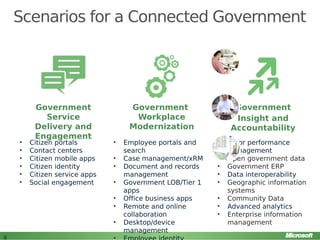
The document discusses the critical role of ICT investment in infrastructure for economic growth, especially in regions like Iraq and Egypt. It highlights the necessity of good governance, clear policies, and partnerships with international ICT companies to foster innovation and improve government services. The presentation also outlines Microsoft's strategic partnerships and initiatives to build an ICT ecosystem that supports SMEs and enhances government service delivery through modern technologies like cloud computing.