The document discusses key topics in e-government services including:
1. An overview of front-office citizen-facing services and back-office internal government services.
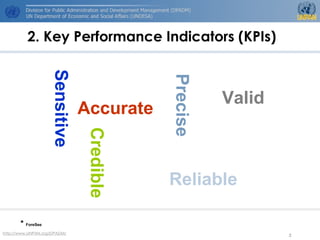
2. The importance of key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring success and improving services.
3. The rise of mobile (m-government) services using smartphones to provide timely information to citizens.