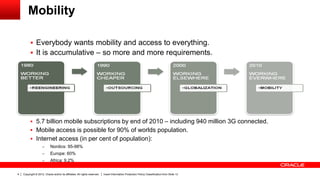
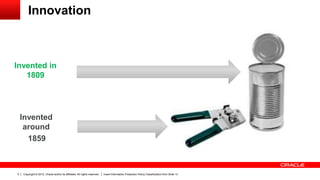
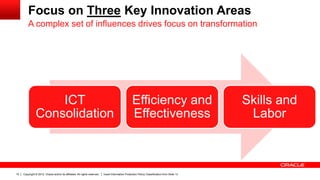
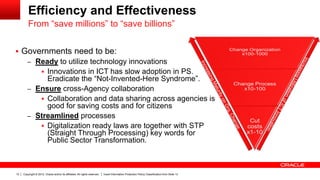
The document discusses the role of ICT innovation in transforming the public sector, emphasizing the need for better technology adoption and data management to enhance efficiency and citizen experience. It outlines trends in mobility and the importance of core infrastructures for enabling digital services. Additionally, it provides recommendations for governments on how to assess and implement new technologies effectively.