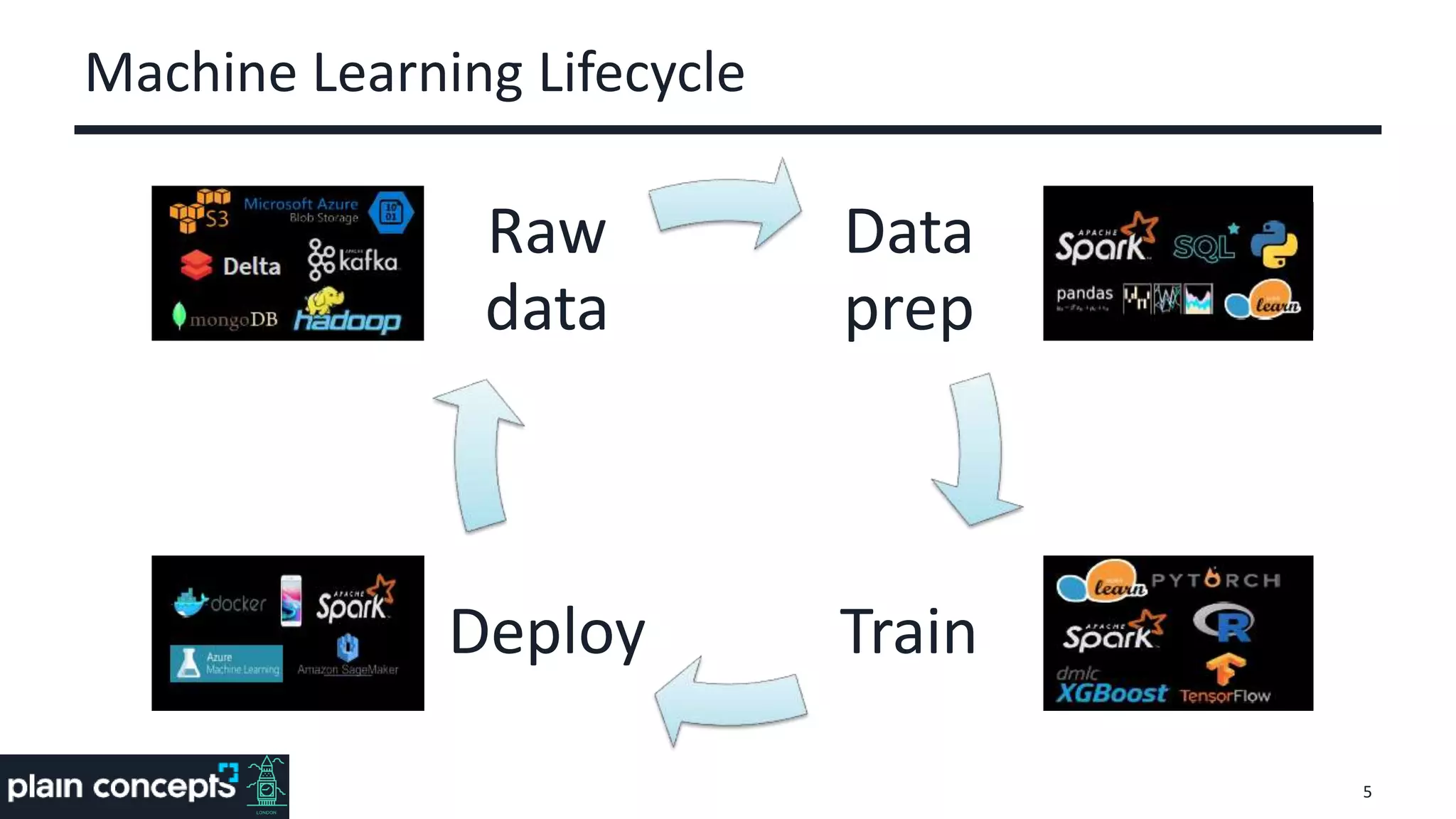
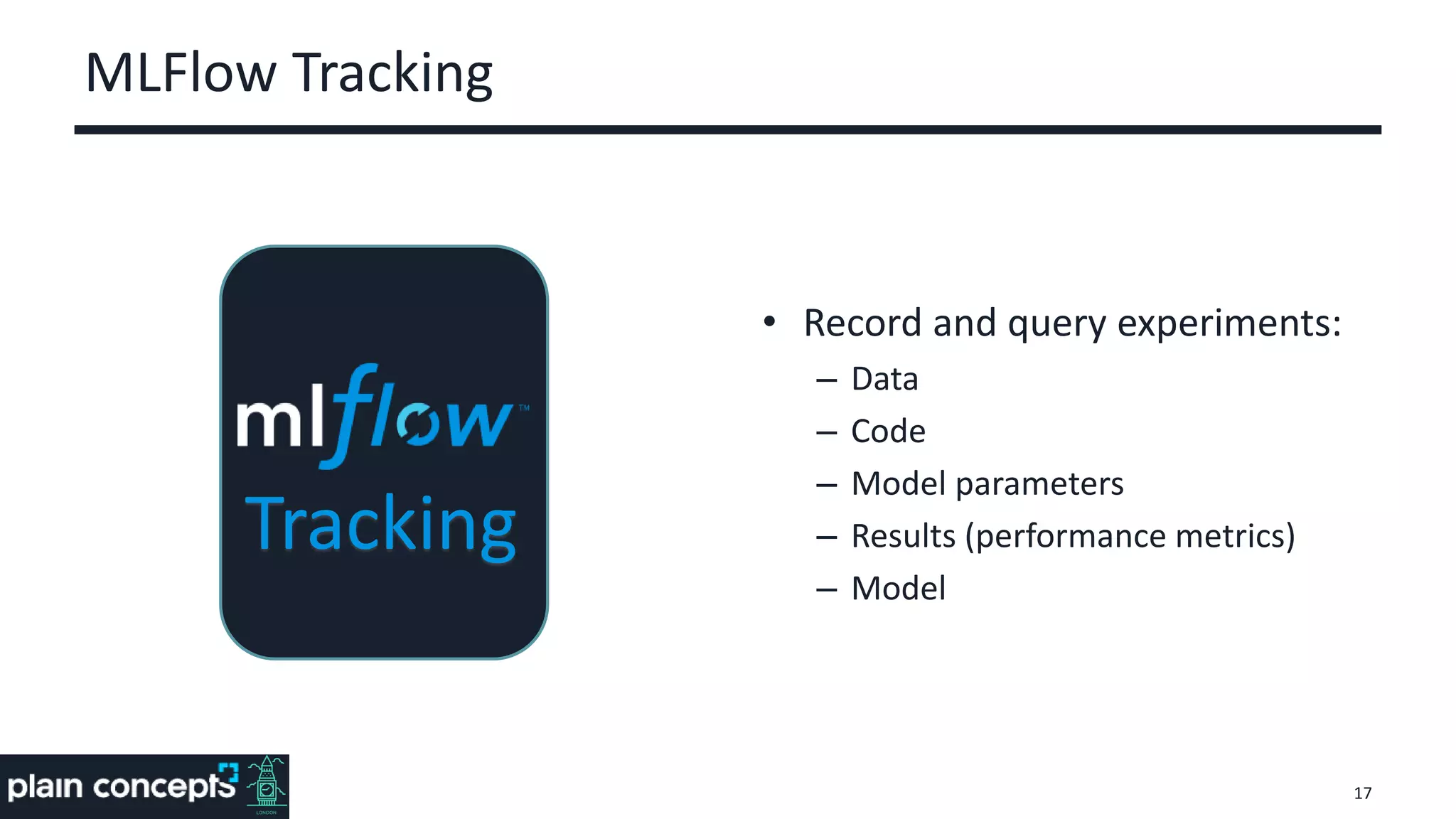
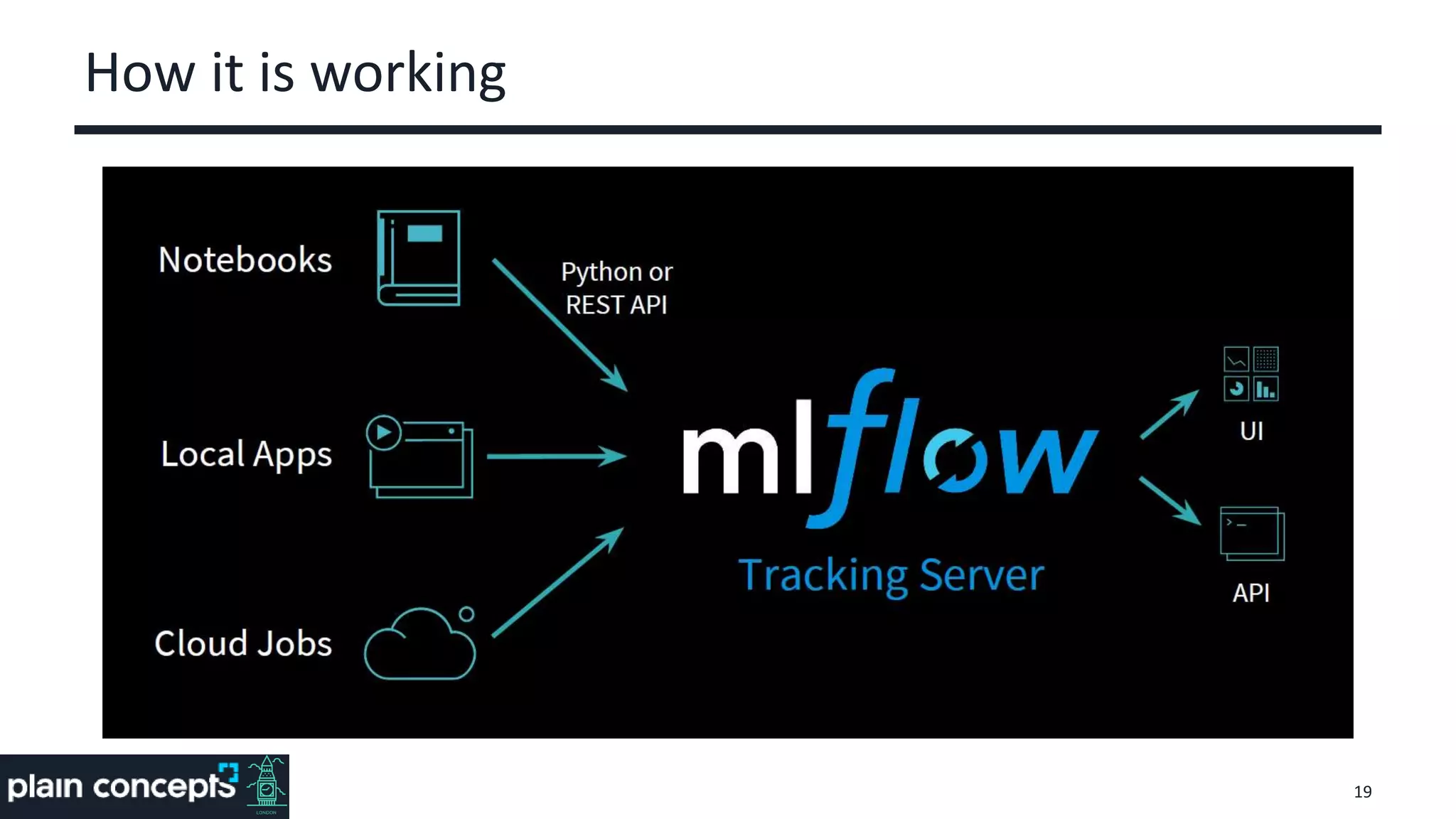
