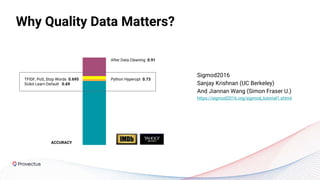
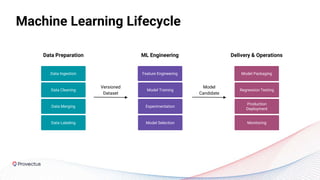
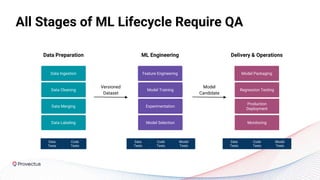
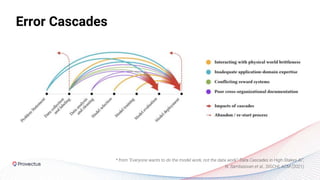
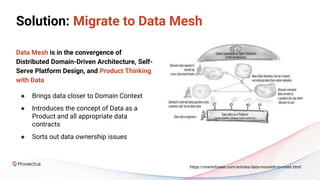
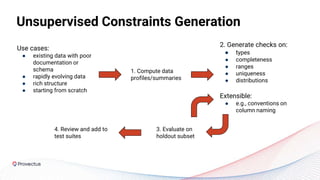
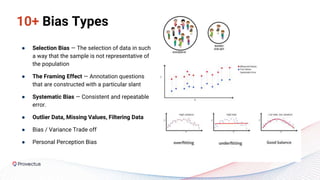
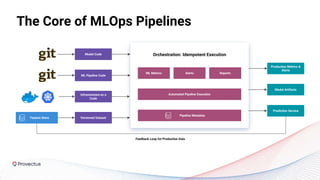
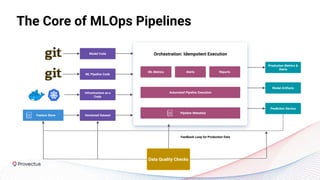
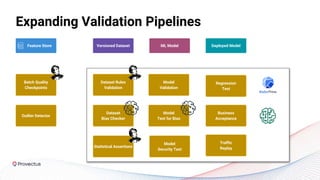
The webinar discusses best practices for deploying reliable machine learning models through effective MLOps and emphasizes the importance of data quality. It outlines common challenges in data accessibility and quality assurance, recommending solutions such as data mesh and the use of global data catalogs. Best practices in model testing and data quality checks are highlighted, along with the call for a robust data QA strategy as foundational to successful ML deployment.