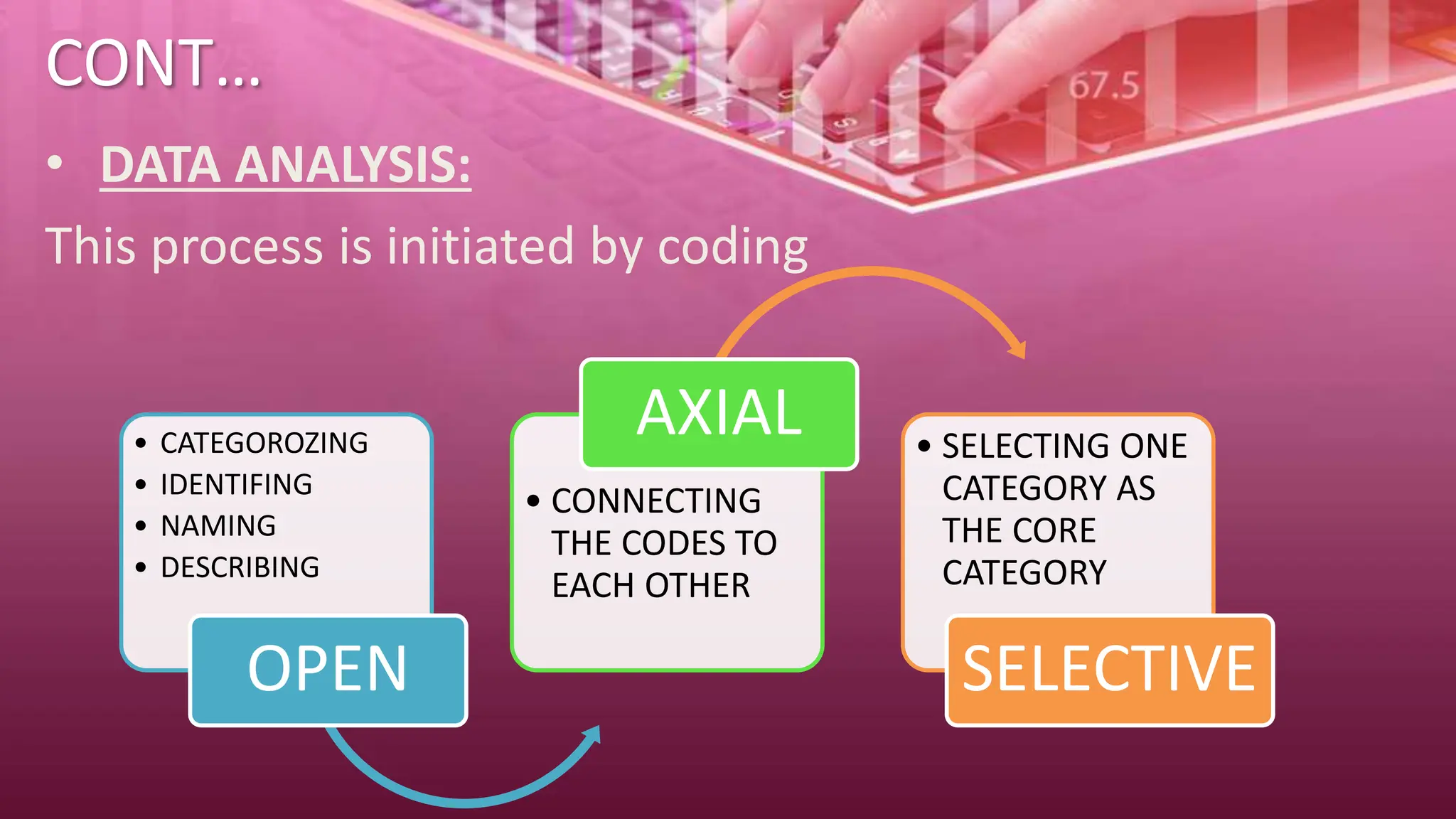
The document provides an overview of qualitative research methods, emphasizing their value in understanding social contexts and cultural perspectives. Various approaches such as phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography, historical research, action research, and case studies are detailed, each with specific methodologies and applications in nursing and social sciences. Importance is placed on flexible data collection strategies and the role of researchers in interpreting and analyzing data to support findings.















![ETHNOGRAPHY:
• Ethnography studies are involved in
collection and analysis of data about
cultural groups.
• Ethnography is classified into 2 types-
Macroenthnography [broadly defined
cultural group]
Microenthnography [narrowly defined
cultural group]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qulitativeresearchmethod-240225192251-8bae35ba/75/QUALITATIVE-RESEARCH-METHOD-it-s-types-22-2048.jpg)