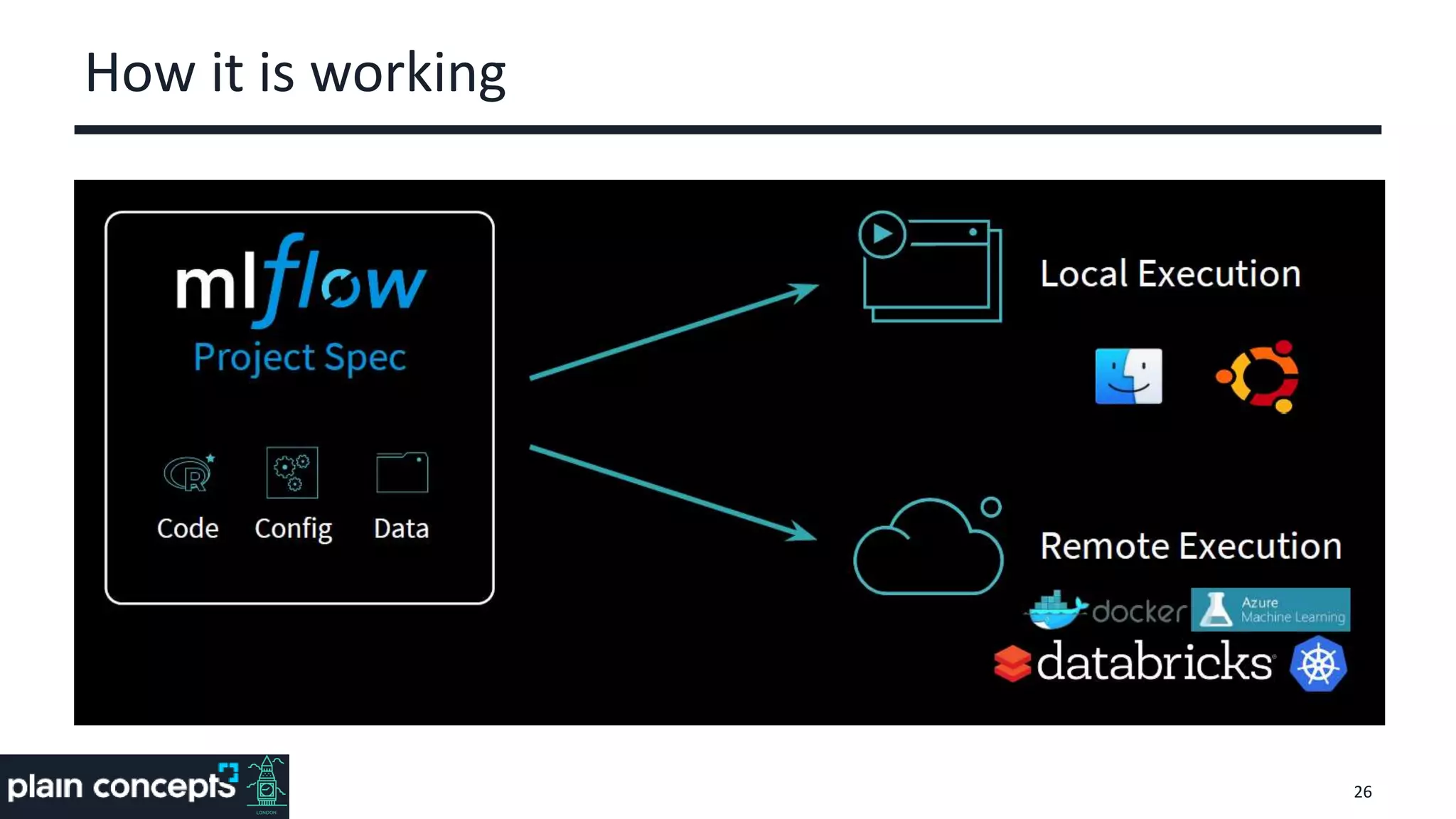
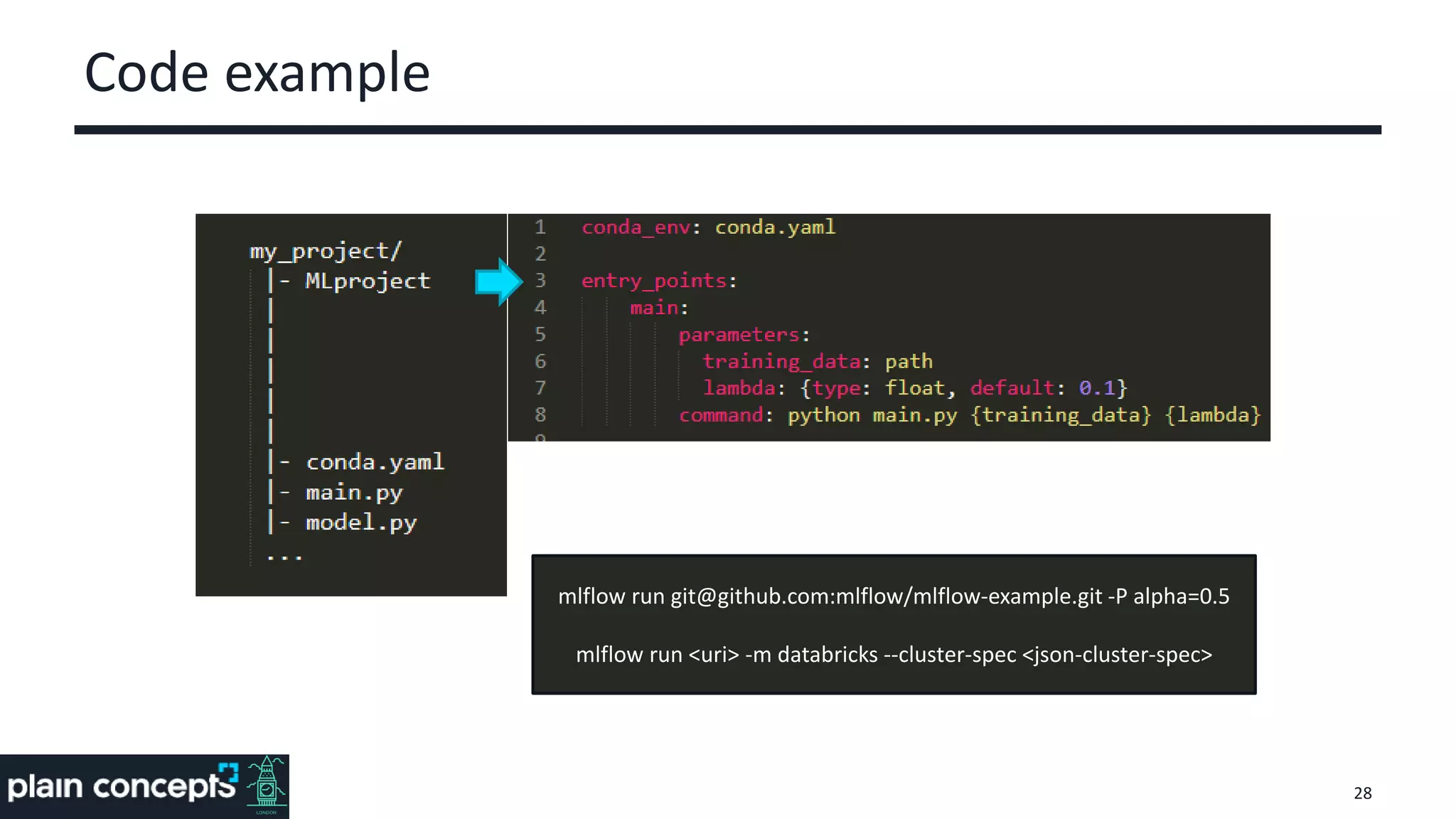
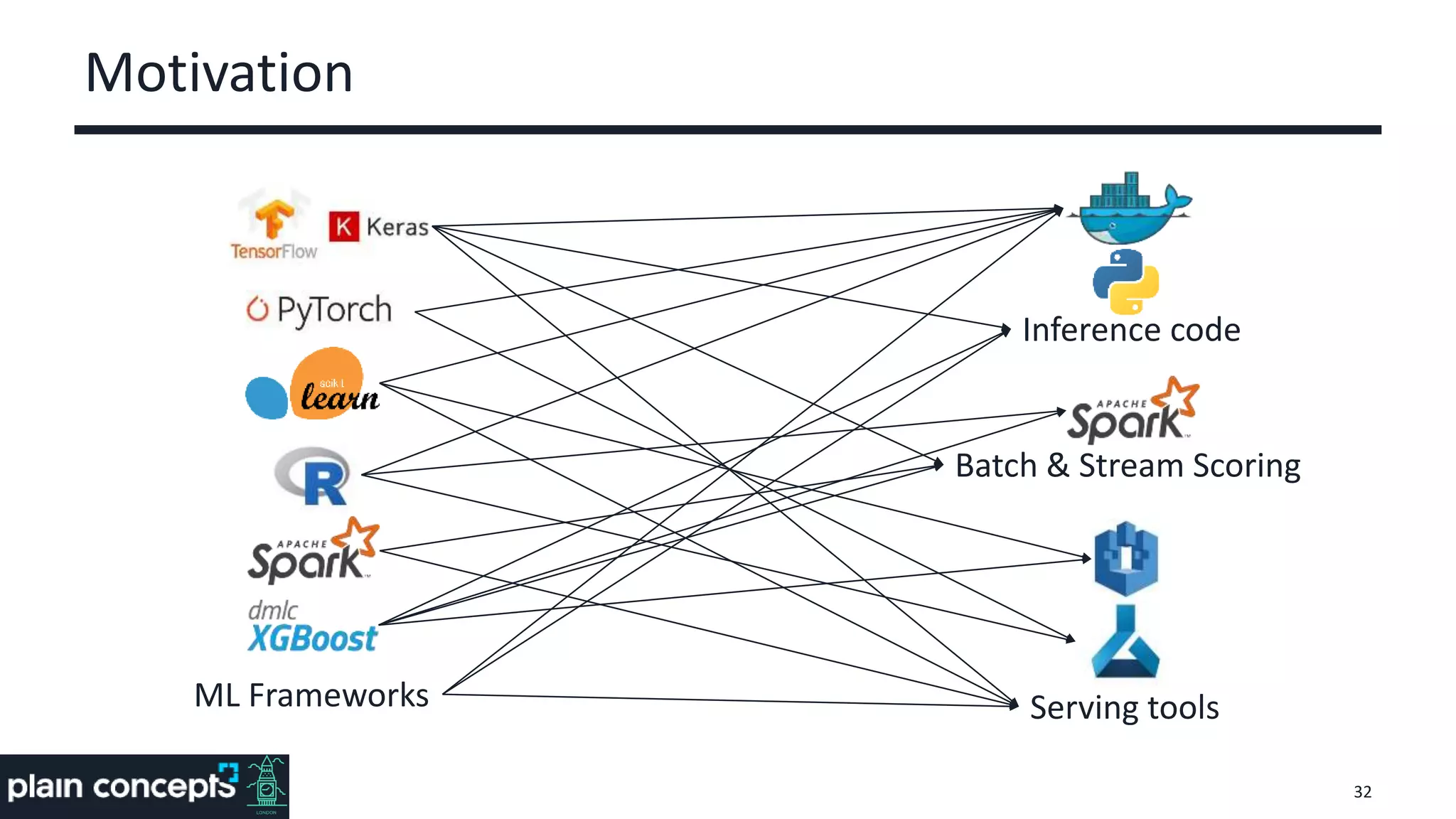
