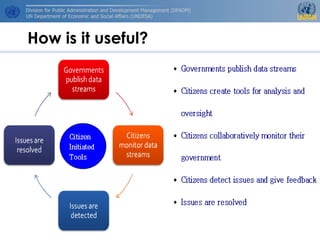
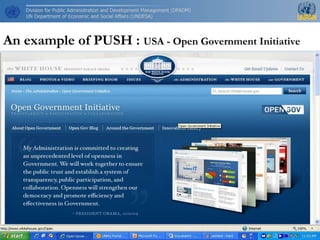
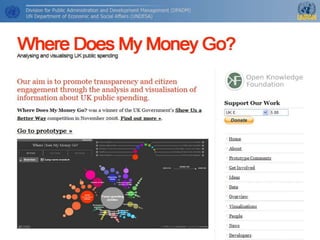
The document outlines e-government services focusing on front-office (G2C and G2B) and back-office (G2G) functions while emphasizing the importance of key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring success. It addresses the rise of mobile government (m-government) as a crucial tool for modernizing public sector delivery through technology, alongside the challenges and benefits of cloud computing. Additionally, it stresses the importance of open government data in fostering trust between citizens and the government, recommending a multi-channel approach to enhance citizen satisfaction.