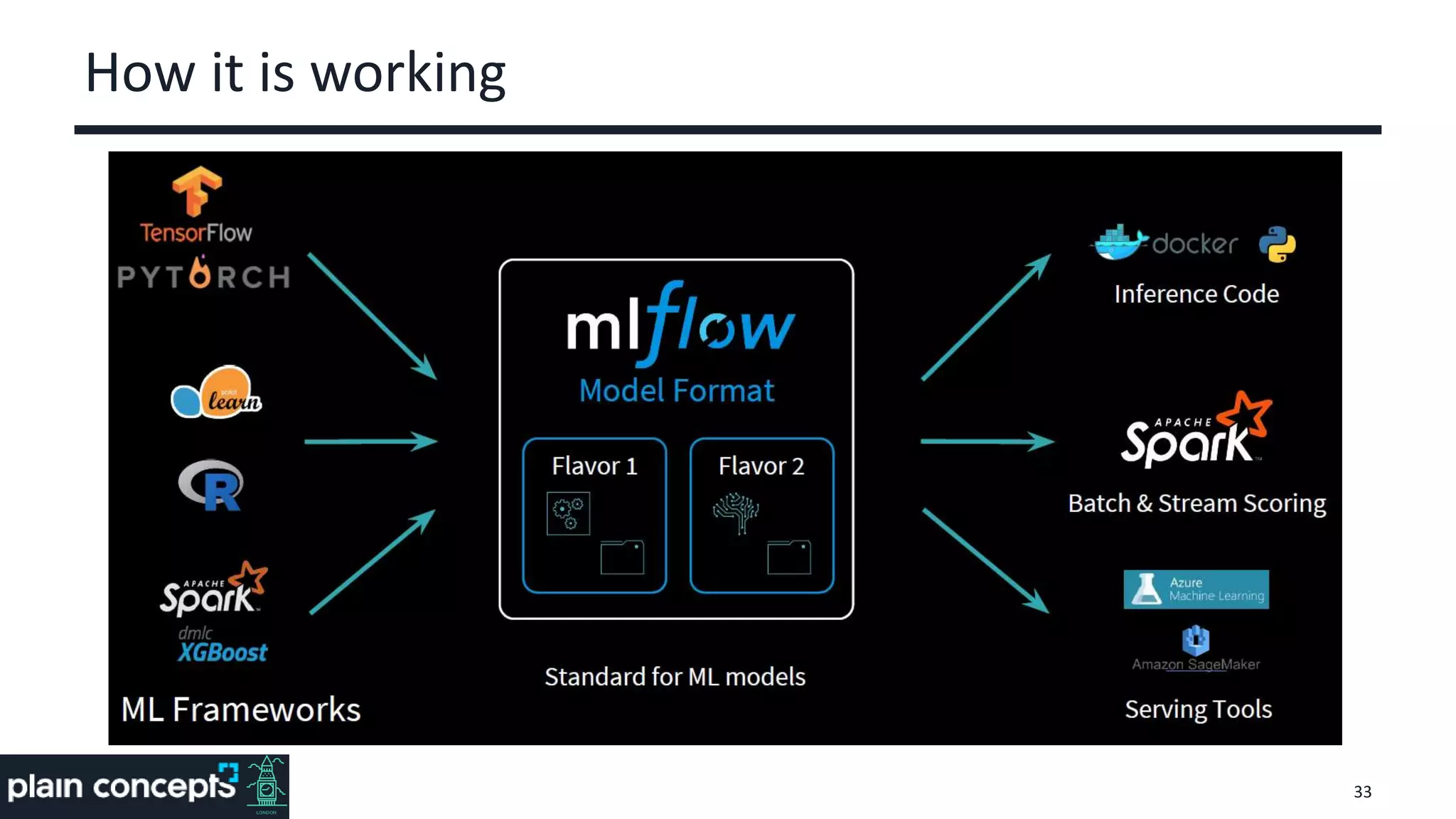
The document provides an overview of MLflow, a platform designed to streamline the machine learning lifecycle by addressing key challenges such as experiment reproducibility, model comparison, data sharing, and deployment. It highlights the components of MLflow, including tracking, projects, and models, emphasizing its compatibility with various ML libraries and environments. Recent updates and future directions for MLflow are also discussed, showcasing its growing capabilities and community support.